您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >《链》接未来:力扣“复制带随机指针的链表”题解网站首页学无止境
《链》接未来:力扣“复制带随机指针的链表”题解
简介《链》接未来:力扣“复制带随机指针的链表”题解

本篇博客会讲解力扣“138. 复制带随机指针的链表”的解题思路,这是题目链接。
先来审题:
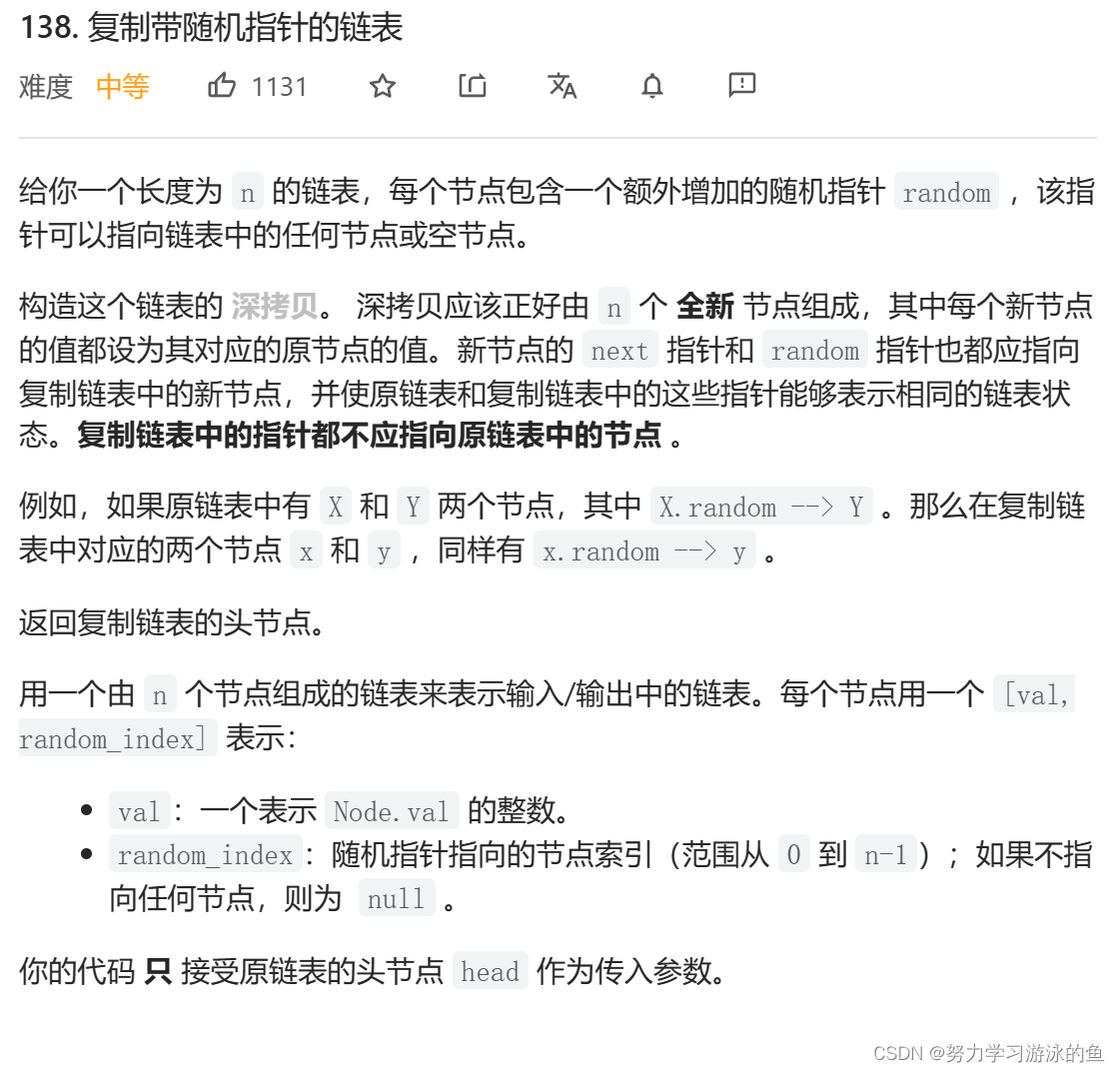
以下是输出示例:
以下是提示:

本题要实现复杂链表的深拷贝。复杂链表,是正常的单链表,每个结点中多存了一个指针,这个指针指向了链表的随机结点(也可能是NULL)。
本题的实现分为3个步骤:
- 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点。
- 设置拷贝结点的random指针。
- 把拷贝结点解下来,恢复原链表。
1.链接拷贝结点
我们使用cur结点来遍历链表。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
while (cur)
{
}
}
拷贝出一个结点。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
while (cur)
{
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
}
}
把这个结点插入到cur和cur->next中间。为了防止代码顺序书写事物,建议先用next指针保存cur->next。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
}
}
最后cur结点再往后走。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
}
2.设置random指针
再次遍历链表。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
}
}
找到cur对应的copy和next。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
}
}
设置copy结点的random指针。分类讨论:
- 如果cur的random指针为NULL,则copy的random指针也为NULL。
- 如果cur的random指针不为NULL,则copy的random指针在cur的random指针的下一个结点。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 设置random
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
}
}
最后cur往后走。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 设置random
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
}
3.解下拷贝结点,恢复原链表
再开始新的一轮的遍历。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 设置random
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 解下copy结点,恢复原链表
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
}
}
还是先找到对应的copy和next。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 设置random
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 解下copy结点,恢复原链表
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
}
}
我们要把copy结点解下来,可以考虑尾插到新的链表中。先定义哨兵位的头结点。同时,为了省去单链表找尾结点的过程,最好记录尾指针。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 设置random
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 解下copy结点,恢复原链表
// 定义哨兵位
struct Node* newHead = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newHead->val = 0;
newHead->next = NULL;
// 记录尾结点
struct Node* tail = newHead;
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
}
}
把copy结点尾插到新链表中,同时更新尾指针。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 设置random
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 解下copy结点,恢复原链表
// 定义哨兵位
struct Node* newHead = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newHead->val = 0;
newHead->next = NULL;
// 记录尾结点
struct Node* tail = newHead;
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 尾插copy
tail->next = copy;
tail = copy;
}
}
别忘了恢复原链表,让cur指向next。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 设置random
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 解下copy结点,恢复原链表
// 定义哨兵位
struct Node* newHead = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newHead->val = 0;
newHead->next = NULL;
// 记录尾结点
struct Node* tail = newHead;
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 尾插copy
tail->next = copy;
tail = copy;
// 恢复原链表
cur->next = next;
}
}
最后迭代走起来。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 设置random
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 解下copy结点,恢复原链表
// 定义哨兵位
struct Node* newHead = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newHead->val = 0;
newHead->next = NULL;
// 记录尾结点
struct Node* tail = newHead;
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 尾插copy
tail->next = copy;
tail = copy;
// 恢复原链表
cur->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
}
在返回前,需要释放哨兵位,然后返回新链表即可。
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
// 在每个结点后面链接一个拷贝结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
// 拷贝结点
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
// 在cur和next中间插入copy
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 设置copy结点的random指针
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 设置random
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 解下copy结点,恢复原链表
// 定义哨兵位
struct Node* newHead = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newHead->val = 0;
newHead->next = NULL;
// 记录尾结点
struct Node* tail = newHead;
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
// 尾插copy
tail->next = copy;
tail = copy;
// 恢复原链表
cur->next = next;
// 迭代
cur = next;
}
// 释放哨兵位
struct Node* del = newHead;
newHead = newHead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
return newHead;
}
这样就通过了。
总结
- 总思路分为3步:链接拷贝结点,设置random,解下拷贝结点。
- 链接拷贝结点的核心逻辑是:单链表的插入结点操作。
- 设置random时的核心逻辑是:copy->random = cur->random->next。
- 解下拷贝结点的核心逻辑是:把copy结点尾插到新链表。
感谢大家的阅读!
风语者!平时喜欢研究各种技术,目前在从事后端开发工作,热爱生活、热爱工作。






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结