您现在的位置是:首页 >其他 >后端学vue2网站首页其他
后端学vue2
工程创建
安装vue脚手架
安装好nodejs之后,安装vue脚手架
npm install -g @vue/cli
- -g 参数表示全局安装,这样在任意目录都可以使用 vue 脚本创建项目
- 安装时候使用
vue ui创建
安装 vue调试工具devtools
- devtools 插件网址:https://devtools.vuejs.org/guide/installation.html
运行项目
npm run serve
修改端口
默认8080
-
文档地址:DevServer | webpack
-
打开 vue.config.js 添加
const { defineConfig } = require('@vue/cli-service') module.exports = defineConfig({ // ... devServer: { port: 7070 } })
添加代理
作用:避免跨域问题
-
文档地址同上
-
打开 vue.config.js 添加
const { defineConfig } = require('@vue/cli-service') module.exports = defineConfig({ // ... devServer: { port: 7070, proxy: { '/api': { target: 'http://localhost:8080', changeOrigin: true } } } })
Vue项目结构
- assets - 静态资源
- components - 可重用组件
- router - 路由
- store - 数据共享
- views - 视图组件
- App.vue - 根组件
- main.js - 入口组件
- pockage.json - 相当于pom文件
以后还会添加
- api - 跟后台交互,发送 fetch、xhr 请求,接收响应
- plugins - 插件
HelloWorld
先删除原有代码,来个 Hello, World 例子
<template>
<h1>{{msg}}</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: "Hello, Vue!"
}
}
}
</script>
<--scoped的作用是缩小作用范围,只在这个文件内生效-->
<style scoped>
<style>
解释
- export default 导出组件对象,供 main.js 导入使用
- 这个对象有一个 data 方法,返回一个对象,给 template 提供数据
{{}}在 Vue 里称之为插值表达式,用来绑定 data 方法返回的对象属性,绑定的含义是数据发生变化时,页面显示会同步变化
vue入门程序原理
- main.js里面
import App from './App.vue'引入App.vue组件中的模板(template) - 通过h函数解析模板(template),生成虚拟节点
- $mount函数把解析好的代码(虚拟节点)放到"#app",在
public/index.heml中有个div标签,id为app
Vue组件
文本插值{{}}
- {{}}里面只能有一个属性,绑定多个要使用多个{{}}
- 插值里面可以有简单的运算符,三元表达式等等
- template只能有一个根元素
属性绑定v-bind
简写形式可以省略 v-bind 只保留冒号
事件绑定
<!-- 事件绑定 -->
<template>
<div>
<div><input type="button" value="点我执行m1" v-on:click="m1"></div>
<div><input type="button" value="点我执行m2" @click="m2"></div>
<div>{{count}}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const options = {
data: function () {
return { count: 0 };
},
methods: {
m1() {
this.count ++;
console.log("m1")
},
m2() {
this.count --;
console.log("m2")
}
}
};
export default options;
</script>
- 简写方式:可以把 v-on: 替换为 @
- 在 methods 方法中的 this 代表的是 data 函数返回的数据对象
双向绑定
<template>
<div>
<div>
<label for="">请输入姓名</label>
<input type="text" v-model="name">
</div>
<div>
<label for="">请输入年龄</label>
<input type="text" v-model="age">
</div>
<div>
<label for="">请选择性别</label>
男 <input type="radio" value="男" v-model="sex">
女 <input type="radio" value="女" v-model="sex">
</div>
<div>
<label for="">请选择爱好</label>
游泳 <input type="checkbox" value="游泳" v-model="fav">
打球 <input type="checkbox" value="打球" v-model="fav">
健身 <input type="checkbox" value="健身" v-model="fav">
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const options = {
data: function () {
return { name: '', age: null, sex:'男' , fav:['打球']};
},
methods: {
}
};
export default options;
</script>
- 用 v-model 实现双向绑定,即
- javascript 数据可以同步到表单标签
- 反过来用户在表单标签输入的新值也会同步到 javascript 这边
- 双向绑定只适用于表单这种带【输入】功能的标签,其它标签的数据绑定单向就足够了,标签内容,使用文本差值,如果是普通标签的属性使用v-bind
- 复选框这种标签,双向绑定的 javascript 数据类型一般用数组
计算属性
<!-- 计算属性 -->
<template>
<div>
<h2>{{fullName}}</h2>
<h2>{{fullName}}</h2>
<h2>{{fullName}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const options = {
data: function () {
return { firstName: '三', lastName: '张' };
},
/* methods: {
fullName() {
console.log('进入了 fullName')
return this.lastName + this.firstName;
}
},*/
computed: {
fullName() {
console.log('进入了 fullName')
return this.lastName + this.firstName;
}
}
};
export default options;
- 普通方法调用必须加 (),没有缓存功能
- 计算属性使用时就把它当属性来用,不加 (),有缓存功能:
- 一次计算后,会将结果缓存,下次再计算时,只要数据没有变化,不会重新计算,直接返回缓存结果
axios
默认axios
安装
npm install axios -S
"-S"是npm install 命令中的一个选项,它是–save的缩写。使用该选项将axios安装为项目的依赖项并将其添加到package.json文件的"dependencies"中。这意味着当您以后重新安装项目时,axios将自动安装。
导入
import axios from 'axios'
- axios 默认导出一个对象,这里的 import 导入的就是它默认导出的对象
方法
| 请求 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| axios.get(url[, config]) | ⭐️ |
| axios.delete(url[, config]) | |
| axios.head(url[, config]) | |
| axios.options(url[, config]) | |
| axios.post(url[, data[, config]]) | ⭐️ |
| axios.put(url[, data[, config]]) | |
| axios.patch(url[, data[, config]]) |
- config - 选项对象、例如查询参数、请求头…
- data - 请求体数据、最常见的是 json 格式数据
- get、head 请求无法携带请求体,这应当是浏览器的限制所致(xhr、fetch api 均有限制)
- options、delete 请求可以通过 config 中的 data 携带请求体
例子
<template>
<div>
<input type="button" value="获取远程数据" @click="sendReq()">
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
const options = {
methods: {
async sendReq() {
// 1. 演示 get, post
//const resp = await axios.get('/dish/page',{
//params:{page:'',pageSize:''}//params会翻译成?那种查询参数的格式
//});
// const resp = await axios.post('/api/a2');
// 2. 发送请求头
// const resp = await axios.post('/api/a3',{},{
// headers:{
// Authorization:'abc'
// }
// });
// 3. 发送请求时携带查询参数 ?name=xxx&age=xxx
// const name = encodeURIComponent('&&&');
// const age = 18;
// const resp = await axios.post(`/api/a4?name=${name}&age=${age}`);
// 不想自己拼串、处理特殊字符、就用下面的办法
// const resp = await axios.post('/api/a4', {}, {
// params: {
// name:'&&&&',
// age: 20
// }
// });
// 4. 用请求体发数据,格式为 urlencoded
// const params = new URLSearchParams();
// params.append("name", "张三");
// params.append("age", 24)
// const resp = await axios.post('/api/a4', params);
// 5. 用请求体发数据,格式为 multipart
// const params = new FormData();
// params.append("name", "李四");
// params.append("age", 30);
// const resp = await axios.post('/api/a5', params);
// 6. 用请求体发数据,格式为 json
const resp = await axios.post('/api/a5json', {
name: '王五',
age: 50
});
console.log(resp);
}
}
};
export default options;
</script>
创建实例覆盖默认axios设置
const _axios = axios.create(config);
- axios 对象可以直接使用,但使用的是默认的设置
- 用 axios.create 创建的对象,可以覆盖默认设置,config 见下面说明
常见的 config 项有
| 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| baseURL | 将自动加在 url 前面 |
| headers | 请求头,类型为简单对象 |
| params | 跟在 URL 后的请求参数,类型为简单对象或 URLSearchParams |
| data | 请求体,类型有简单对象、FormData、URLSearchParams、File 等 |
| withCredentials | 跨域时是否携带 Cookie 等凭证,默认为 false |
| responseType | 响应类型,默认为 json |
例
const _axios = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://localhost:8080',
withCredentials: true
});
await _axios.post('/api/a6set')
await _axios.post('/api/a6get')
- 生产环境希望 xhr 请求不走代理,可以用 baseURL 统一修改
- 希望跨域请求携带 cookie,需要配置 withCredentials: true,服务器也要配置 allowCredentials = true,否则浏览器获取跨域返回的 cookie 时会报错
响应格式
| 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| data | 响应体数据 ⭐️ |
| status | 状态码 ⭐️ |
| headers | 响应头 |
- 200 表示响应成功
- 400 请求数据不正确 age=abc
- 401 身份验证没通过
- 403 没有权限
- 404 资源不存在
- 405 不支持请求方式 post
- 500 服务器内部错误
拦截器
请求拦截器
_axions.interceptors.request.use(
function (config) {
// 比如在这里添加统一的 headers
config.headers = {
Authorization: 'fjkasdhfkjdhasfkl'
}
return config;
},
function (error) {
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
响应拦截器
_axios.interceptors.response.use(
function(response) {
// 2xx 范围内走这里
return response;
},
function(error) {
// 超出 2xx, 比如 4xx, 5xx 走这里
return Promise.reject(error);
}
);
拦截器优化
src下新建一个目录util,新建一个myaxios.js文件,配置自定义axios
组件重用
import MyButton from ‘…/components/MyButton.vue’
导入之后,当成标签使用 <my-button></my-button>
可以增加prop属性设置组件扩展性

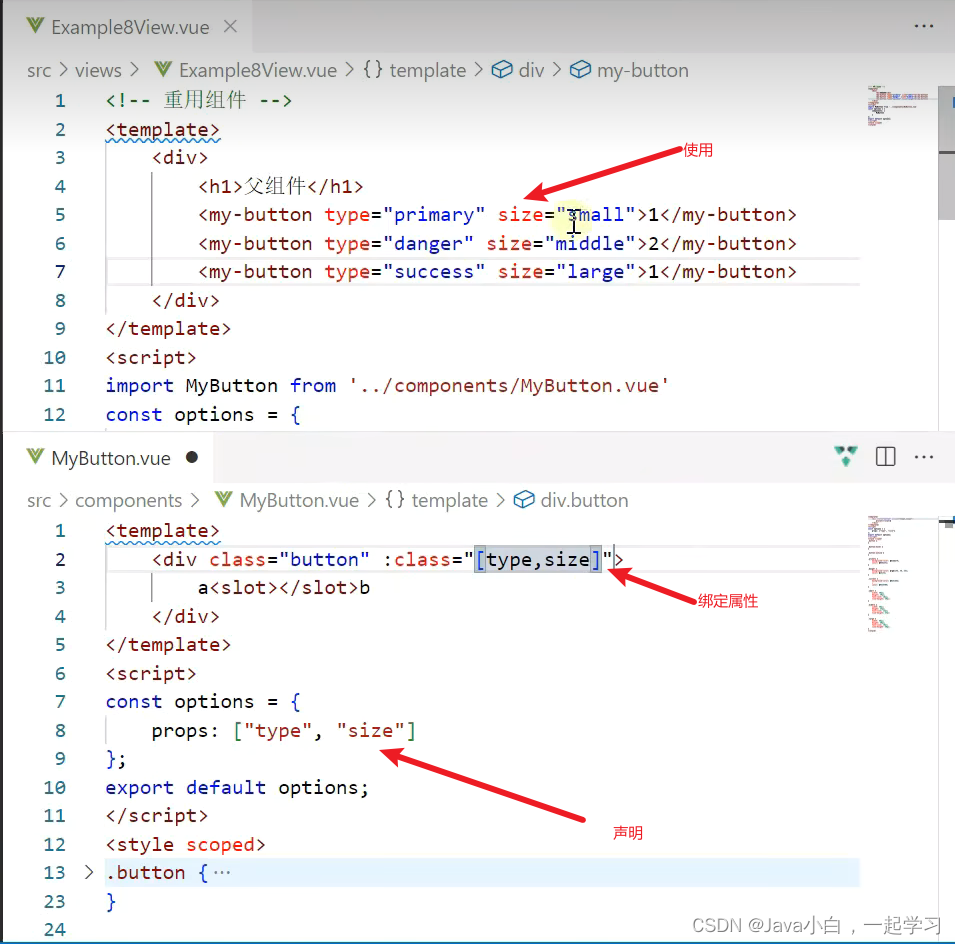
效果如图:

elementUI
官网:elementUI
https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN/component/installation
安装
npm install element ui -S
在main.js里面引入组件
import Element from 'element-ui'
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'
Vue.use(Element)
小细节
<div>
<el-table :data="tableData" style="width: 100%">
<el-table-column prop="date" label="日期" width="180">
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="name" label="姓名" width="180">
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="address" label="地址">
</el-table-column>
</el-table>
<div class="block">
<span class="demonstration">完整功能</span>
<el-pagination @size-change="handleSizeChange" @current-change="handleCurrentChange" :current-page="currentPage"
:page-sizes="[100, 200, 300, 400]" :page-size="100" layout="total, sizes, prev, pager, next, jumper"
:total=total>
</el-pagination>
</div>
</div>
如果属性没有’ : ‘,就当做普通的赋值来处理,如果有’ : ',就要解析,比如说page-sizes是一个number类型的数组,如果不加冒号就无法解析
clearable:属性可清除
el属性::unique-opened=‘true’,左侧菜单项只能打开一个
Vue-Router vue路由
vue属于单页面应用,路由根据浏览器路径不同,用不同的视图组件替换页面内容显示
在router/index.js中设置路径
<router-view></router-view>表示要替换的位置
下面代码块中,ex2使用的是动态导入,动态导入就是被访问时才加载响应的组件,更高效。
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Example1View from '@/views/Example1View.vue'
//import Example2View from '../views/Example2View.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'ex1',
component: Example1View,
redirect:'p1/c1',//默认跳转
children:[//子路由
{
path:'p1/c1',
component:()=> import('../views/ChildrenView1.vue')
},
{
path:'p1/c2',
component:()=> import('../views/ChildrenView2.vue')
}
]
},
{
path: '/ex2',
name: 'ex2',
component: ()=> import('../views/Example2View.vue')
},
{
path:'*',//上面的路径都没有匹配到,就重定向到404
redirect:'/404'
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router
路由跳转
三种实现方法
其一:超链接<router-link to = " ">员工管理</router-link>
其二:按钮单击事件等方法@click="jump('/c/p1')"
其三:elementUI导航菜单加上router属性,index='路径’跳转
methods:{
jump(url){
this.$router.push(url);//获取路由对象调用铺设方法进行跳转
}
}
动态路由
//动态路由添加
//参数1:父路由名称
//参数2:路由信息对象
for(const {id,path,component} of array){
if(component !== null){
this.$router.addRoute('c',{
path:path
name:id,
component:()=>import('@views/example/${component}')
})
}
}
重置路由方法
把这个方法放在路由的index.js文件里面
export function resetRouter(){
router.matcher = new VueRounter({
routes
}).matcher
}
页面刷新
localStorage 即使浏览器关闭,存储的数据仍在
sessionStorage 以标签页为单位,关闭标签页时,数据被清除
sessionStorage.setItem('serverRoutes',JSON.stringify(array))
在router/index.js里
//从session中恢复路由
const serverRoutes = sessionStorage.getItem('serverRoutes');
if(serverRoutes){
const array = JSON.parse(serverRoutes);
addServerRoutes(array);
}
VueX数据共享
在store/index.js里设置共享变量,以及操作变量的方法
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
/*
读取数据,走state,getters
修改数据,走mutations,actions
*/
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
name:''//设置共享变量
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
updateName(state,name){//改变共享变量的值
state.name = name;
}
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
在其他页面中使用一下示例调用
< @click="update()">
//设置值
methods:{
update(){
this.$store.commit('updateName',this.name);//使用store对象找到mutations中的同名方法
}
}
//简化
< @click="updateName(name)">//需要传入要改变的变量名
import {mapMutations} from 'vuex'
methods:{
...mapMutations(['updateName']);//生成的方法名叫updateName
}
//获取值
//插值表达式
{{$store.state.name}}
//用计算属性简化
{{name}}
computed:{
name(){
return this.$store.name;
}
}
//再简化
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
computed:mapState(['name','age'])
另一种写法
computed:{
...mapState(['name','age'])
}
从服务器获取数据
store/index.js里面只能有让改动立即生效的方法
mutations:{
updateServerName(state,user){
const {name,age} = user;
state.name = name;
state.age = age;
}
},
actions:{
async updateServerName(context){
const resp = await axios.get('/api/user');
context.commit('updateServerName',resp.data.data);
}
},
页面改动
import {mapActions} from 'vuex'
methods:{
...mapActions(['updateServerName']);
}
//另一种方法
methods:{
this.$store.dispatch('updateServerName',如果需要其他参数可以谢在这里,context不用写);使用store对象找到actions中的同名方法
}
总结
computed:计算属性
components:重用组件






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结