您现在的位置是:首页 >技术教程 >python一天速成(附源码)网站首页技术教程
python一天速成(附源码)
python一天速成
图片上传参考:Typora笔记上传到CSDN解决图片问题---亲测有效!
Python简介

print('hello world')#字符串
print(99.6)#浮点数/整数
print(3 + 4)#表达式
#输出到文件,使用file=...的形式
fp = open('D:/text.txt','a+')
print('helloworld',file=fp)
fp.close()
#不进行换行输出
print('hello','world','python')
转义字符
print('hello
world')#/n换行 newline
print('hello world')#/t制表,占四位
print('hello
world')#回车(光标移动到开头)
print('helloworld')#退格
print('老师说:'大家好'')
#原字符,不希望字符串中的转义字符起作用,最后一个字符不能是反斜杠
print(r'hrllo
world')
二进制与字符编码
8bit = 1byte
1024byte = 1kb
1024kb = 1mb
1024mb = 1gb

常用的ASCII
A = 65
a = 97
0 = 48
标识符和保留字
import keyword print(keyword.kwlist)
['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'async', 'await', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']

变量的定义和使用
name = 'YangSheng'
print(name)
print('标识', id(name))
print('类型', type(name))
print('值', name)
输出结果
YangSheng 标识 1940806642480 类型 <class 'str'> 值 YangSheng
内存分析图

变量的多次赋值
多次赋值后变量名会指向新的空间
name = 'YangSheng' name = 'QQxing' print(name) #输出QQxing
Python中常见的数据类型

整数类型:
可以表示整数、负数、0
整数可以表示为:二进制(0b开头)、十进制、八进制(0o开头)、十六进制(0x开头)
浮点数
-
由整数+小数组成
-
浮点存储不精确
解决方案:导入模块decimal
print(1.1 + 2.2)
from decimal import Decimal
print(Decimal('1.1') + Decimal('2.2'))
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/浮点数.py 3.3000000000000003 3.3
字符串类型

str1 = '人生苦短,我用python' str2 = "人生苦短,我用python" str3 = '''人生苦短, 我用python''' print(str1,type(str1)) print(str2,type(str2)) print(str3,type(str3))
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/字符串类型.py 人生苦短,我用python <class 'str'> 人生苦短,我用python <class 'str'> 人生苦短, 我用python <class 'str'>
进程已结束,退出代码0
数据类型转换
不做具体介绍
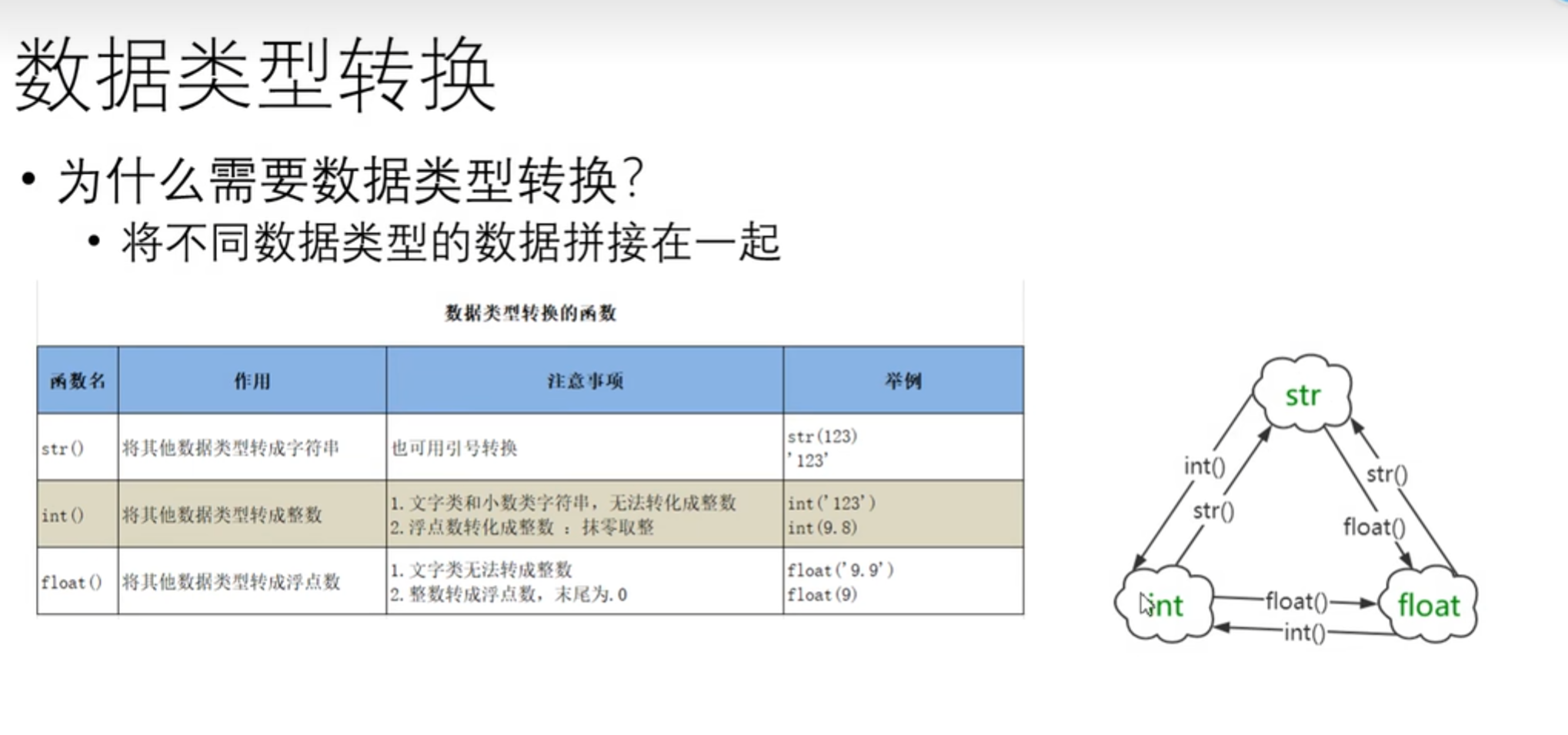
name = '张三'
age = 20
print(type(name),type(age))
print('我叫'+name+'今年'+str(age) + '岁')
print('我叫'+name+'今年',age,'岁')
python中的注释

input函数的使用
name = input('输入你的姓名
')
print(name+'你好')
#计算a + b a = float(input()) b = float(input()) print(a + b)
运算符
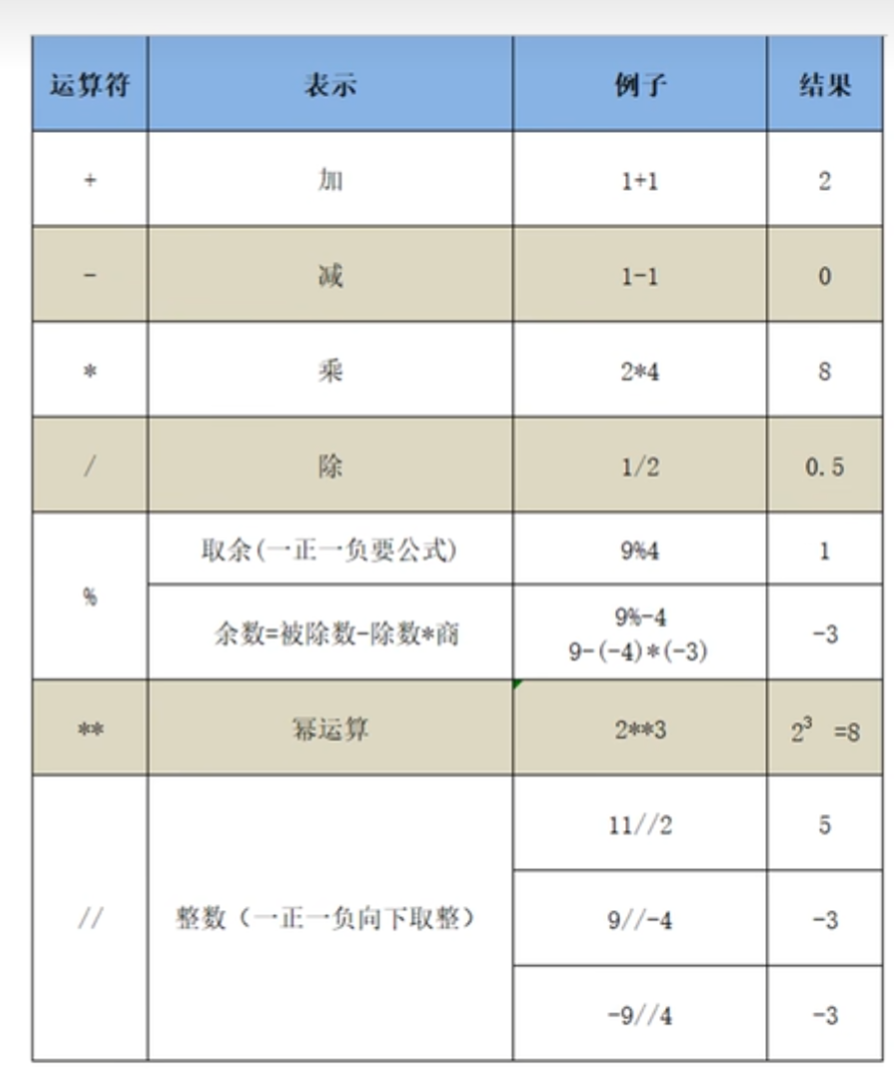
位运算符
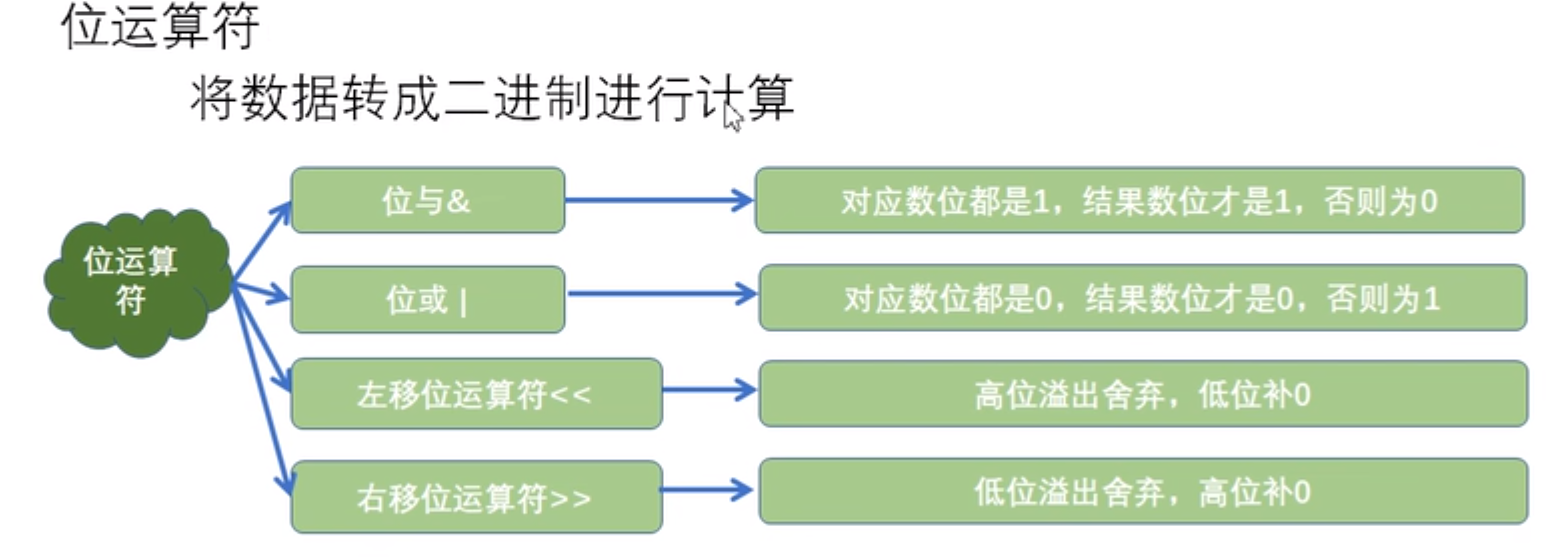
运算符优先级
算数运算——>位运算——>比较运算
顺序结构
对象的布尔值
print(bool(False))
print(bool(0))
print(bool(0.0))
print(bool(None))
print(bool(''))
print(bool(""))
print(bool([]))#空列表
print(bool(list()))#空列表
print(bool(()))#空元组
print(bool(tuple()))#空元组
print(bool({}))#空字典
print(bool(dict()))#空字典
print(bool(set()))#空集合
#以上对象布尔值位False
#其他对象布尔值都为True
条件表达式
#输入两个整数
a = int(input('请输入第一个数: '))
b = int(input('请输入第二个数: '))
#比较大小
if a >= b:
print(a , '大于等于', b)
else:
print(a, '小于', b)
#条件表达式
print( str(a) + '大于等于' + str(b) if a >= b else str(a)+ '小于'+ str(b))
pass语句

answer = input('您是会员吗?y/n
')
if answer == 'y':
pass
else:
pass
range函数的使用
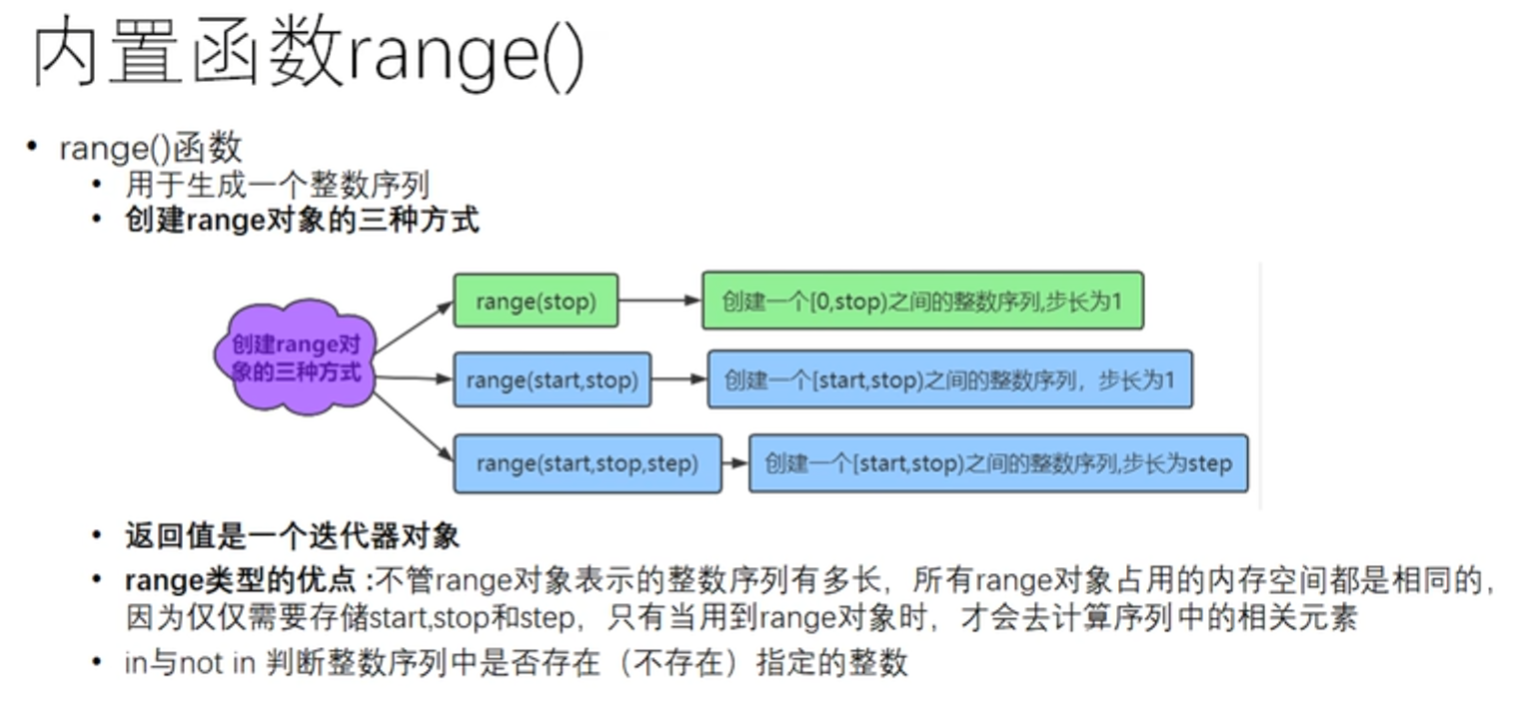
r = range(10)# [0, 1, 2, ... ,9]默认0开始,步长为1 print(r) print(list(r))#查看range对象中的整数序列 x = range(2, 10) print(list(x)) t = range(0,10,2) print(list(t)) print(10 in r)#判断10是否在r序列中 print(10 not in r)#判断10是否不在r序列中 print(range(1,20,1)) print(range(1,101,1))
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/range函数的使用.py range(0, 10) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] [0, 2, 4, 6, 8] False True range(1, 20) range(1, 101)
进程已结束,退出代码0

# #计算1-100之间的偶数和
#方法1
a = 0
sum = 0
while a <= 100:
sum += a
a += 2
print('1-100之间的偶数和为',sum)
#方法2
a = 0
sum = 0
while a <= 100 and a % 2 == 0:
sum += a
a += 2
print('1-100之间的偶数和为',sum)
#方法3
a = 0
sum = 0
for a in range(1, 101):
if a % 2 == 0:
sum += a
a += 1
print('1-100之间的偶数和为',sum)
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/while循环.py 1-100之间的偶数和为 2550 1-100之间的偶数和为 2550 1-100之间的偶数和为 2550
进程已结束,退出代码0
for_in循环
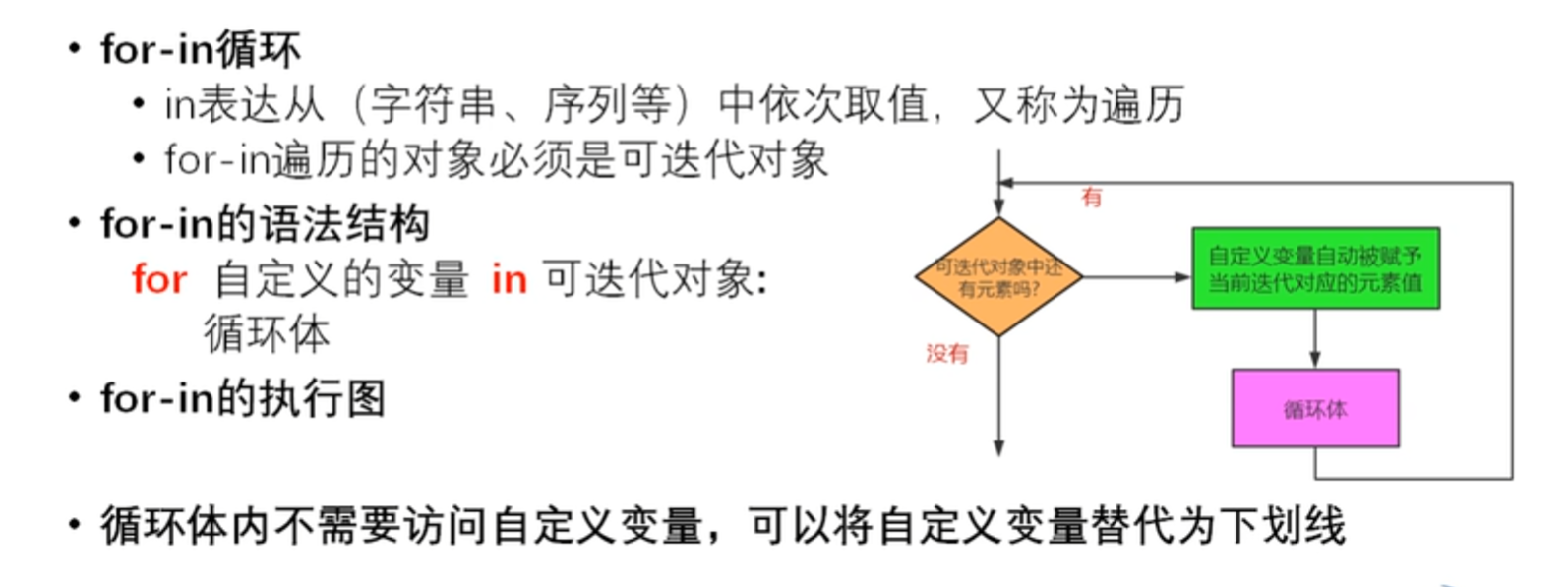
#判断100到999之间的水仙花数
print('100到999之间的水仙花数有:')
for n in range(100, 1000):
a = n % 10
b = n // 10 % 10
c = n // 100
if a ** 3 + b ** 3 + c ** 3 == n:
print(n, end=' ')
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/for_int循环.py 100到999之间的水仙花数有: 153 370 371 407 进程已结束,退出代码0
流程控制语句break
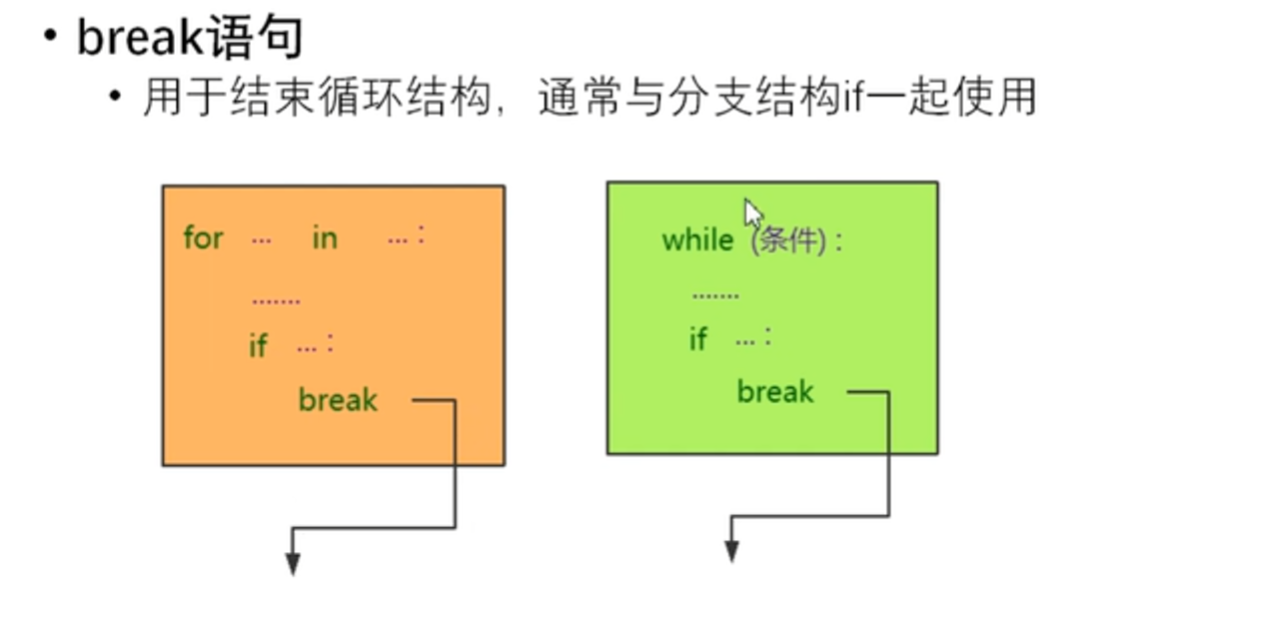
#录入密码,最多3次
for n in range(3):
pwd = input("请输入密码:")
if pwd == '8888':
print('密码正确')
break
else:
print('密码错误')
b = 0
while b < 3:
pa = input('请输入密码:')
if pa == '123':
print('密码正确')
break
else:
print('密码不正确')
流程控制语句continue
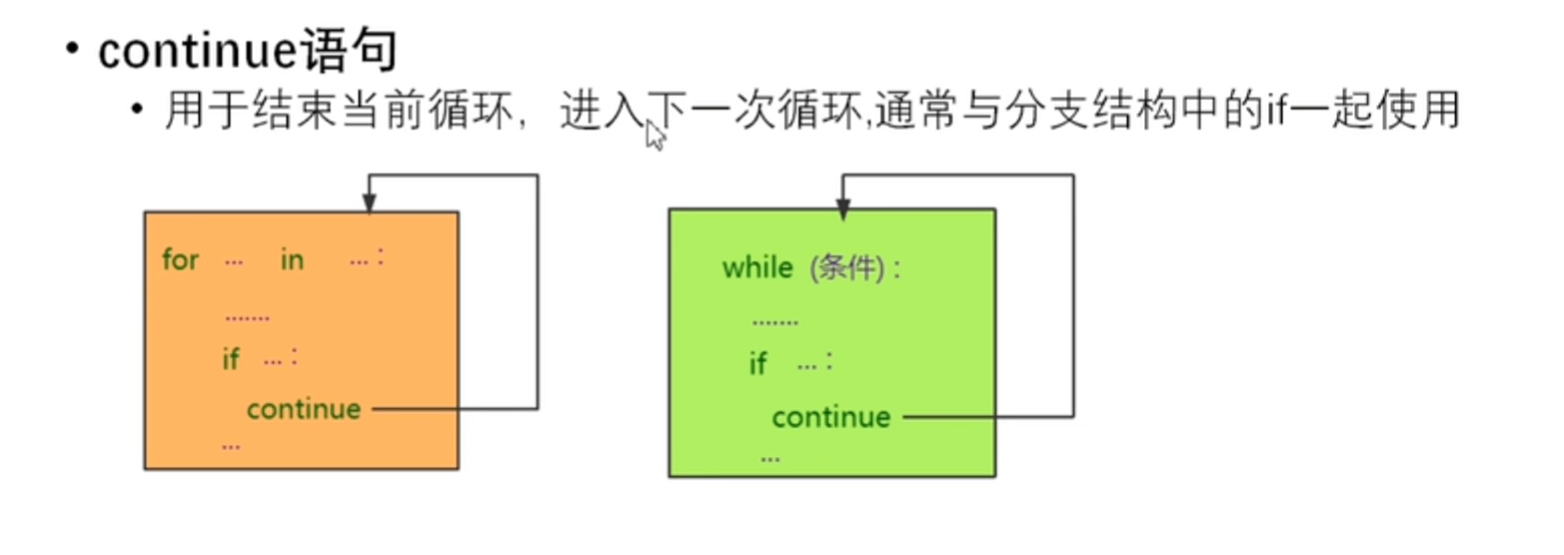
#输出1-50之间所有5的倍数 for n in range(1, 51): if(n % 5 != 0): continue else: print(n, end=" ") print() for n in range(1, 51): if(n % 5 == 0): print(n, end=" ")
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/流程控制语句continue.py 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 进程已结束,退出代码0
else语句
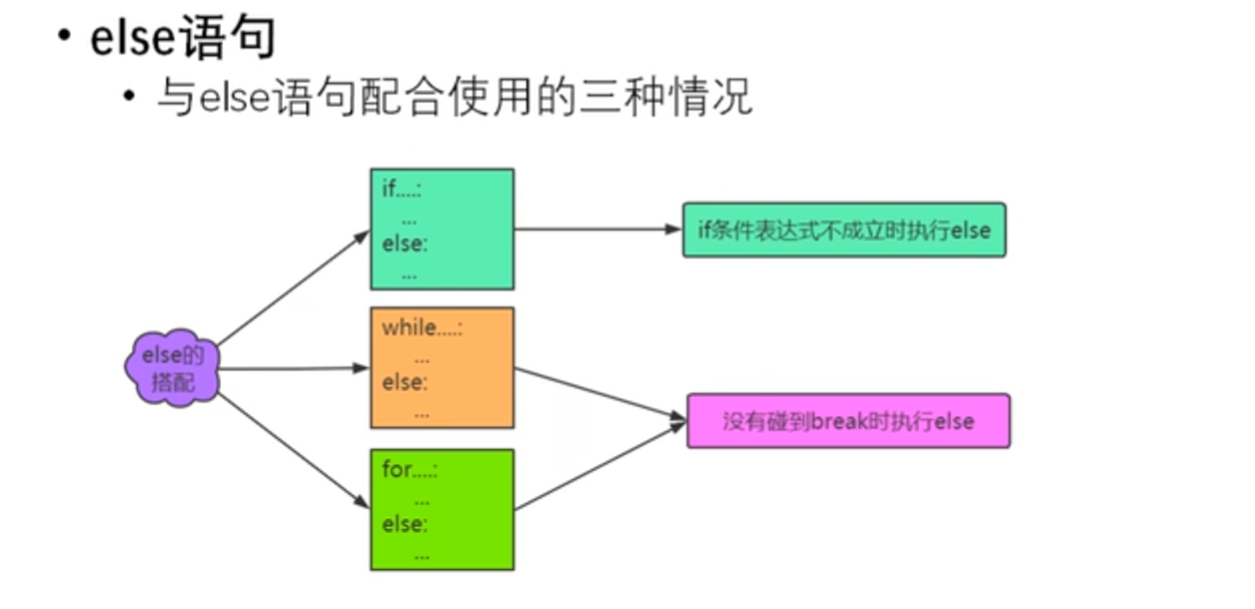
for n in range(3):
pwd = input('请输入密码:')
if pwd == '123':
print('密码正确')
break
else:
print('密码不正确')
else:
print('对不起,三次机会均没有猜对')
#------------------------------------------
a = 0
while a < 3:
pwd = input('请输入密码:')
if pwd == '333':
print('密码正确')
break
else:
print('密码错误')
a += 1
else:
print('对不起,三次机会均没有猜对')
嵌套循环
#9 * 9 乘法表 for i in range(1, 10): for j in range(1, i + 1): print(i , '*', j, '=', i * j,end=' ') print()
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/嵌套循环.py
1 * 1 = 1 2 * 1 = 2 2 * 2 = 4 3 * 1 = 3 3 * 2 = 6 3 * 3 = 9 4 * 1 = 4 4 * 2 = 8 4 * 3 = 12 4 * 4 = 16 5 * 1 = 5 5 * 2 = 10 5 * 3 = 15 5 * 4 = 20 5 * 5 = 25 6 * 1 = 6 6 * 2 = 12 6 * 3 = 18 6 * 4 = 24 6 * 5 = 30 6 * 6 = 36 7 * 1 = 7 7 * 2 = 14 7 * 3 = 21 7 * 4 = 28 7 * 5 = 35 7 * 6 = 42 7 * 7 = 49 8 * 1 = 8 8 * 2 = 16 8 * 3 = 24 8 * 4 = 32 8 * 5 = 40 8 * 6 = 48 8 * 7 = 56 8 * 8 = 64 9 * 1 = 9 9 * 2 = 18 9 * 3 = 27 9 * 4 = 36 9 * 5 = 45 9 * 6 = 54 9 * 7 = 63 9 * 8 = 72 9 * 9 = 81
进程已结束,退出代码0
二重循环中的break和continue
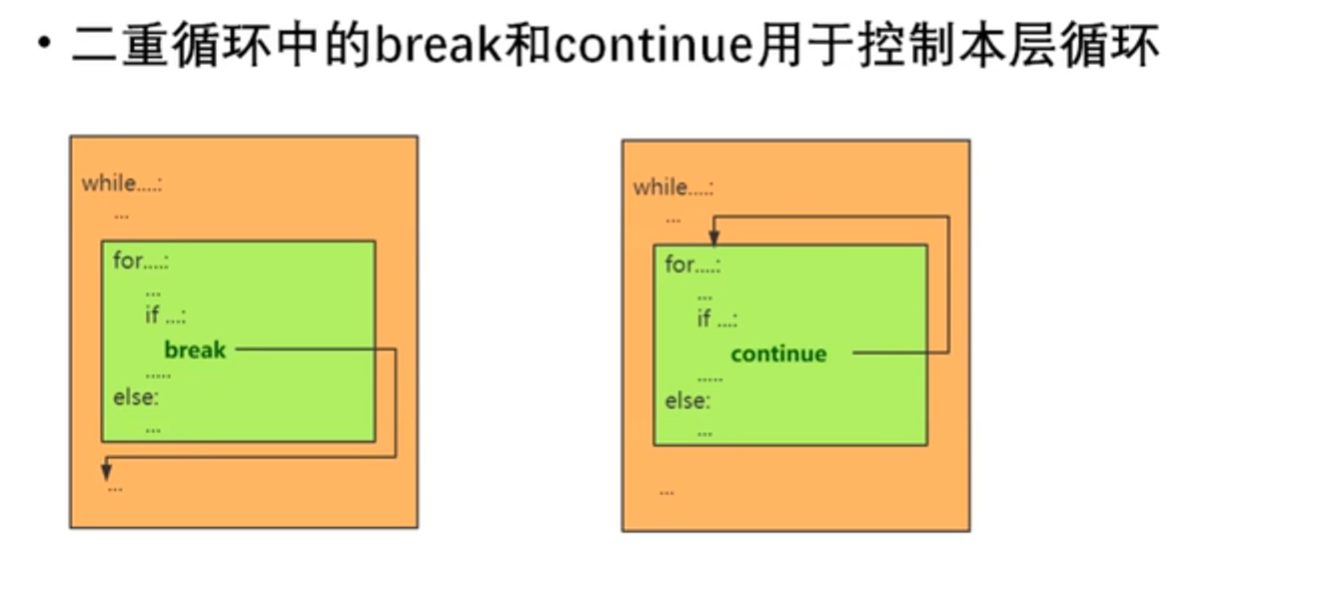
for i in range(5): for j in range(1, 11): if j % 2 == 0: break print(j) for i in range(5): for j in range(1, 11): if j % 2 == 0: continue print(j,end=' ') print()
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/二重循环中的break和continue.py 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 5 7 9 1 3 5 7 9 1 3 5 7 9 1 3 5 7 9 1 3 5 7 9
进程已结束,退出代码0
知识点总结

列表
创建,删除,增删查改
为什么需要列表
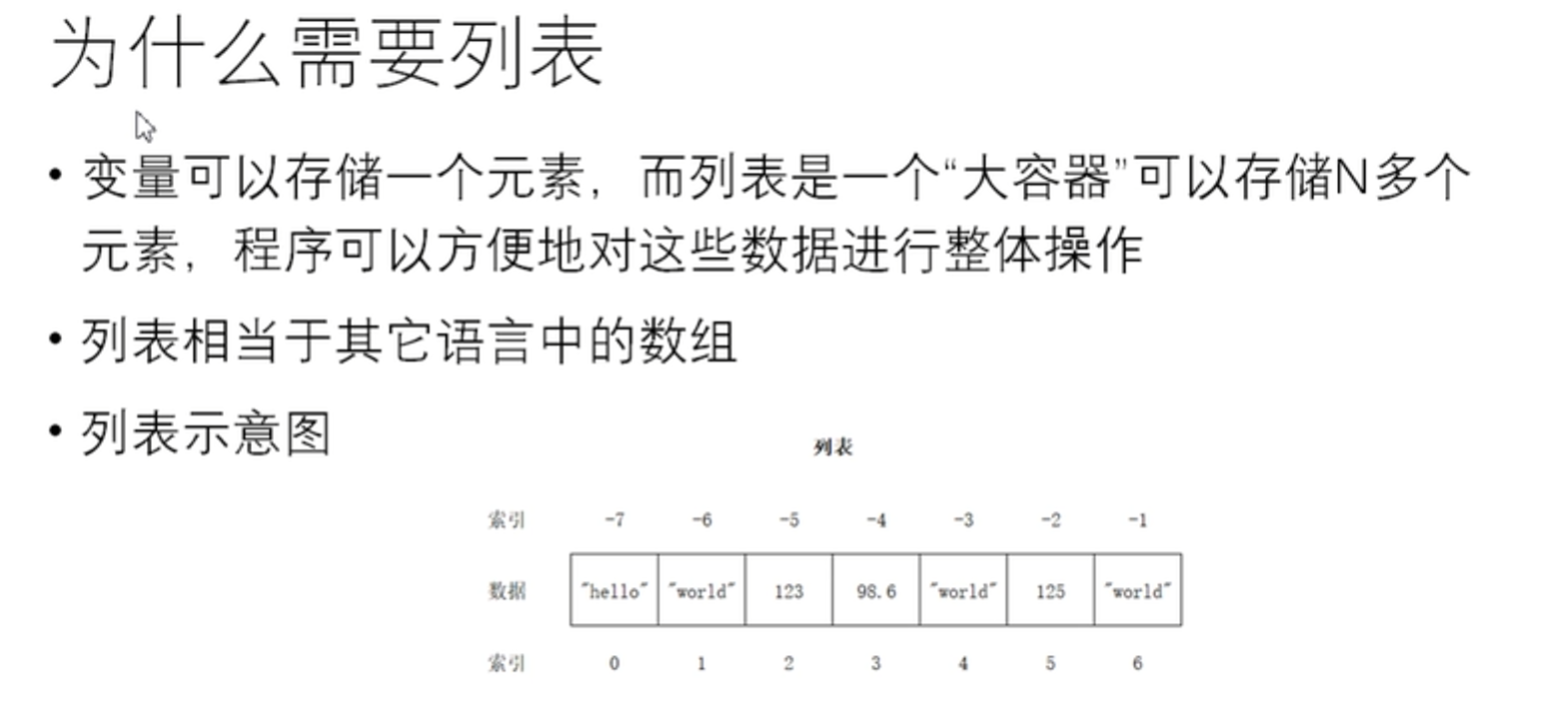
a = 10 list = ['hello','world', 100] print(id(list)) print(type(list)) print(list)
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/列表.py 1952402173568 <class 'list'> ['hello', 'world', 100]
进程已结束,退出代码0
内存分析图
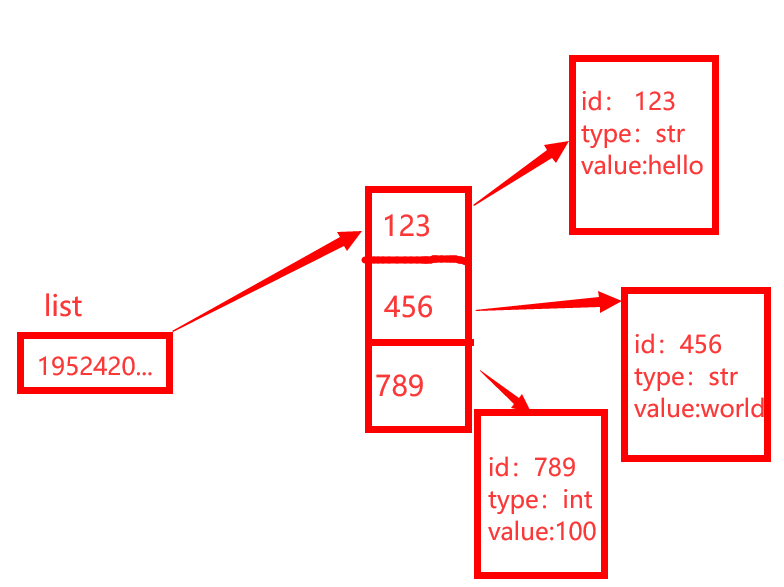
列表的创建
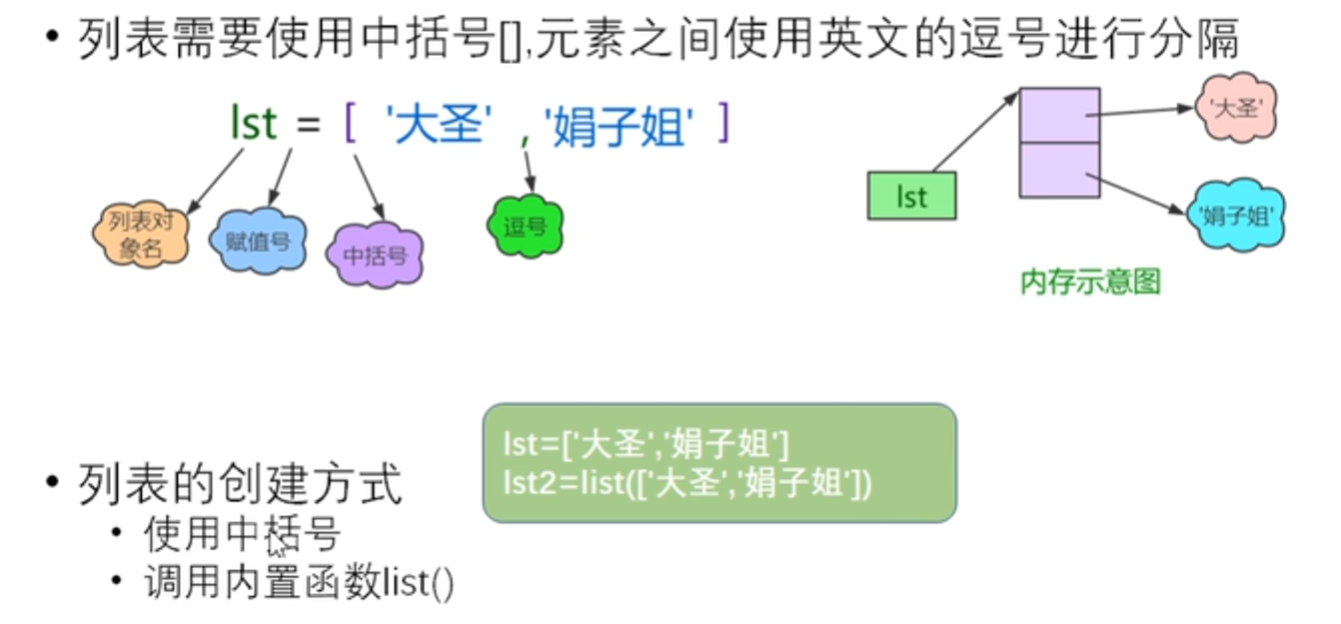
lst = ['hello','world',666] lst1 = list(['ni','hao','ya']) print(lst) print(lst1)
输出
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/列表.py ['hello', 'world', 666] ['ni', 'hao', 'ya']
进程已结束,退出代码0
列表的特点
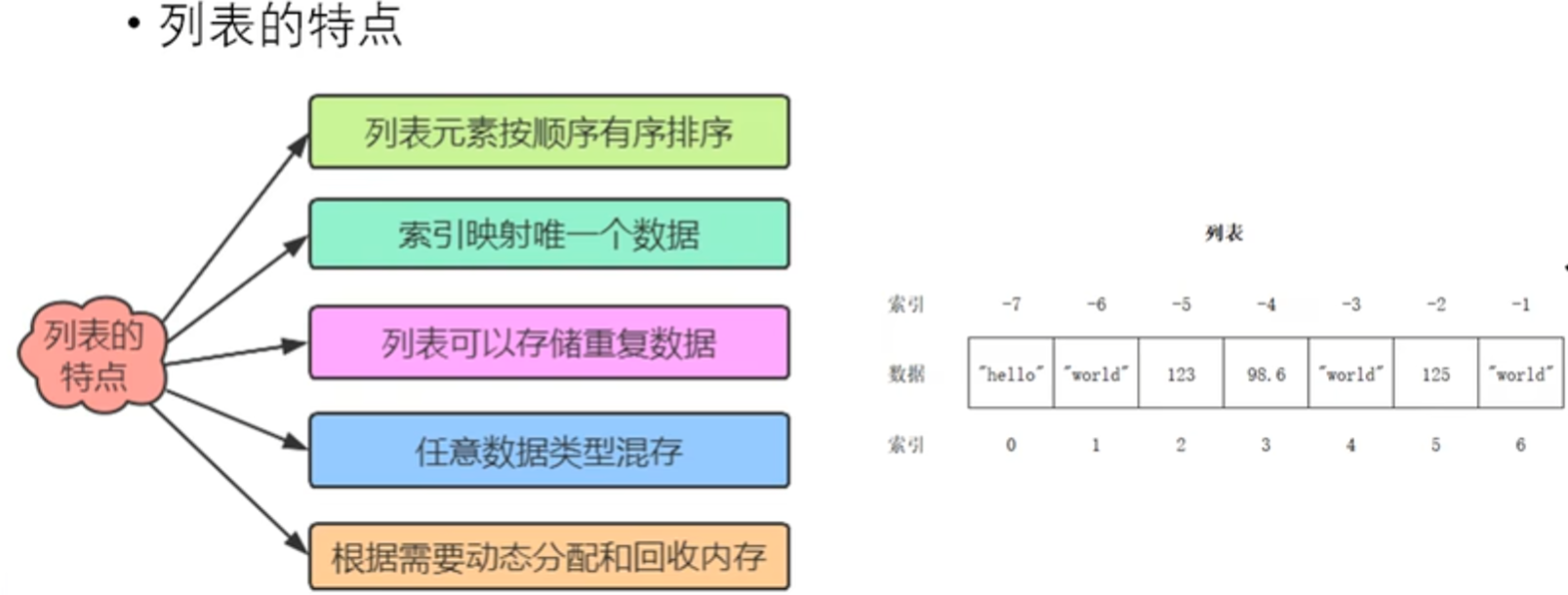
获取指定元素索引

lst = ['hello','world',666,'hello']
print(lst.index('hello'))
# print(lst.index('nihao'))
print(lst.index('hello',1,4))#[1,3)
获取表中指定的元素
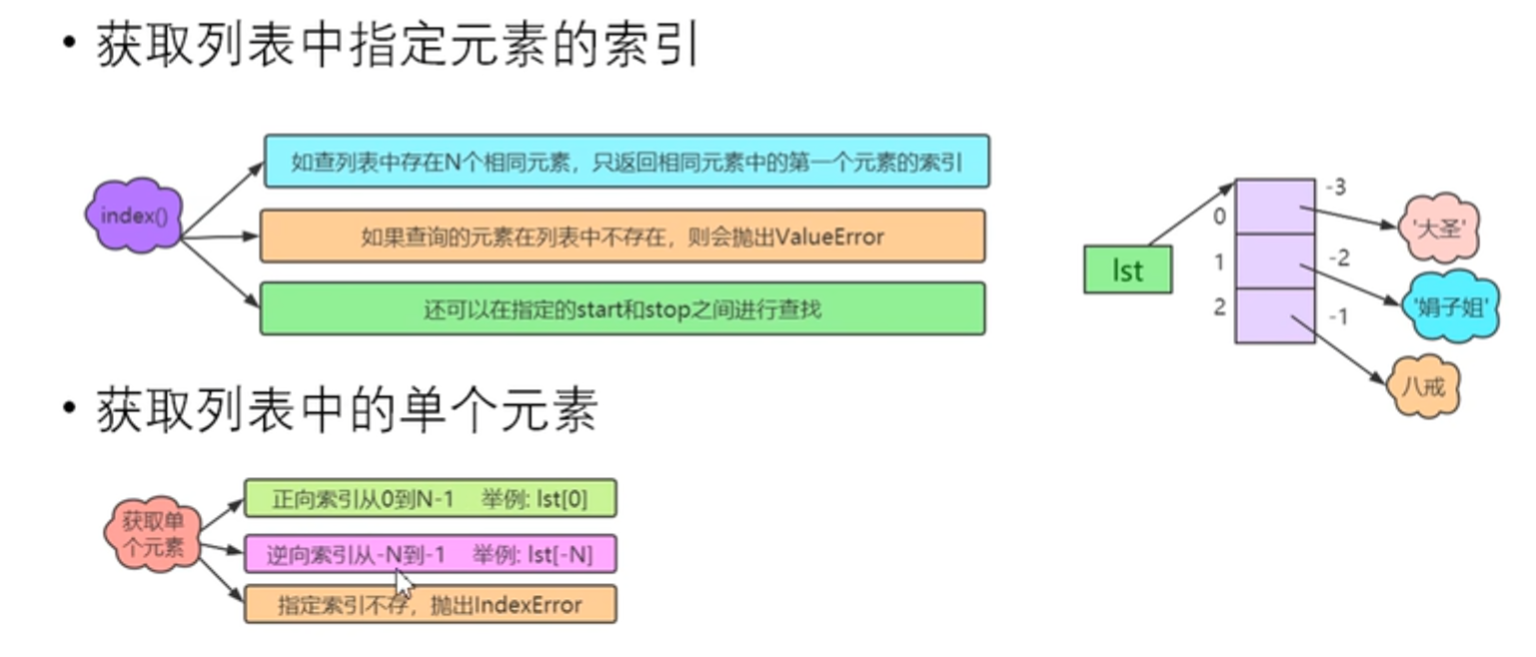
lst = ['hello','world',666,'hello','aaa'] #获取索引为2的元素 print(lst[2]) print(lst[-3]) print(lst[10])#超出范围则抛异常
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/列表.py Traceback (most recent call last): File "D:pythonProject列表.py", line 5, in <module> print(lst[10]) IndexError: list index out of range 666 666
进程已结束,退出代码1
获取列表中多个元素__切片操作
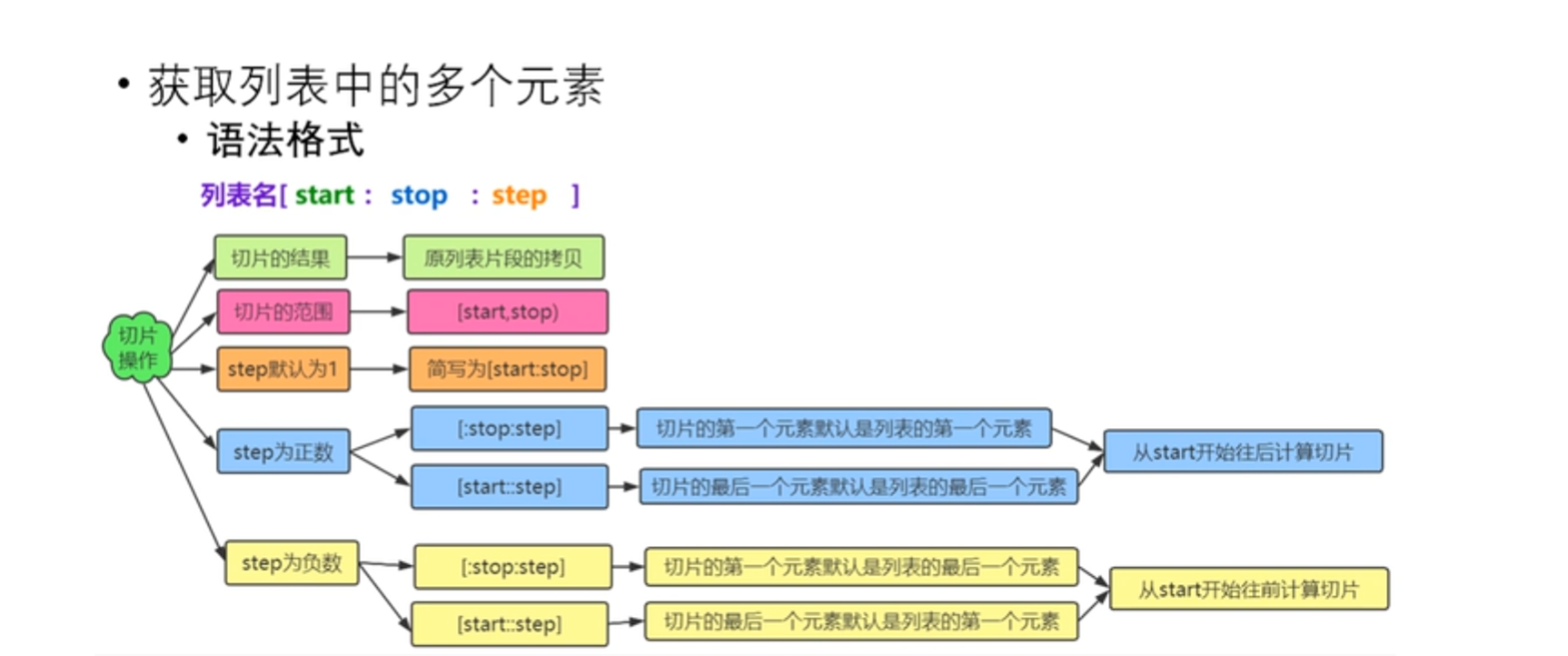
lst = [10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80]
print('原列表',id(lst))
lst2 = lst[1:6:1]
print('切的片段',id(lst2))
print(lst[1:6])
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/获取列表中多个元素__切片操作.py 原列表 2139436019328 切的片段 2139437744960 [20, 30, 40, 50, 60]
进程已结束,退出代码0
列表元素的判断及遍历

print('p' in 'python')
print('k' not in 'python')
lst = [10,20,'python','hello']
print(10 in lst)
print(100 in lst)
print(10 not in lst)
print(100 not in lst)
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/列表元素的判断及遍历.py True True True False False True
进程已结束,退出代码0
遍历操作
lst = [10,20,'python','hello'] for item in lst: print(item, end=' ')
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/列表元素的判断及遍历.py 10 20 python hello 进程已结束,退出代码0
列表元素的增删改操作
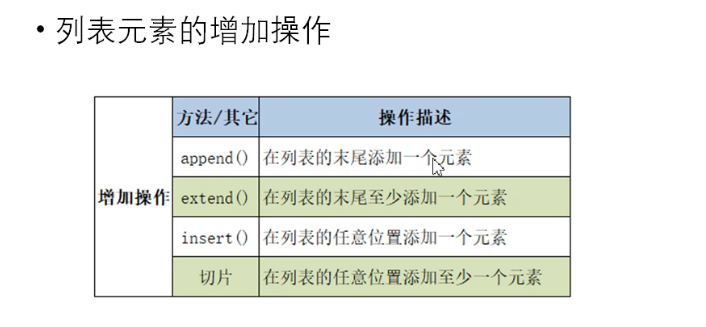
```
lst = [10,20,30]
print('原列表',lst)
lst.append(100)
print('添加元素后',lst)
lst2 = ['hello','world']
lst.extend(lst2)
print('添加元素后',lst)
lst.insert(2,40)
print('插入元素后',lst)
lst3 = [True,False,'hello']
lst[1:] = lst3
print(lst)
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/列表元素的增删改操作.py 原列表 [10, 20, 30] 添加元素后 [10, 20, 30, 100] 添加元素后 [10, 20, 30, 100, 'hello', 'world'] 插入元素后 [10, 20, 40, 30, 100, 'hello', 'world'] [10, True, False, 'hello']
进程已结束,退出代码0
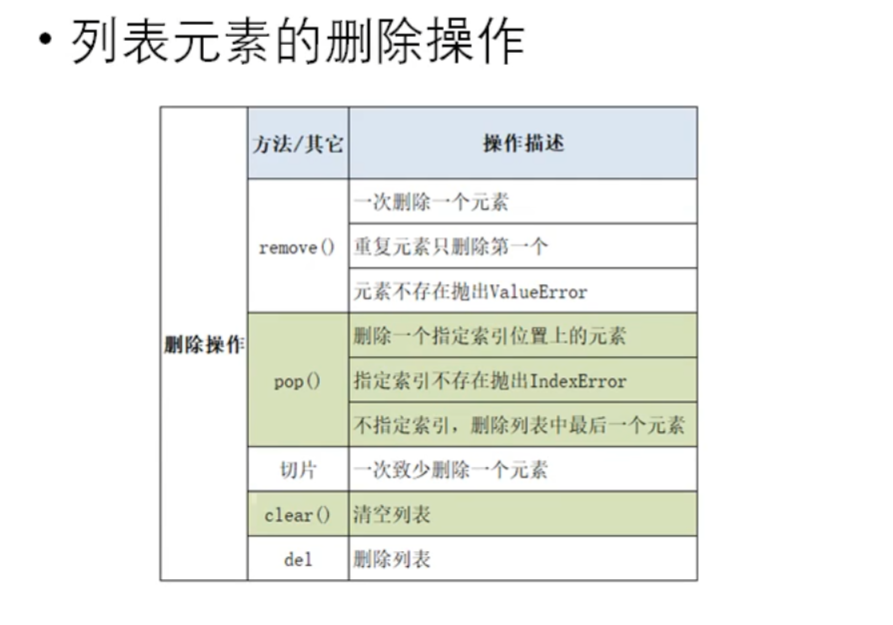
lst = [10,20,30,40,30,50]
print('---------remove操作----------')
lst.remove(30)
print(lst)
print('---------pop操作----------')
# lst.remove(100) 元素不存在则抛出异常
lst.pop(1)
lst.pop()#不指定默认移除最后一位
# lst.pop(100)索引不存在则抛出异常
print(lst)
print('---------切片操作----------')
lst[1:3]=[]
print(lst)
print('---------clear操作----------')
lst.clear()
print(lst)
del lst#删除列表对象
输出:
lst = [10,20,30,40,30,50] print('---------remove操作----------') lst.remove(30) print(lst) print('---------pop操作----------') # lst.remove(100) 元素不存在则抛出异常 lst.pop(1) lst.pop()#不指定默认移除最后一位 # lst.pop(100)索引不存在则抛出异常 print(lst) print('---------切片操作----------') lst[1:3]=[] print(lst) print('---------clear操作----------') lst.clear() print(lst)
列表元素的修改

lst = [10,20,30,40] lst[2] = 100 print(lst) lst[1:3]=[300,400,500,600] print(lst)
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/列表元素的修改.py [10, 20, 100, 40] [10, 300, 400, 500, 600, 40]
进程已结束,退出代码0
列表元素的排序

lst = [20,10,30,60,50] lst.sort() print(lst) #通过关键字进行升序排序 lst.sort(reverse=True) print(lst) #使用内置函数sorted进行排序 lst1 = sorted(lst) print(lst1) desc_lst = sorted(lst,reverse=True) print(desc_lst)
输出;
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/列表元素的排序.py [10, 20, 30, 50, 60] [60, 50, 30, 20, 10] [10, 20, 30, 50, 60] [60, 50, 30, 20, 10]
进程已结束,退出代码0
列表生成式
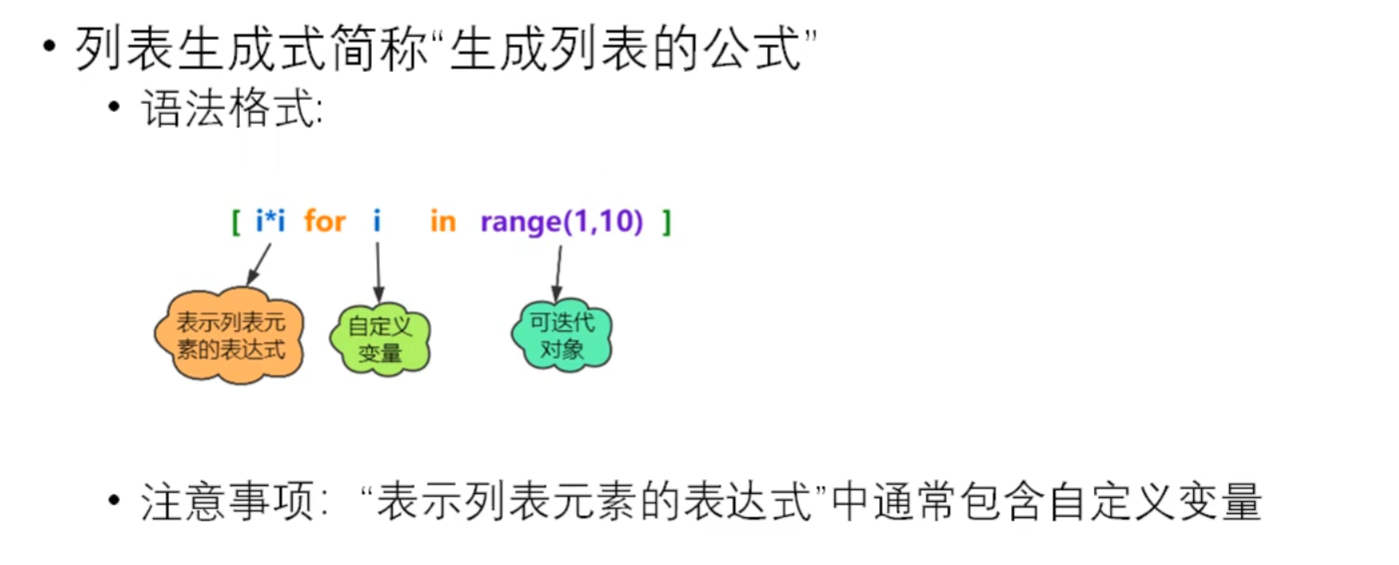
lst = [i*i for i in range(1,10)] print(lst) lst2 = [i * 2 for i in range(1,6)] print(lst2)
输出:
D:pythonpython.exe D:/pythonProject/列表生成式.py [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81] [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
进程已结束,退出代码0
列表总结
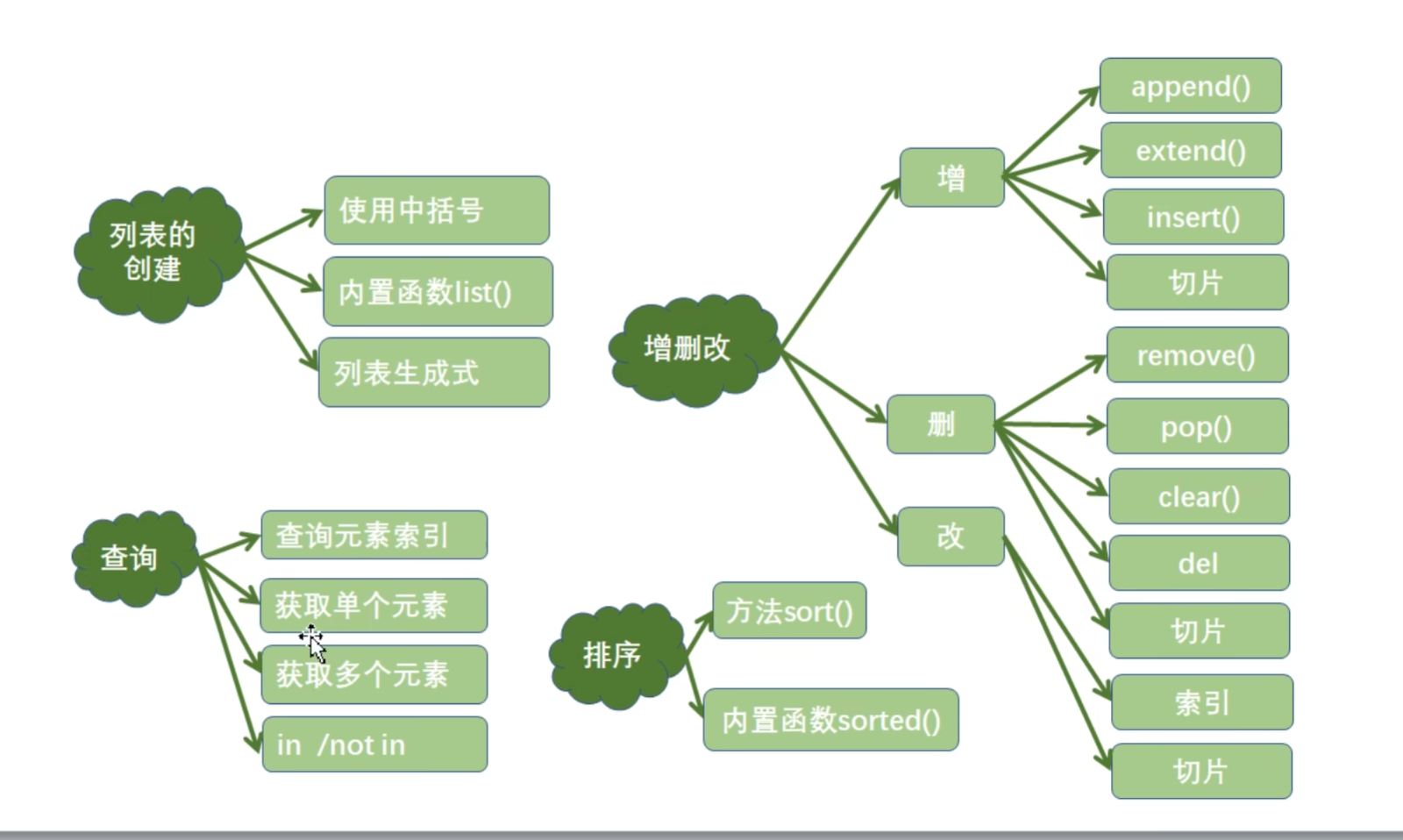






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结