您现在的位置是:首页 >技术教程 >STL容器 —— list 了解、接口使用,以及模拟实现list(部分常用接口)网站首页技术教程
STL容器 —— list 了解、接口使用,以及模拟实现list(部分常用接口)
注意 : 以下所有文档都来源此网站 : http://cplusplus.com/
一、vector的介绍及使用
list文档的介绍:https://cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/
1. vector 的介绍
1. list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
2. list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
3. list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高效。
4. 与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好。
5. 与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这可能是一个重要的因素)
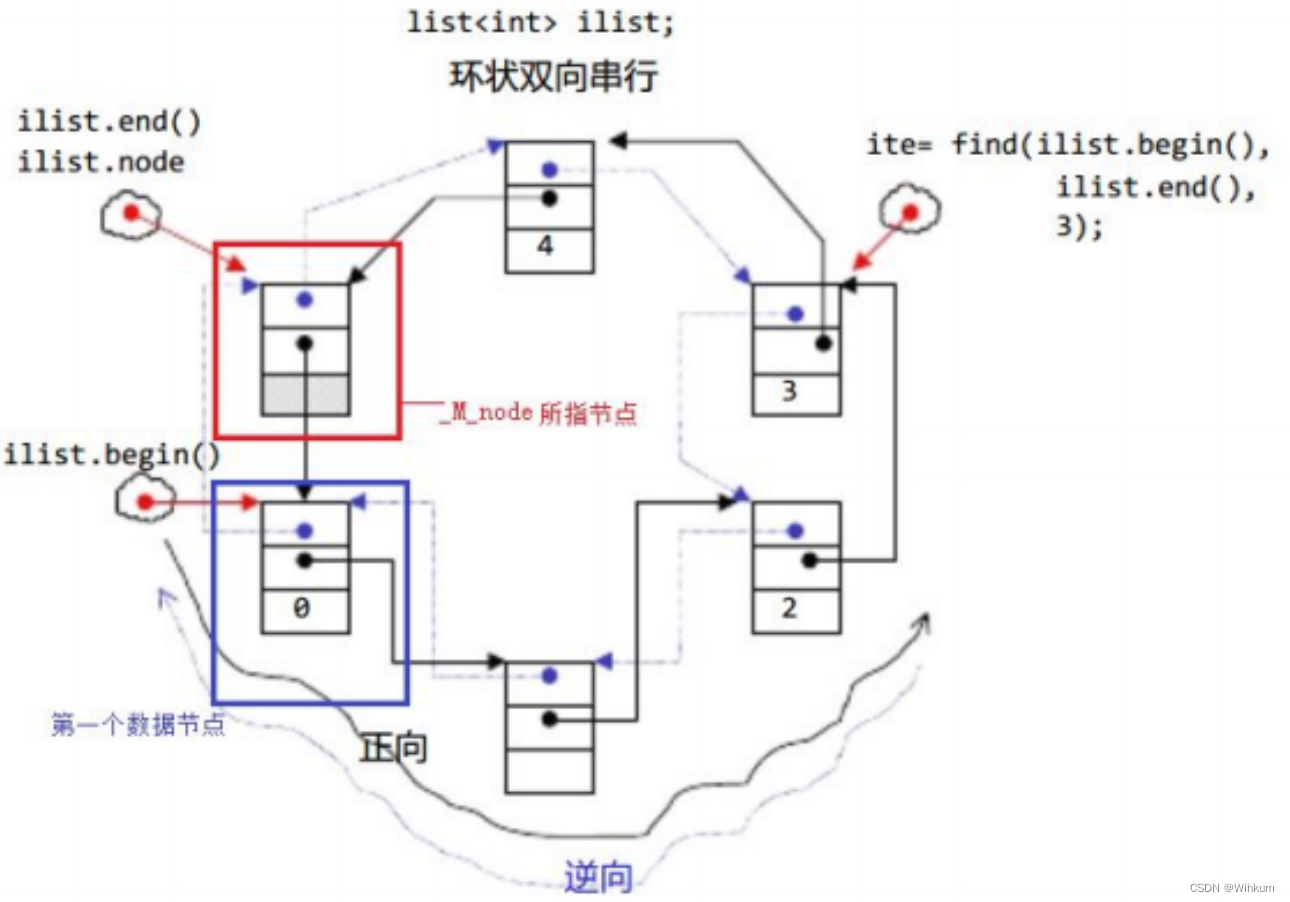
二、list 常用接口说明
1. list 的构造
|
接口说明
| |
|
list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type())
|
构造的
list
中包含
n
个值为
val
的元素
|
|
list()
|
构造空的
list
|
|
list (const list& x)
|
拷贝构造函数
|
|
list (InputIterator fifirst, InputIterator last)
|
用
[first, last)
区间中的元素构造
list
|
2. list 迭代器的使用
迭代器可以理解为像指针一样,但可能是指针可能不是。
|
函数声明
|
接口说明
|
|
返回第一个元素的迭代器
+
返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器
| |
|
返回第一个元素的
reverse_iterator,
即
end
位置
,
返回最后一个元素下一个位置的
reverse_iterator,
即
begin
位置
|
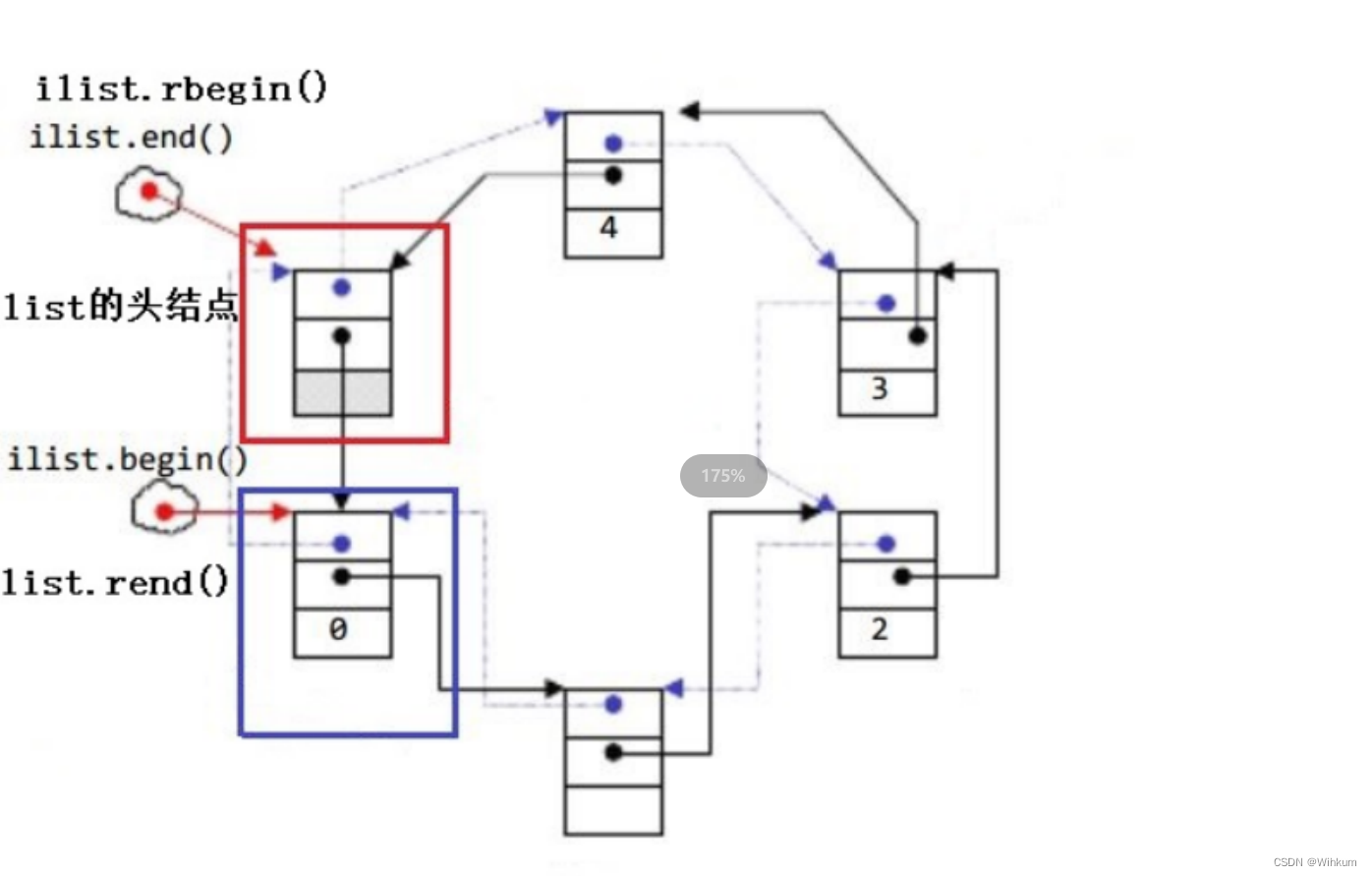
(1) begin、end 是正向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向后移动
(2)rbegin(end)与rend(begin)为反向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向前移动
3. list capacity
|
函数声明
|
接口说明
|
|
检测
list
是否为空,是返回
true
,否则返回
false
| |
|
返回
list
中有效节点的个数
|
4. list element access
|
函数声明
|
接口说明
|
|
返回
list
的第一个节点中值的引用
| |
|
返回
list
的最后一个节点中值的引用
|
5. list modifiers
|
函数声明
|
接口说明
|
|
在
list
首元素前插入值为
val
的元素
| |
| 删除list中第一个元素 | |
| push_back | 在list尾部插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_back | 删除list中最后一个元素 |
| insert | 在list position 位置中插入值为val的元素 |
| erase | 删除list position位置的元素 |
| swap | 交换两个list中的元素 |
| clear |
清空
list
中的有效元素
|
三、常用接口的使用
这里就简单使用一下,与前面的 vector string 的使用接口差别不大,这也就是 C++ 的封装的体现,底层都不一样,但是上层来看都是一样!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <list>
#include <vector>
// list的构造
void TestList1()
{
list<int> l1; // 构造空的l1
list<int> l2(4, 100); // l2中放4个值为100的元素
list<int> l3(l2.begin(), l2.end()); // 用l2的[begin(), end())左闭右开的区间构造l3
list<int> l4(l3); // 用l3拷贝构造l4
// 以数组为迭代器区间构造l5
int array[] = { 16,2,77,29 };
list<int> l5(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(int));
// 列表格式初始化C++11
list<int> l6{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
// 用迭代器方式打印l5中的元素
list<int>::iterator it = l5.begin();
while (it != l5.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
// C++11范围for的方式遍历
for (auto& e : l5)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// list迭代器的使用
// 注意:遍历链表只能用迭代器和范围for
void PrintList(const list<int>& l)
{
// 注意这里调用的是list的 begin() const,返回list的const_iterator对象
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
// *it = 10; 编译不通过
}
cout << endl;
}
void TestList2()
{
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));
// 使用正向迭代器正向list中的元素
// list<int>::iterator it = l.begin(); // C++98中语法
auto it = l.begin(); // C++11之后推荐写法
while (it != l.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
// 使用反向迭代器逆向打印list中的元素
// list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = l.rbegin();
auto rit = l.rbegin();
while (rit != l.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
}
// list插入和删除
// push_back/pop_back/push_front/pop_front
void TestList3()
{
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
list<int> L(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));
// 在list的尾部插入4,头部插入0
L.push_back(4);
L.push_front(0);
PrintList(L);
// 删除list尾部节点和头部节点
L.pop_back();
L.pop_front();
PrintList(L);
}
// insert /erase
void TestList4()
{
int array1[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
list<int> L(array1, array1 + sizeof(array1) / sizeof(array1[0]));
// 获取链表中第二个节点
auto pos = ++L.begin();
cout << *pos << endl;
// 在pos前插入值为4的元素
L.insert(pos, 4);
PrintList(L);
// 在pos前插入5个值为5的元素
L.insert(pos, 5, 5);
PrintList(L);
// 在pos前插入[v.begin(), v.end)区间中的元素
vector<int> v{ 7, 8, 9 };
L.insert(pos, v.begin(), v.end());
PrintList(L);
// 删除pos位置上的元素
L.erase(pos);
PrintList(L);
// 删除list中[begin, end)区间中的元素,即删除list中的所有元素
L.erase(L.begin(), L.end());
PrintList(L);
}
// resize/swap/clear
void TestList5()
{
// 用数组来构造list
int array1[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
list<int> l1(array1, array1 + sizeof(array1) / sizeof(array1[0]));
PrintList(l1);
// 交换l1和l2中的元素
list<int> l2;
l1.swap(l2);
PrintList(l1);
PrintList(l2);
// 将l2中的元素清空
l2.clear();
cout << l2.size() << endl;
}四、 模拟实现 list
下面就来模拟实现一下 list,还是与以往一样建两个文件
一个负责测试所模拟实现的接口文件(Test.cpp),一个负责实现接口的文件(list.hpp)
1. 下面是负责测试所模拟实现的接口 Test.cpp文件的代码:
void Test_list1()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
*it *= 2;
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& e : lt)
{
cout << e*2 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void Test_list2()
{
//std::list<int> lt;
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
auto pos = std::find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 4);
if (pos != lt.end())
{
lt.insert(pos, 55);
//*pos *= 2;
}
cout << *pos << endl;
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void Test_list3()
{
//std::list<int> lt;
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = lt.rbegin();
while (rit != lt.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void Test_list()
{
//std::list<int> lt;
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = lt.rbegin();
while (rit != lt.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
}
cout << endl;
auto pos = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 4);
if (pos != lt.end())
{
pos = lt.insert(pos, 22);
cout << *pos << endl;
}
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
auto ret = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 4);
if (ret != lt.end())
{
lt.erase(ret);
}
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
}
}2. 下面是负责实现接口的文件 list.hpp 文件的代码:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <assert.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include "reverse_iterator.hpp"
using namespace std;
namespace HK
{
template <class T>
class list_node
{
public:
T _data;
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
list_node(const T& x = T())
:_data(x)
,_next(nullptr)
,_prev(nullptr)
{}
};
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class __list_iterator
{
public:
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> iterator;
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef Ptr pointer;
typedef Ref reference;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
__list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
bool operator!=(const iterator& it) const
{
return this->_node != it._node;
}
bool operator==(const iterator& it) const
{
return this->_node == it._node;
}
// 解引用 取数据
//T& operator*()
Ref operator*()
{
return this->_node->_data;
}
//
//T* operator->()
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(this->operator*());
}
// 前置++
iterator& operator++()
{
this->_node = this->_node->_next;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
iterator& operator++(int)
{
iterator ret(*this);
this->_node = this->_node->_next;
return ret;
}
// 前置--
iterator& operator--()
{
this->_node = this->_node->_prev;
return *this;
}
// 后置--
iterator& operator--(int)
{
iterator ret(*this);
this->_node = this->_node->_prev;
return ret;
}
//private:
Node* _node;
};
template <class T>
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
typedef __reverse_iterator<iterator, T&, T*> reverse_iterator;
typedef __reverse_iterator<const_iterator, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const
{
return const_reverse_iterator(end());
}
const_reverse_iterator rend() const
{
return const_reverse_iterator(begin());
}
reverse_iterator rbegin()
{
return reverse_iterator(end());
}
reverse_iterator rend()
{
return reverse_iterator(begin());
}
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//Node* cur = _head->_prev;
//Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//
//_head->_prev = newnode;
//newnode->_next = _head;
//
//newnode->_prev = cur;
//cur->_next = newnode;
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
return iterator(newnode);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
//iterator erase(iterator pos)
//{
// // 不能删头
// assert(pos != end());
//
// Node* cur = pos._node;
// Node* prev = cur->_prev;
// Node* next = cur->_next;
// prev->_next = next;
// next->_prev = prev;
// delete cur;
// return iterator(next);
//}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
return iterator(next);
}
private:
Node* _head;
};





 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结