您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >Deeplearing.AI 课程笔记(DLAI)网站首页学无止境
Deeplearing.AI 课程笔记(DLAI)
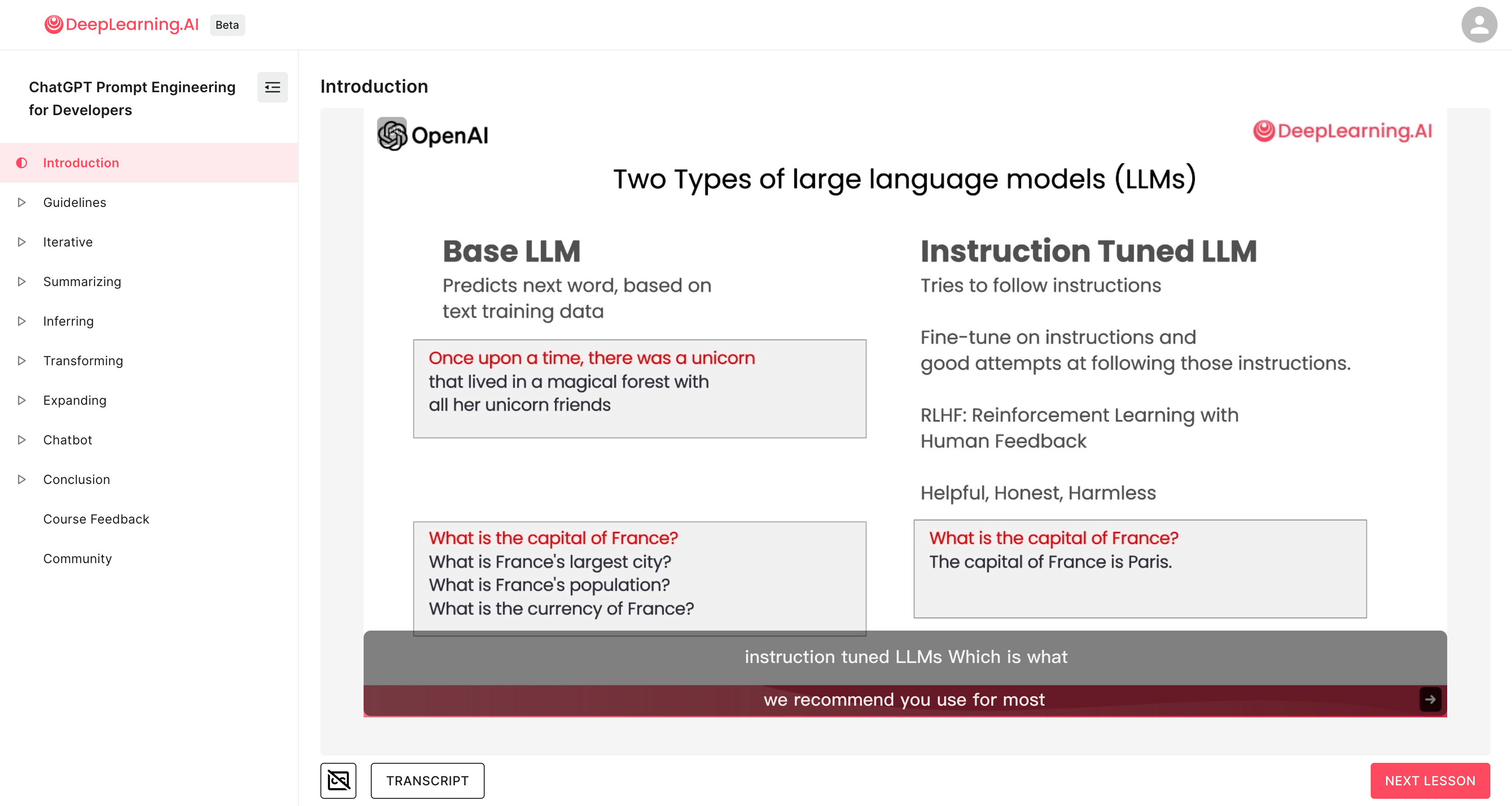
课程地址: https://learn.deeplearning.ai/chatgpt-prompt-eng
@OpenAI & @ Deeplearing.ai
Lesson 2:准则
Prompting 的两个基本原则:
- write clear and specific instructions,第一原则是写清楚提示并给出具体说明
- to give the model time to think,第二个原则是给予模型思考时间
需要注意的是:
- clear 并不等于 short,也就是说清楚的提示内容并不一定是简短的
Principal 1 - write clear and specific instructions
技巧1: 使用界定符,以避免注入
eg:使用 ``` 来包裹用户的提示内容,以避免提示注入 prompt injections
- Triple quotes:
""" - Triple backticks: ```
- Triple dashes:
--- - Angle brackets:
<> - XML Tags:
<tag> </tag>
示例内容
text = f"""
You should express what you want a model to do by
providing instructions that are as clear and
specific as you can possibly make them.
This will guide the model towards the desired output,
and reduce the chances of receiving irrelevant
or incorrect responses. Don't confuse writing a
clear prompt with writing a short prompt.
In many cases, longer prompts provide more clarity
and context for the model, which can lead to
more detailed and relevant outputs.
"""
prompt = f"""
Summarize the text delimited by triple backticks
into a single sentence.
```{text}```
"""
response = get_completion(prompt)
print(response)
OutPut:Clear and specific instructions should be provided to guide a model towards the desired output, and longer prompts can provide more clarity and context for the model, leading to more detailed and relevant outputs.
技巧2: 指定输出的内容格式
指定输出的内容格式为 HTML 或 JSON
prompt = f"""
Generate a list of three made-up book titles along
with their authors and genres.
Provide them in JSON format with the following keys:
book_id, title, author, genre.
"""
response = get_completion(prompt)
print(response)
技巧3: 增加判断
检查条件是否都已经满足 Check whether conditions are satisified, Check assumptions required to do the task, indicate this and kind of stop short of a full task completion attempt.
text_1 = f"""
Making a cup of tea is easy! First, you need to get some
water boiling. While that's happening,
grab a cup and put a tea bag in it. Once the water is
hot enough, just pour it over the tea bag.
Let it sit for a bit so the tea can steep. After a
few minutes, take out the tea bag. If you
like, you can add some sugar or milk to taste.
And that's it! You've got yourself a delicious
cup of tea to enjoy.
"""
prompt = f"""
You will be provided with text delimited by triple quotes.
If it contains a sequence of instructions,
re-write those instructions in the following format:
Step 1 - ...
Step 2 - …
…
Step N - …
If the text does not contain a sequence of instructions,
then simply write "No steps provided."
"""{text_1}"""
"""
response = get_completion(prompt)
print("Completion for Text 1:")
print(response)
技巧4: 少样本提示 Few-shot prompting
prompt = f"""
Your task is to answer in a consistent style.
<child>: Teach me about patience.
<grandparent>: The river that carves the deepest
valley flows from a modest spring; the
grandest symphony originates from a single note;
the most intricate tapestry begins with a solitary thread.
<child>: Teach me about resilience.
"""
response = get_completion(prompt)
print(response)
Principal 2 - give the model time to think
有些时候,如果您给模型一个太复杂的任务,在短时间内或用少量的单词完成,它可能作出不正确的猜测。如果模型在匆忙地得出错误的结论,您应该尝试重新构思查询,要求在模型提供最终答案之前请求一系列相关推理。
为避免模型由于时间限制或语言表达能力限制而过快得出错误结论,我们应该:
- 重新构造查询,要求模型提供一系列相关的推理过程,而不仅仅是最终答案。
- 避免给模型过于复杂的任务,超出其在有限时间和语言条件下解决的能力。 否则模型可能会猜测,导致错误结论。
- 给模型更多时间和更宽松的语言条件来推理和表达,避免其"赶时间猜测"。
技巧1: 给出完成任务所需的步骤
Step1: ...
Step2: ...
...
StepN: ...
演示示例:
prompt_2 = f"""
Your task is to perform the following actions:
1 - Summarize the following text delimited by
<> with 1 sentence.
2 - Translate the summary into French.
3 - List each name in the French summary.
4 - Output a json object that contains the
following keys: french_summary, num_names.
Use the following format:
Text: <text to summarize>
Summary: <summary>
Translation: <summary translation>
Names: <list of names in Italian summary>
Output JSON: <json with summary and num_names>
Text to summarize : <{text}>
"""
response = get_completion(prompt_2)
print("
Completion for prompt 2:")
print(response)
技巧2: 让模型自己找解决方案
Instruct the model to work out its own solution before rushing to a conclusion,指示模型在匆忙得出结论之前先解决自己的解决方案。
我们明确指示模型在得出结论之前先解决自己的解决方案时,有时会得到更好的结果。这与我们之前讨论的给模型时间来真正解决问题而不仅仅是确定答案是否正确的想法是相同的。
演示示例:
prompt = f"""
Your task is to determine if the student's solution
is correct or not.
To solve the problem do the following:
- First, work out your own solution to the problem.
- Then compare your solution to the student's solution
and evaluate if the student's solution is correct or not.
Don't decide if the student's solution is correct until
you have done the problem yourself.
Use the following format:
Question:
```
question here
```
Student's solution:
```
student's solution here
```
Actual solution:
```
steps to work out the solution and your solution here
```
Is the student's solution the same as actual solution
just calculated:
```
yes or no
```
Student grade:
```
correct or incorrect
```
Question:
```
I'm building a solar power installation and I need help
working out the financials.
- Land costs $100 / square foot
- I can buy solar panels for $250 / square foot
- I negotiated a contract for maintenance that will cost
me a flat $100k per year, and an additional $10 / square
foot
What is the total cost for the first year of operations
as a function of the number of square feet.
```
Student's solution:
```
Let x be the size of the installation in square feet.
Costs:
1. Land cost: 100x
2. Solar panel cost: 250x
3. Maintenance cost: 100,000 + 100x
Total cost: 100x + 250x + 100,000 + 100x = 450x + 100,000
```
Actual solution:
"""
response = get_completion(prompt)
print(response)
仔细看上面这个示例,会发现很有意思,会要求模型先用自己的方式来作出解答,然后对比给出的结果再做判断,其中还特别强调了 Don't decide if the student's solution is correct until you have done the problem yourself.
模型的局限性
Makes statements that sound plausible but are not actually true.
幻觉——虚构内容,尽管模型在训练过程中接触到了大量知识,但它并没有完美地记住所看到的信息,因此它不太了解其知识的边界。这意味着它可能会尝试回答一些关于晦涩主题的问题,并且可能会编造一些听起来合理的但实际上并不真实的事情。我们将这些虚构的想法称为幻觉。
为了减少幻觉,当您希望模型基于文本生成答案时,可以采取的另一个策略是要求模型首先从文本中找到任何相关引用,然后要求模型使用这些引用来回答问题。
让答案能够追溯到源文件通常对于减少幻觉非常有帮助。
Lesson 3:迭代提示 iterative prompt development
Idea -- Implement --> Implementation(code/data)
Implementation(code/data) -- Train model --> Experimental result
Error Analysis -- Change --> Idea

Prompt guidelines
- Be clear and specific
- Analyze why result does not give desired output
- Refine the idea and the prompt
- Repeat
迭代提示的方式可以用于的场景包括:
- Output 过长,Limit the number of words/sentences/characters。可以通过迭代增加输出的内容限制(可以是文字数量/ words、可以是字符数量/ characters,甚至可以是句子的数量/ sentences);
- Output 的重点调整,Text focuses on the wrong details, Ask it to focus on the aspects that are relevant to the intended audience。可以通过迭代来调整输出中要重点关注的内容,可以是基于场景、面向的用户群体、内容中需要包含特定内容等;
- Description needs a table of dimensions, Ask it to extract information and organize it in a table。
总结的整个迭代的过程(Iterative Process)如下:
- Try something
- Analyze where the result does not give what you want
- Clarify instructions, give more time to think
- Refine prompts with a batch of examples
Lesson 4:归纳和总结 summarize
当今世界有如此多的文本,我们几乎没有足够的时间阅读我们希望有时间阅读的所有内容。所以一个我见过的最令人兴奋的应用程序大型语言模型就是用它来总结文本。
summarize 的用法包括:
- 总结和归纳文字
- 限定返回内容长度(words, characters, sentences etc.)
- 限定返回内容的重点
- 多段内容的总结和归纳
通过归纳和总结,可以让人们能够快速的了解大长度短内容的重点,对该内容有个大概的了解,当需要精读、或者需要了解更多详情的时候,用户可以选择去查看原文,是一个是很便利、高效的阅读用具。
个人觉得有点类似于之前得到的每天读本《电子书》,或者是视频网站上流行的 5 分钟看完一部电影的感觉。
Lesson 5:推断 inferring
通过推断,LLM 可以从文本中提取标签、名字等信息,并通过这些信息来判断文本中所包含的情感信息(positive & negative)。
相比传统的机器学习方法,LLM 这种方式,可以节省包括标注数据、训练多个模型等在内的很多繁琐的工作,也能够快速的判断出内容中的情感倾向、信息。
inferring 的用法包括:
- 情感判断(positive / negative)
- 情绪表达(Identify types of emotions)
- 判断是否包含特定情绪(eg: Identify ange)
- 信息提取(eg: Extract product and company name from customer reviews)
- 以上 4 类任务的组合,即通过一个 prompt 完成以上 4 个任务
- 话题总结(inferring topics),有点类似于 summarize,但总结出来的内容可能会比 summarize 更为抽象一点
Lesson 6:转换 Transforming
大型语言模型非常擅长将其输入转换为不同的格式,例如输入一种语言的文本和转换它或将其翻译成不同的语言,或者帮助拼写和语法纠正,帮助你纠正一段可能不是很符合语法的文本,甚至转换格式,比如将 HTML 转换为 JSON。
大语言模型的一个主要功能是进行不同形式的"格式转换"或"翻译"。它可以在语言层面上翻译文本,可以在语法和拼写层面上"校正"文本,甚至可以在web格式等层面上转换输入格式。这些都是大语言模型的显著长处和主要用途。大语言模型擅长"翻译"、“转换"和"校正”,通过在不同层面展现语言表达能力,来实现人们在这些应用场景中的需求。
transforming 的用法包括:
- 翻译(Translation),不同语种的翻译、语言检测等
- 通用翻译(Universal Translator),于翻译类似,可以同时翻译多个语种的内容
- 语气模仿(Tone Transformation),可以根据需要来模仿不同的口吻进行表达(比如模仿律师的口吻、正式文书的口吻等)
- 格式转换(Format Conversion),不同格式之间的转换,比如 HTML 2 Json,HTML 2 Markdown 等
- 拼写/语法检查(Spellcheck/Grammar check),通过
proofread或proofread and correct命令来对文本进行拼写和语法检查,并提供纠正后的结果
Lesson 7:扩展/发散 Expanding
“发散/扩展”任务充分展示了大语言模型强劲的语言生成能力,以及这种能力在拓展人类思考、激发灵感和创意方面的应用潜力。我们可以利用大语言模型强大的语言生成能力,自动扩展和丰富我们的初步思路、话题和提示。
- “发散/扩展”是一种语言生成任务,要求模型基于较短的文本输入生成较长而完整的语言表达。
- 输入可以是一组说明,一个话题列表等较短的文本。
- 可以要求模型产生较长的语言输出,如一封电子邮件,一篇文章等。
- 通过发散我们可以与语言模型一起进行头脑风暴,产生更丰富的话题和思路。
关于 temperature
在 ChatGPT 的 API 中,temperature 这个参数是用来控制模型响应的随机性的。具体来说:
- temperature 值越高,模型的响应越随机,可能产生更多样化和意想不到的回复。这会使对话显得更自然和人性化。
- temperature 值越低,模型的响应越 deterministic, 回复会更加标准和预期。这会使对话显得更一致和可预测。
所以通过调整 temperature 参数的值,可以在随机性和一致性之间找到平衡,产生更自然的对话效果。常见的 temperature 设置有:
- 0:用于对可靠性、可预测性有较高要求的任务。
- 0.7 - 0.9: 产生较自然的对话,有一定的随机性。这是 ChatGPT 默认的参数设置。
- 1.0 - 1.2:更高的随机性,可能产生更意想不到的回复。
- 0.5 - 0.7: 更低的随机性,回复更加标准和一致。
总之,temperature 参数给了 ChatGPT 模型一定的自由度和个性,这有助于产生更人性化的交互体验。通过调整这个参数,可以实现不同的对话风格。
Lesson 8:聊天机器人ChatBot
构建各类聊天机器人是大语言模型功能的一个重要应用方向。它们需要理解复杂语言输入并作出相应响应,这正是大语言模型的专长所在。通过聊天的方式与针对特定任务或行为进行个性化或专门化的聊天机器人进行对话。
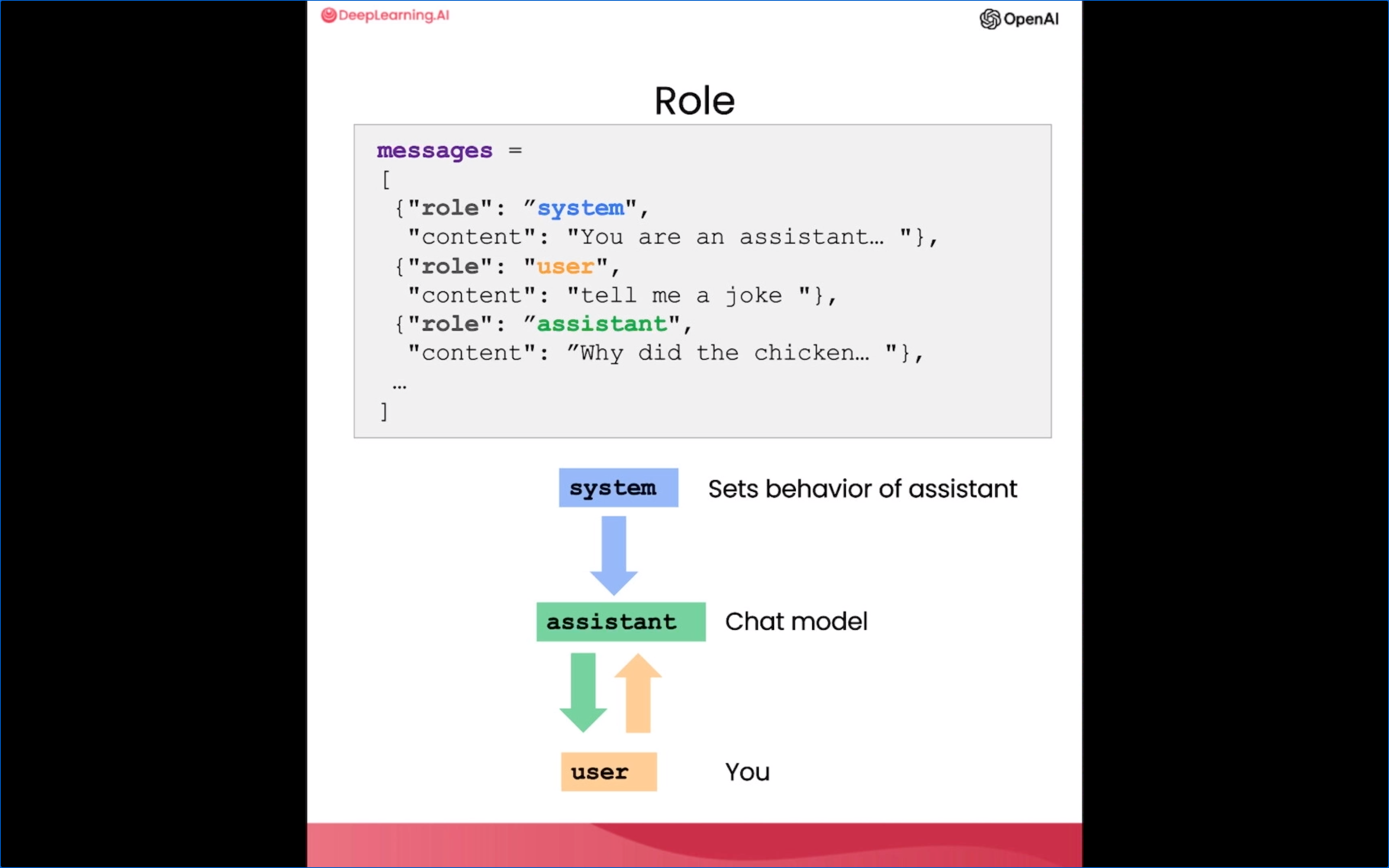
- 我们可以利用大语言模型的语言理解和生成能力来构建聊天机器人。
- 这种聊天机器人可以在各种场景中发挥作用,如客户服务或餐馆点单等。
结尾 Conclusion







 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结