您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >代码随想录之额外题目网站首页学无止境
代码随想录之额外题目
数组
1207 独一无二的出现次数

看数组的大小和长度都没有很大,所以可以直接用数组来做哈希表,用一个数组来记录出现次数,再用一个数组来标记出现次数的值是否出现过。就是O(n)
class Solution {
public boolean uniqueOccurrences(int[] arr) {
//07
// 排序 nlogn 用两个hash O(n)
int[] hash = new int[2001];
Arrays.fill(hash,0);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
hash[arr[i]+1000]++;
}
// Arrays.sort(hash);//将出现次数排序
// for(int i=1;i<hash.length;i++){
// if(hash[i]==hash[i-1]&&hash[i]!=0) return false;
// }
// return true;
boolean[] flag = new boolean[1002]; // 标记相同频率是否重复出现
Arrays.fill(flag,false);
for(int i=0;i<hash.length;i++){
if(hash[i]>0&&flag[hash[i]]==false){
flag[hash[i]] = true;
}else if(hash[i]>0&&flag[hash[i]]==true){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
189 旋转数组

思路就是反转三次,先全部反转,然后前K个反转一次,后面剩下的反转一次。
要注意的是k大于数组长度的时候要取余
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
//反转三次 原地
//开另外数组
if(k>nums.length) k=k%nums.length; //重要 注意!!!!
reverse(nums,0,nums.length-1);
reverse(nums,0,k-1);
reverse(nums,k,nums.length-1);
}
public void reverse(int[] nums, int begin, int end){
while(begin<end){
int tmp = nums[begin];
nums[begin] = nums[end];
nums[end] = tmp;
begin++;
end--;
}
}
}
34 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置

要求logn 那就明显是二分查找算法
class Solution {
int[] res = new int[2];
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
//要求logn 那就二分查找
int begin = 0;
int end = nums.length-1;
res[0] = -1;//如果没找到就是-1
res[1] = -1;
while(begin<=end){//注意要相等
int mid = (begin+end)/2;
if(nums[mid]==target){
int j=mid-1;
while(j>=0&&nums[j]==target){//找到了之后开始向两边扩展搜索
j--;
}
res[0] = j+1;
int k=mid+1;
while(k<nums.length&&nums[k]==target){
k++;
}
res[1] = k-1;
return res;
}else if(nums[mid]<target){
begin=mid+1;
}else{
end = mid-1;
}
}
return res; //如果没找到 就不会更新 返回初始值-1
}
}
922 按奇偶排序数组 II

一开始就没想用额外的数组,不然本地就太简单,然后我看了实例,因为奇数和偶数是连续的,就只有连续奇数+偶数 和连续偶数+奇数两种情况,然后才发现是可以不连续的,所以才改了很久。只要两个指针去判断和交换即可
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParityII(int[] nums) {
//17 -46 原地 一半一半 没说是不是连续的!!!不一定是连续的奇数和偶数!!
for(int i=0,j=1;i<nums.length&&j<nums.length;){
if(nums[i]%2==1&&nums[j]%2==0){
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
i+=2;
j+=2;
}
else if(nums[i]%2==0){
i+=2;
}else if(nums[j]%2==1){
j+=2;
}
}
return nums;
}
}
链表
143 重排链表(美团一面题目)

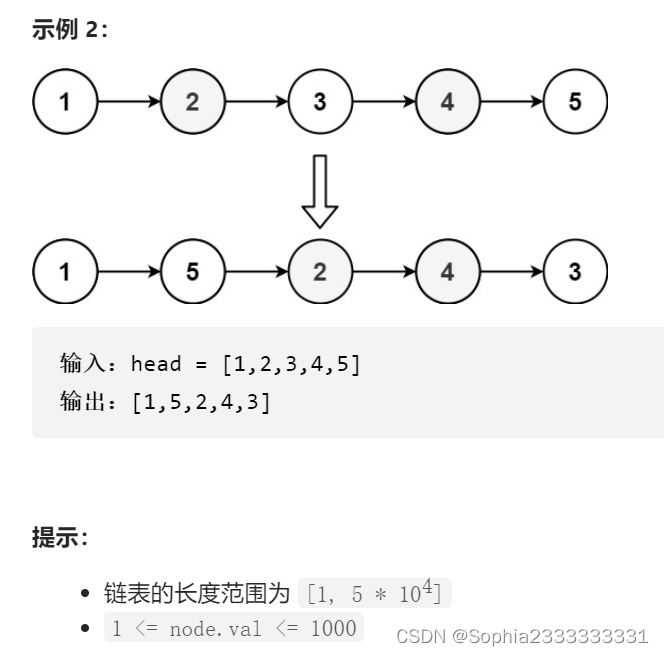
简单做法,先用数组存起来,一个一个去改变指向,注意不是新建节点,而是直接利用这些节点,只是改变指向,所以也是符合要求的。 时间复杂度O(N)和空间复杂度都是O(n)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
//35-49
//简单做法,先用数组存起来,一个一个去改变指向 时间复杂度O(N)和空间复杂度都是O(n)
ArrayList<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode node = head;
while(node!=null){
list.add(node);
node = node.next;
}
node = head;
int left =1;//从1开始 因为头不用变
int right = list.size()-1;
int count=0;
while(left<=right){
if(count%2==0){
node.next = list.get(right);
node = node.next;
right--;
}else{
node.next = list.get(left);
node = node.next;
left++;
}
count++;
}
node.next = null;
}
}
然后是原地改变指向,不用额外数组。思路就是反转后半部分链表,然后交替指向,需要注意反转之后结尾要null,然后判断奇数偶数
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
//53-05
//原地改变指向 反转后半部分链表 然后交替指向
ListNode node = new ListNode(-1);
node.next = head;
ListNode fast = node,slow = node;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode pre,cur;
if(fast!=null){//链表长度是偶数
pre = null;
}else pre = slow;//链表长度是奇数
cur = slow.next;
//开始反转
while(cur!=null){
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
slow.next = null;//要记得!!
//两个头分别是head和pre
node = head;
while(node!=null&&pre!=null){ //交替指向
ListNode node2 = node.next;
ListNode pre2 = pre.next;
node.next = pre;
pre.next = node2;
node = node2;
pre = pre2;
}
}
}
160 链表相交
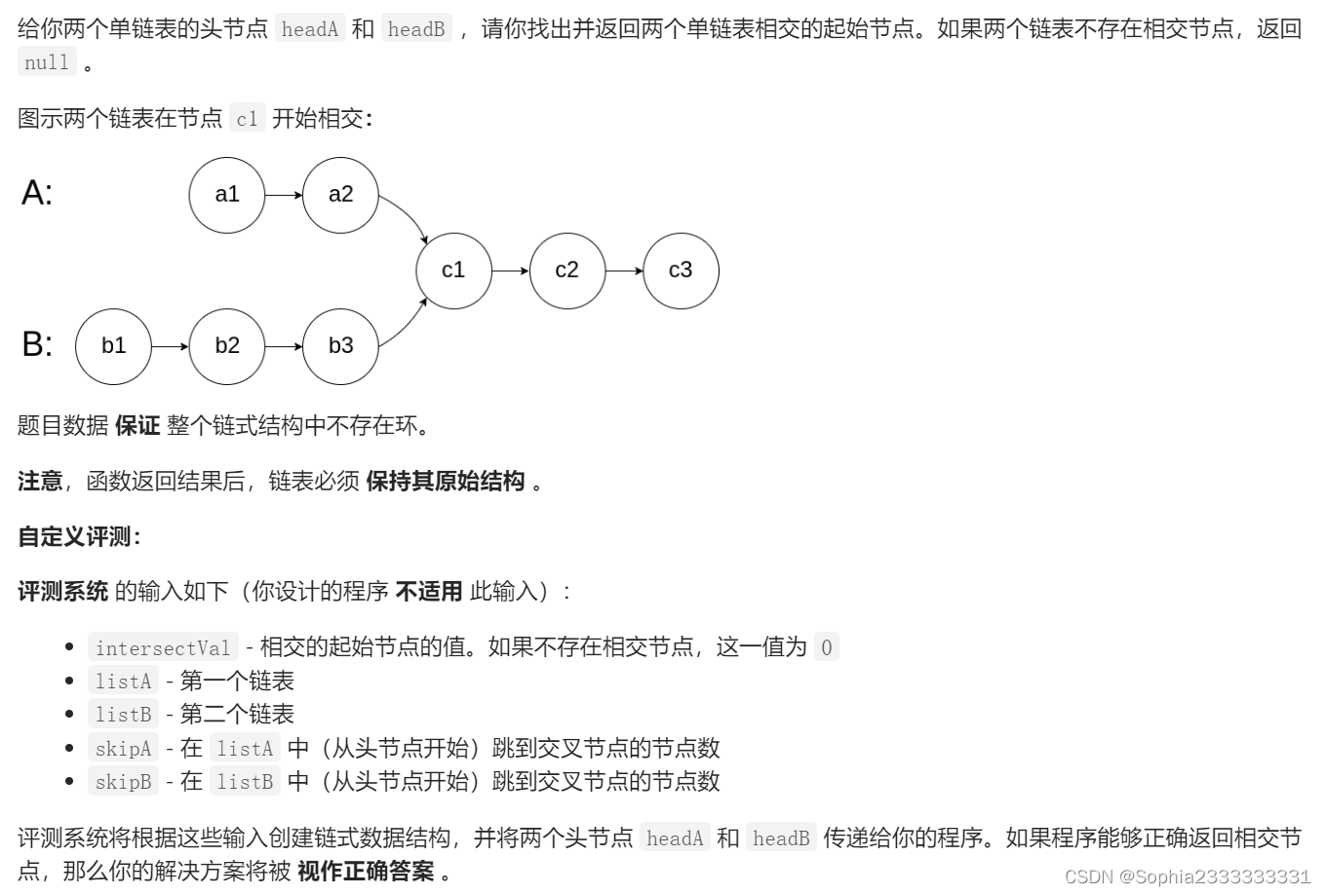
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
//13
//长的走完走短的
ListNode a = headA, b = headB;
int fa = 0;
int fb = 0;//标记是否连接过一次
while(a!=null||b!=null){
if(a==b) return a; //要放在前面 因为可能第一个节点就相交
if(a.next==null&&fa==0){
a = headB;
fa=1;
}else a = a.next;
if(b.next==null&&fb==0){
b = headA;
fb=1;
}else b = b.next;
}
return null;
}
}
字符串
205 同构字符串

要注意的是多个key映射到相同的value也是不行的,第一次提交忽略了这种情况
class Solution {
public boolean isIsomorphic(String s, String t) {
//00-09
Map<Character,Character> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(!map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))){
if(map.containsValue(t.charAt(i))) return false;//多个key对应相同的value也是不行的
map.put(s.charAt(i),t.charAt(i));
}
else{
if(t.charAt(i)!=map.get(s.charAt(i))) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
1002 查找公用字符

感觉这题的难度不像是简单题,整体思路就是统计出搜索字符串里26个字符的出现的频率,然后取每个字符频率最小值,最后转成输出格式就可以了
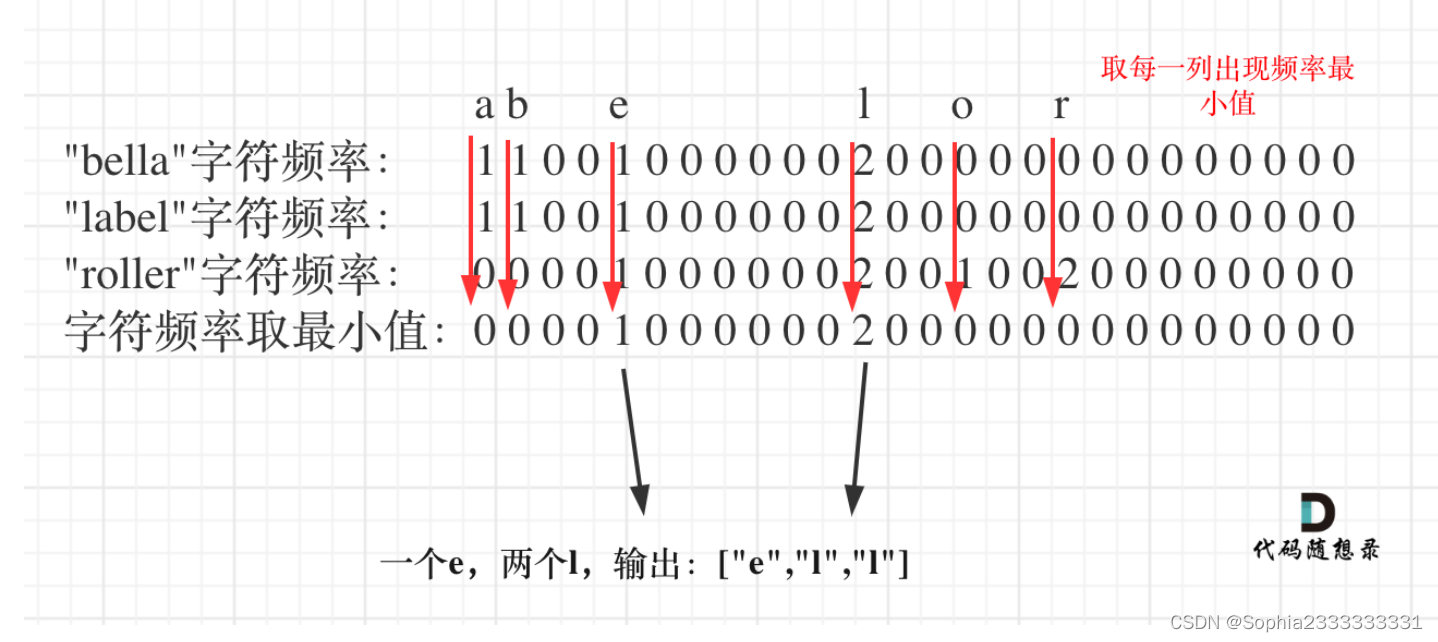
知道了思路之后第一时间也没有想好怎么做,总之就是用第一个字符串初始化之后,和之后的每个字符串出现的次数取最小
class Solution {
public List<String> commonChars(String[] words) {
//11
int[] hash = new int[26];
Arrays.fill(hash,0);
for(int i=0;i<words[0].length();i++){
hash[words[0].charAt(i)-'a']++; //用第一个字符给hash初始化
}
//其他字符的出现次数
for(int i=1;i<words.length;i++){
int[] hashOther = new int[26];
Arrays.fill(hashOther,0);
for(int j=0;j<words[i].length();j++){
hashOther[words[i].charAt(j)-'a']++;
}
//更新最小值
for(int k=0;k<26;k++){
hash[k] = Math.min(hash[k],hashOther[k]);
}
}
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<26;i++){
while(hash[i]>0){
char c = (char)('a'+i);
res.add(String.valueOf(c)); //char能不能转换为String
hash[i]--;
}
}
return res;
}
}
字符串
925 长键按入

思路很简单,就是写起来判断条件有点多
两个指针同时向后,判断第一个字符是否相同,不同直接false,然后各自计算连续相同的字符有多少个,如果输入的不够名字的重复字符个数返回false,然后就是各自判断有没有结束,谁还没结束都是不行
class Solution {
public boolean isLongPressedName(String name, String typed) {
//15-30
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
while(right<typed.length()){
if(left>=name.length()) return false; //name已经结束了 字符更长
if(name.charAt(left)!=typed.charAt(right)){
return false;
}
int count=1;//name的当前字符连续的有几个
while(left+1<name.length()&&name.charAt(left+1)==name.charAt(left)){
count++;
left++;
}
left++; //每次在的都是新字符的第一位
//这里就相等了
int c_right = 1;
while(right+1<typed.length()&&typed.charAt(right+1)==typed.charAt(right)){
c_right++;
right++;
}
right++; //每次在的都是新字符的第一位
if(c_right<count) return false; //字符数量不够匹配
}
if(left<name.length()) return false;//名字还没结束 名字更长
return true;
}
}
二叉树
从根节点到叶节点数字之和

层次遍历,每次遍历的时候把子节点的值加上根节点的值,把所有叶子节点的值相加就得到结果
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
//15-25
//怎么遍历都行 更新节点值
int sum = 0;
//层次遍历
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if(node.left!=null){
node.left.val = node.val*10+node.left.val;
q.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null){
node.right.val = node.val*10+node.right.val;
q.offer(node.right);
}
if(node.left==null&&node.right==null) sum+=node.val;
}
return sum;
}
}
1382. 将二叉搜索树变平衡
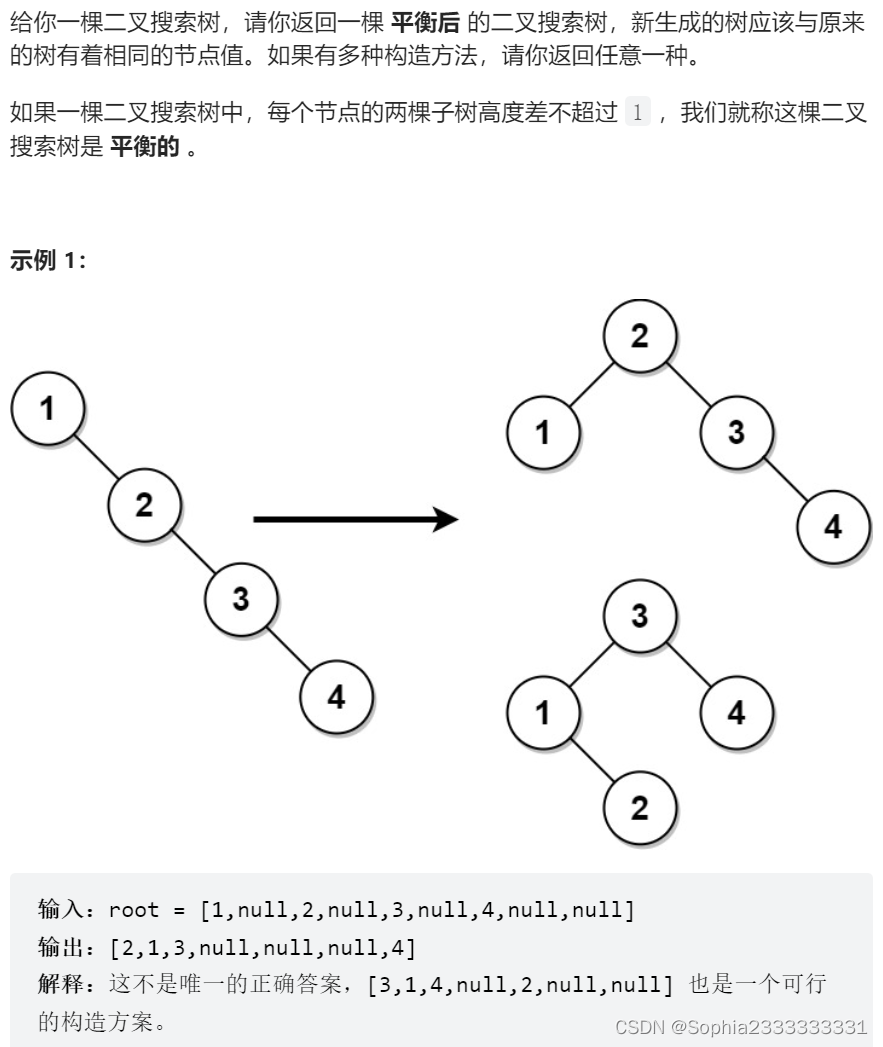
第一次看到还是无从下手,明明昨天才刚复习了将有序数组转换成平衡二叉搜索树!!思路就是分两步,先将搜索树转换为有序数组,再将有序数组转换为平衡二叉搜索树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode balanceBST(TreeNode root) {
//06 将树转换成有序数组,再将有序数组构建平衡二叉树 -23
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(list,root);
//将有序数组转换成平衡二叉搜索树
return makeTree(list,0,list.size()); //左开右闭
}
public void inorder(ArrayList<Integer> list, TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
inorder(list, root.left);
list.add(root.val);
inorder(list, root.right);
}
public TreeNode makeTree(ArrayList<Integer> list,int begin, int end){
if(begin>=end) return null;
if(end-begin==1) return new TreeNode(list.get(begin)); //记得这个!!!
int mid = begin + (end-begin)/2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(list.get(mid));
root.left = makeTree(list,begin,mid);
root.right = makeTree(list,mid+1,end);
return root;
}
}
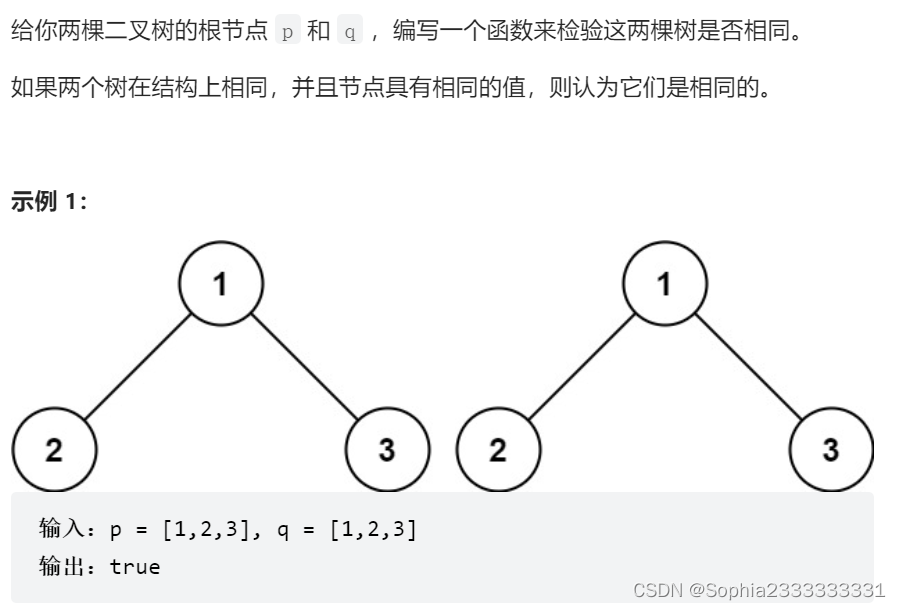
100 相同的树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//27 随意一种遍历都行
if(p==null&&q==null) return true;
else if(p==null||q==null) return false;
else if(p.val!=q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left)&& isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
}
贪心
649 data2参议院

思路很简单,就是实现的时候一开始觉得有点难,可能复杂度有点高。思路就是每次消灭后面的对手,遍历字符串,可以记录之前出现过的未行使权力的对手的数量,遍历到的时候如果前面还有未行使权力的对手,当前的就被消灭了,记录两个字符剩下的个数,直到有一方先消失
class Solution {
public String predictPartyVictory(String senate) {
//16-41
//每次消除在自己后面的对手
char[] chars = senate.toCharArray();
int r = 0;
int d = 0;//表示剩下的分别的个数
for(int i=0;i<chars.length;i++){
if(chars[i]=='R') r++;
if(chars[i]=='D') d++;
}
int rr = 0, dd=0;//表示前面出现过的,还没行使消除权力的数量 不能放在while循环内 因为不是每轮都清空 上一轮的后面字符指定消灭下一轮前面的
while(r>0&&d>0){
for(int i=0;i<chars.length;i++){
if(chars[i]=='R'){
if(dd>0){//前面还有d未行使权力
dd--;
chars[i]=0;
r--;
}else{
rr++;
}
}
if(chars[i]=='D'){
if(rr>0){
rr--;
chars[i]=0;
d--;
}else{
dd++;
}
}
}
}
return r>0?"Radiant":"Dire";
}
}
1221 分割平衡字符串

很简单,只要标记未被分割的两个字符的数量,相等时就分割,然后变量清零
class Solution {
public int balancedStringSplit(String s) {
//46-49
int r = 0,l=0;
int count = 0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s.charAt(i)=='R'){
r++;
}
else if(s.charAt(i)=='L'){
l++;
}
if(r==l){//分割 清零
count++;
r=0;
l=0;
}
}
return count;
}
}
动态规划
5 最长回文子串

class Solution {
int be = 0;
int len = 0;
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
//26-37 中心向两边扩展
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
huiwen(s,i,i);
huiwen(s,i,i+1);
}
return s.substring(be,be+len);
}
public void huiwen(String s, int begin, int end){
while(begin>=0&&end<s.length()&&begin<=end&&s.charAt(begin)==s.charAt(end)){
begin--;
end++;
}
if(end-begin-1>len){
len = end-begin-1;
be = begin+1;
}
}
}
132 分割回文串2

这题求的是最小分割次数,只要次数就可以用动态规划,用回溯会超时。之前最小分割次数要求返回的是分割方案,就需要用回溯,也放在了下面,进行对比
class Solution {
public int minCut(String s) {
//20-34
//先构建数组 表示i-j的字符串是不是回文串
boolean[][] isHuiwen = new boolean[s.length()][s.length()];
//初始化为false
for(boolean[] tmp:isHuiwen){
Arrays.fill(tmp,false);
}
//递推公式是dp[i][j]=dp[i+1][j-1]
//遍历要从下到上,从左到右遍历
for(int i=s.length();i>=0;i--){
for(int j=i;j<s.length();j++){
if(s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j)){
if(j-i<=1) isHuiwen[i][j] = true;
else isHuiwen[i][j] = isHuiwen[i+1][j-1];
}
}
}
//dp[i]表示0-i之间的字符串最少分割次数
int[] dp = new int[s.length()];
//初始化 s的最大分割次数是s.length-1
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
dp[i] = i;
}
for(int i=1;i<s.length();i++){
if(isHuiwen[0][i]){ //到i为止已经是回文 不用分割
dp[i] = 0;
continue;
}
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){ //如果j~i是回文,在0-i之间再分割一个j,次数是dp[j]+1
if(isHuiwen[j+1][i]){
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[j]+1);
}
}
}
return dp[s.length()-1];
}
}
131 分割回文串

class Solution {
ArrayList<String> tmp = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
//38-49
dfs(s,0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(String s, int index){
if(index==s.length()){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return;
}
for(int i=index;i<s.length();i++){
if(ishuiwen(s,index,i)){
tmp.add(s.substring(index,i+1));//左闭右开
dfs(s,i+1);
tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1);
}
}
}
public boolean ishuiwen(String s, int begin, int end){//左闭右闭
for(int i=begin,j=end;i<=j;i++,j--){
if(s.charAt(i)!=s.charAt(j)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
673 最长递增子序列的个数

注意是序列个数!而不是序列长度,求长度很简单,求序列个数的话看了很久的题解才写出来。问题出在定义上,count[i]定义是以nums[i]为结尾的最长序列个数,而且不能只判断求出的序列长度,还是要根据nums的大小来更新
class Solution {
public int findNumberOfLIS(int[] nums) {
//52-36!!!
//往前找比自己小的最大的dp 子序列中数字的个数
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(dp,1);
//最长递增子序列的个数 以nums[i]为结尾
int[] count = new int[nums.length];
int res = 0;
int max = 1;
Arrays.fill(count,1);
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
if(nums[j]<nums[i]){
if(dp[j]+1>dp[i]){ //第一次更新,count数量和前面一样,因为是同一个序列
dp[i] = dp[j]+1;
count[i] = count[j];
}
else if(dp[j]+1==dp[i]){//已经更新过的,这次相等就可以直接相加
count[i]+=count[j];
}
}
}
max = Math.max(max,dp[i]);
}
//注意定义 是nums[i]为结尾的子序列的个数,所以要把dp为最长的对应的count相加
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(dp[i]==max){
res+=count[i];
}
}
return res;
}
}
图论
841 钥匙和房间

一开始自己写用list去模拟,要重复插入和删除数据,超内存,还是看了题解,回溯写多了忘了最初的深搜,需要认真看一下这题
class Solution {
int num = 0;//到过的房间数量
public boolean canVisitAllRooms(List<List<Integer>> rooms) {
//46--10!!!!
//深度优先搜索的方式遍历整张图,统计可以到达的节点个数,
//并利用数组 vis标记当前节点是否访问过,以防止重复访问
int len = rooms.size();
boolean[] vis = new boolean[len];
Arrays.fill(vis,false);
dfs(rooms,0,vis);//0表示索引,也就是第几个房间
return num==len;
}
public void dfs(List<List<Integer>> rooms, int index, boolean[] vis){
vis[index] = true;
num++;
for(int x:rooms.get(index)){
if(!vis[x]){
dfs(rooms,x,vis);
}
}
}
}
127 单词接龙

第一反应无从下手,主要还是觉得暴力会复杂度太高,但最后的解法还是暴力匹配+广搜,用了技巧是把list转换为hashset,因为有大量的判断contains的操作,转换后就没超时,用原来的list会超时
用广搜搜到的第一个符合条件的一定就是路径最短的
class Solution {
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
//14-27
HashSet<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordList);//转换为hashset才能通过 否则超时 在查找时contains用的多就用hashset
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(beginWord,1);//数字表示路径中的第几个
if(wordSet.size()==0||!wordSet.contains(endWord)){
return 0;
}
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(beginWord);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
String word = q.poll();
int path = map.get(word);
//遍历
for(int i=0;i<word.length();i++){
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
for(char j = 'a';j<='z';j++){
chars[i] = j;//替换每个字符
String s = String.valueOf(chars);//得到新词
if(s.equals(endWord)){
return path+1;
}else if(wordSet.contains(s)&&!map.containsKey(s)){
map.put(s,path+1);
q.offer(s);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
并查集
684 冗余连接
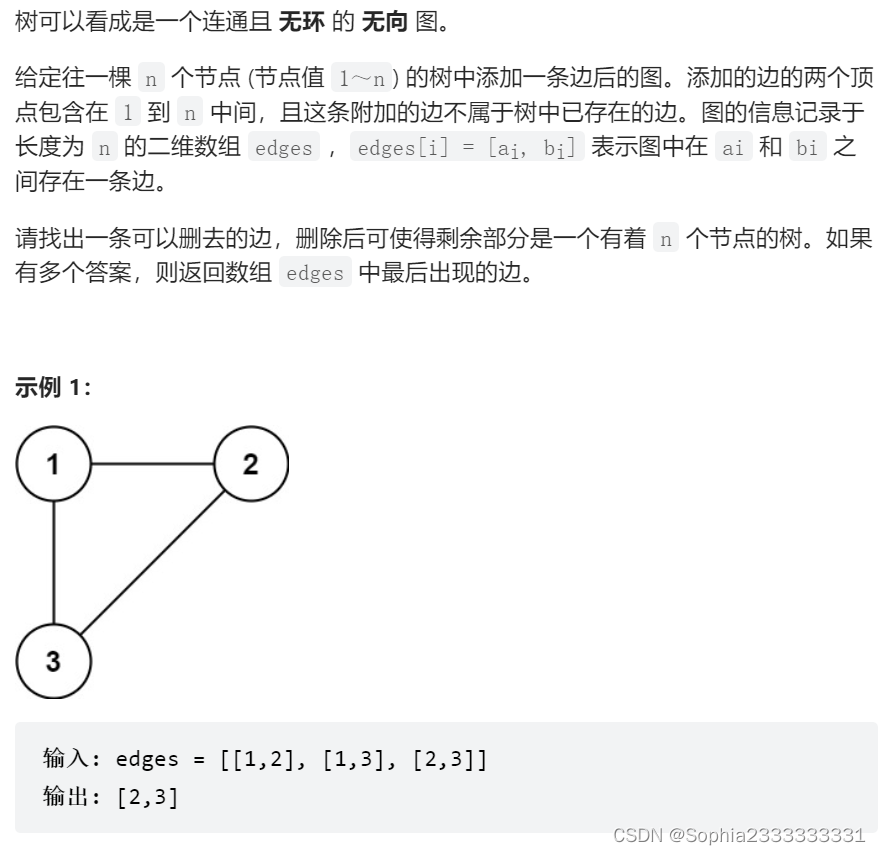
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
//32-45
int n = edges.length;
int[] father = new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
father[i] = i;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(same(father,edges[i][0],edges[i][1])){
return new int[]{edges[i][0],edges[i][1]};
}else{
add(father,edges[i][0],edges[i][1]);
}
}
return null;
}
public boolean same(int[] father, int u, int v){
return find(father, u)==find(father, v);
}
public int find(int[] father, int u){
if(father[u]!=u){
father[u] = find(father, father[u]);
}
return father[u];
}
public void add(int[] father, int u, int v){
u = find(father,u);//注意是父节点
v = find(father,v);
if(u!=v){
// father[u] = v; 两种都可以
father[v] = u;
}
}
}
685 冗余连接2
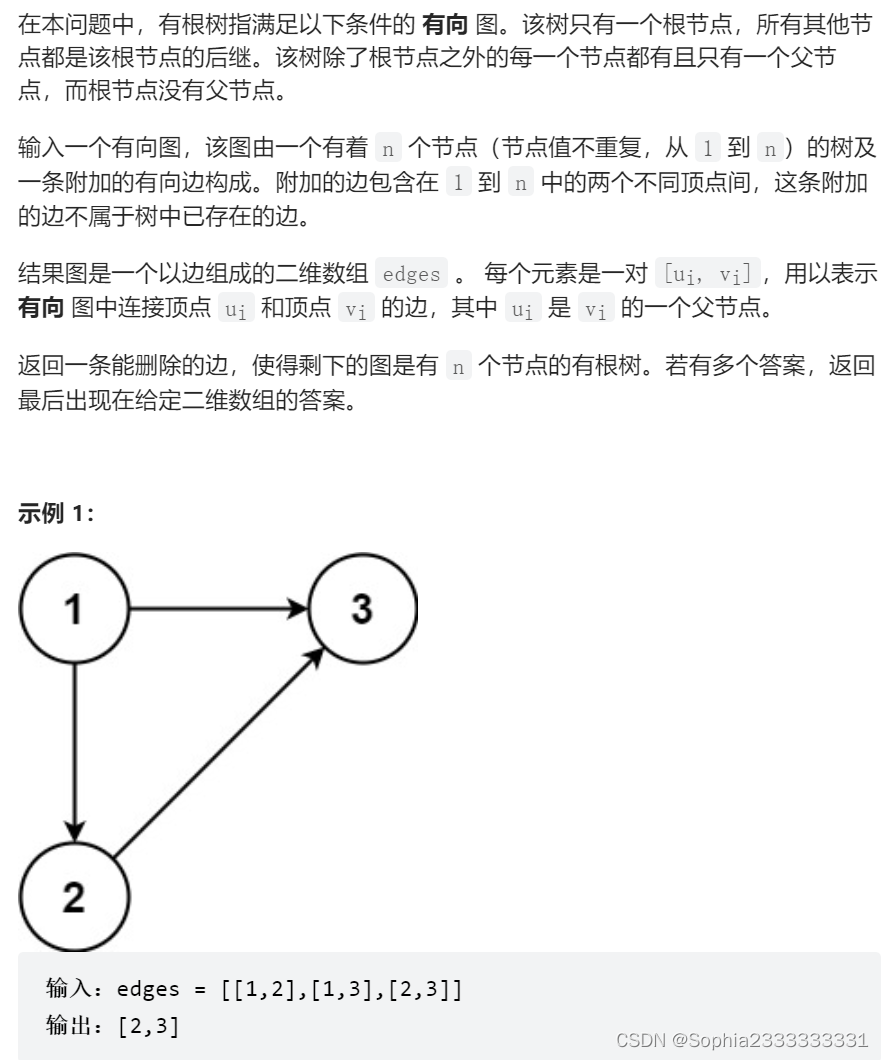
和上题的区别在于这是有向图,用上面的代码只能过30%左右,因为加了方向,就不一定是之前的删除方式。
主要有三种情况
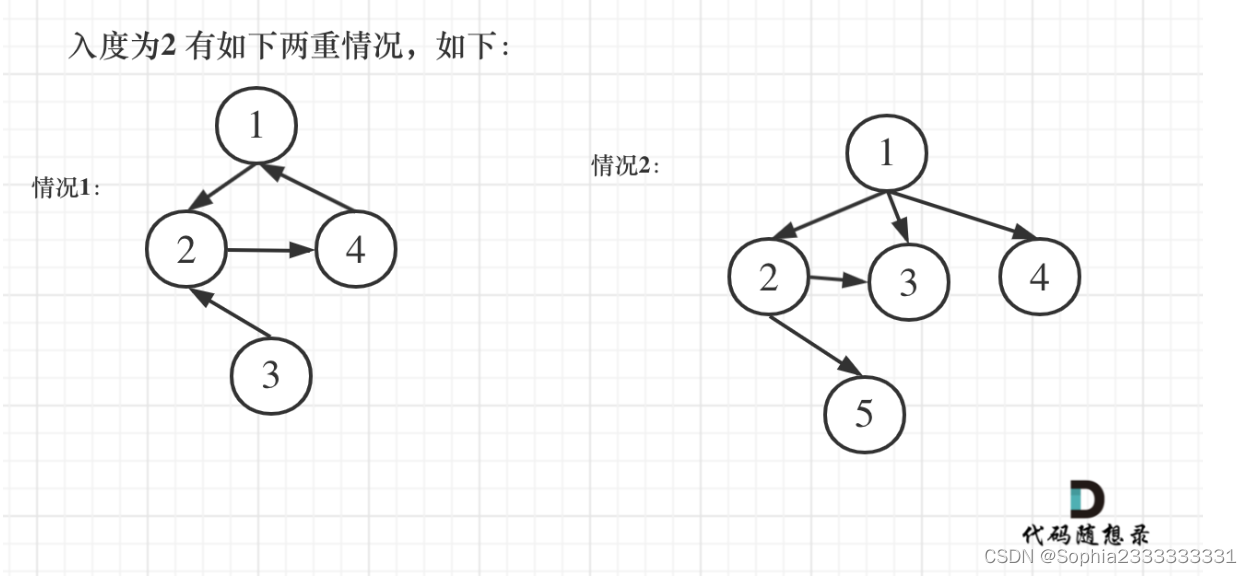
这是存在入度为2的节点,这种情况下,一定是删除入度为2的边的其中一条,要优先删除最后面出现的,
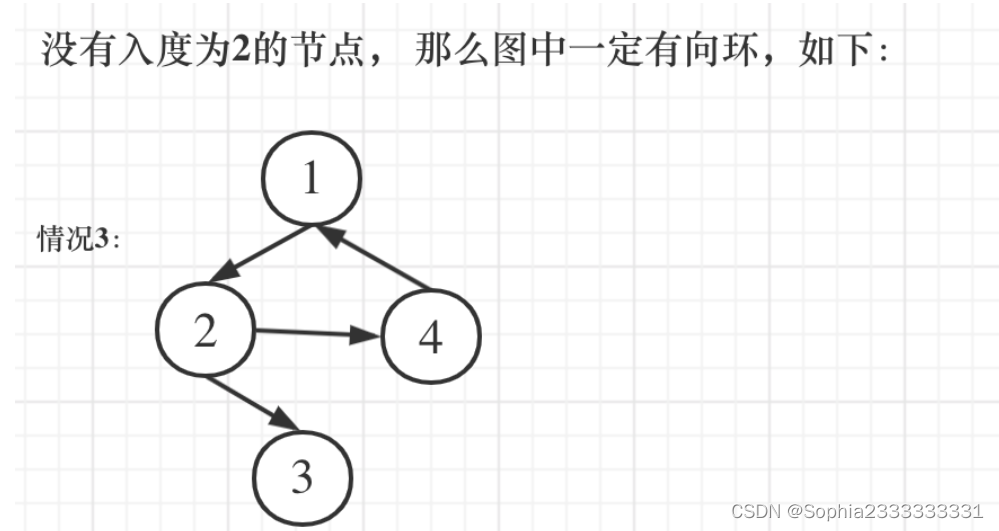
如果不存在入度为2的点一定存在有向环,删除导致出现有向环的边,就和上题一样
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantDirectedConnection(int[][] edges) {
//52 和无向的区别? --26
int n = edges.length;
int[] father = new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
father[i] = i;
}
//计算入度为2的节点
int[] in = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(in,0);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
in[edges[i][1]]++;
}
//找入度为2节点对应的边
//要从后遍历 因为要返回的是最后出现的
ArrayList<Integer> ed = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
if(in[edges[i][1]]==2){
ed.add(i);
}
}
//有入度为2的节点
if(!ed.isEmpty()){
if(isTreeAfterRemoveEdge(father, edges,ed.get(0))){//ed先存的是后出现的,这里要先删除索引为0的,反之就反过来
return edges[ed.get(0)];
}else return edges[ed.get(1)];
}
//没有入度为2的节点
return getRemoveEdge(father, edges);
}
public void init(int[] father, int n){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
father[i] = i;
}
}
public boolean same(int[] father, int u, int v){
return find(father, u)==find(father, v);
}
public int find(int[] father, int u){
if(father[u]!=u){
father[u] = find(father, father[u]);
}
return father[u];
}
public void add(int[] father, int u, int v){
u = find(father,u);//注意是父节点
v = find(father,v);
if(u!=v){
father[u] = v; //两种都可以
//father[v] = u;
}
}
public boolean isTreeAfterRemoveEdge(int[] father, int[][] edges, int index){
int n = edges.length;
init(father, n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i==index) continue;
if(same(father,edges[i][0],edges[i][1])){
return false;
}else{
add(father,edges[i][0],edges[i][1]);
}
}
return true;
}
public int[] getRemoveEdge(int[] father, int[][] edges){
int n = edges.length;
init(father, n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(same(father,edges[i][0],edges[i][1])){
return edges[i];
}else{
add(father,edges[i][0],edges[i][1]);
}
}
return null;
}
}
模拟
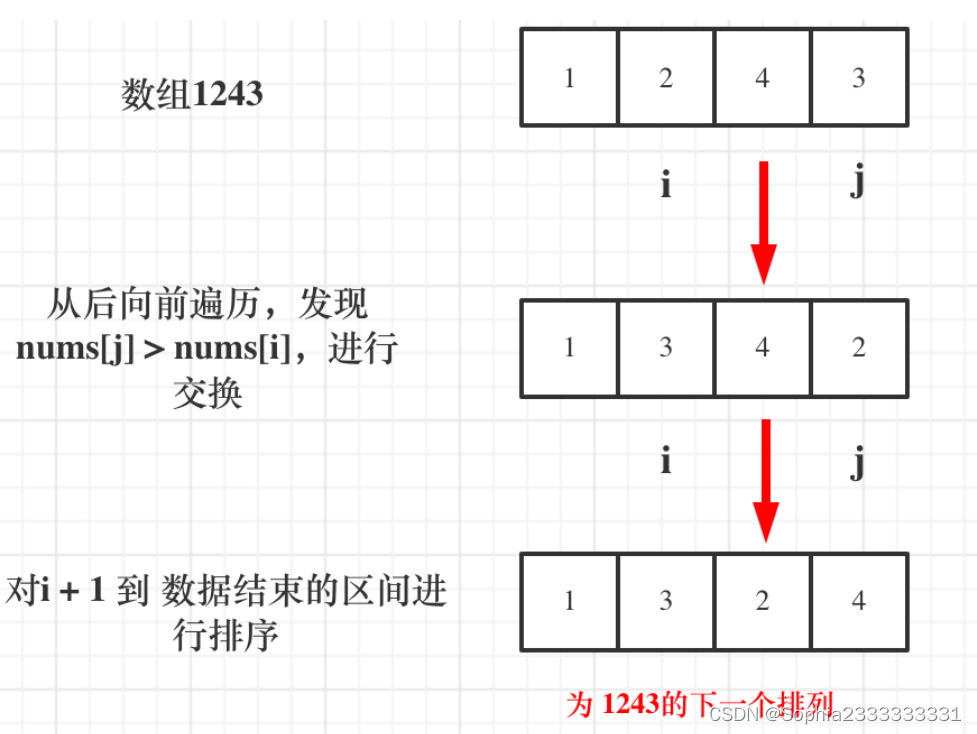
31 下一个排列

可以先把全排列写出来,然后找规律,我第一次没有全写出来,就是凭感觉只交换了一个,过了50%
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
//40
//从尾向前找最 nums[i]<nums[j]的 然后交换 没找到就全部反转
for(int i=nums.length-1;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=nums.length-1;j>i;j--){
if(nums[j]>nums[i]){
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
Arrays.sort(nums,i+1,nums.length);
return;
}
}
}
//没找到就全部反转
Arrays.sort(nums);
}
}
463 岛屿的周长
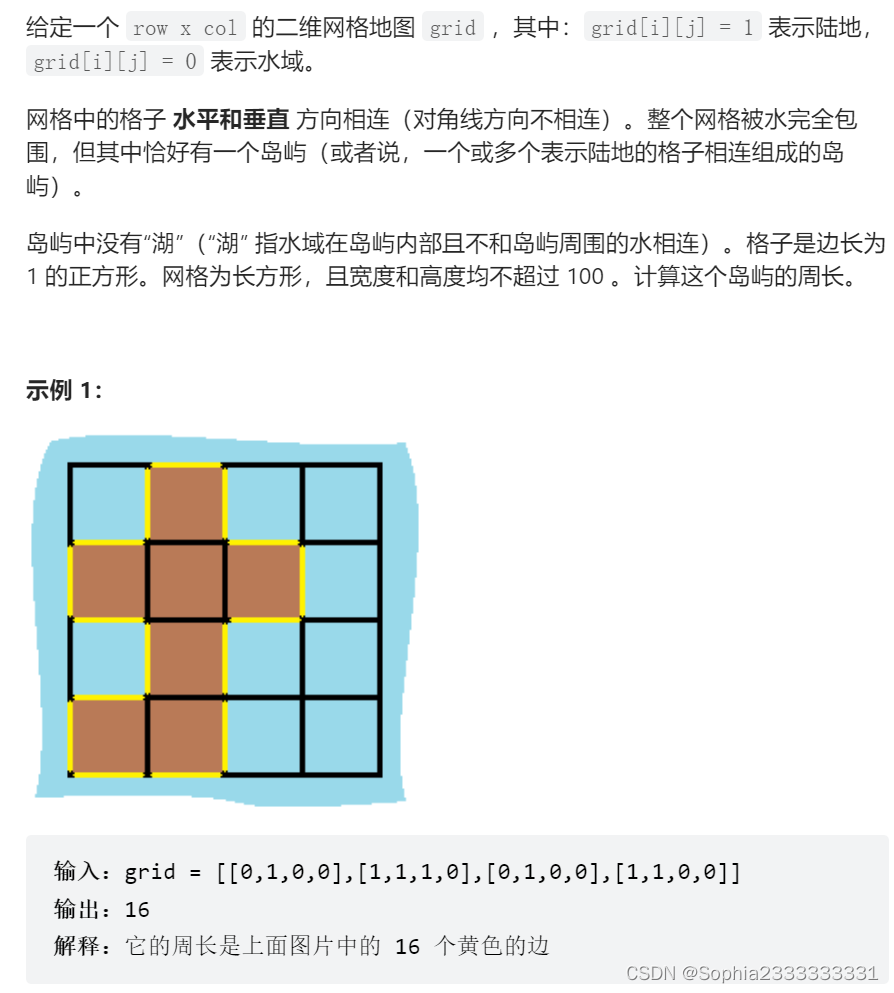
总周长减去相邻的边数
class Solution {
public int islandPerimeter(int[][] grid) {
//04-11
int count = 0;//陆地个数
int edge = 0;//相邻的边
for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1){
count++;
if(i>0&&grid[i-1][j]==1) edge++;
if(i+1<grid.length&&grid[i+1][j]==1) edge++;
if(j>0&&grid[i][j-1]==1) edge++;
if(j+1<grid[0].length&&grid[i][j+1]==1) edge++;
}
}
}
return count*4-edge;
}
}
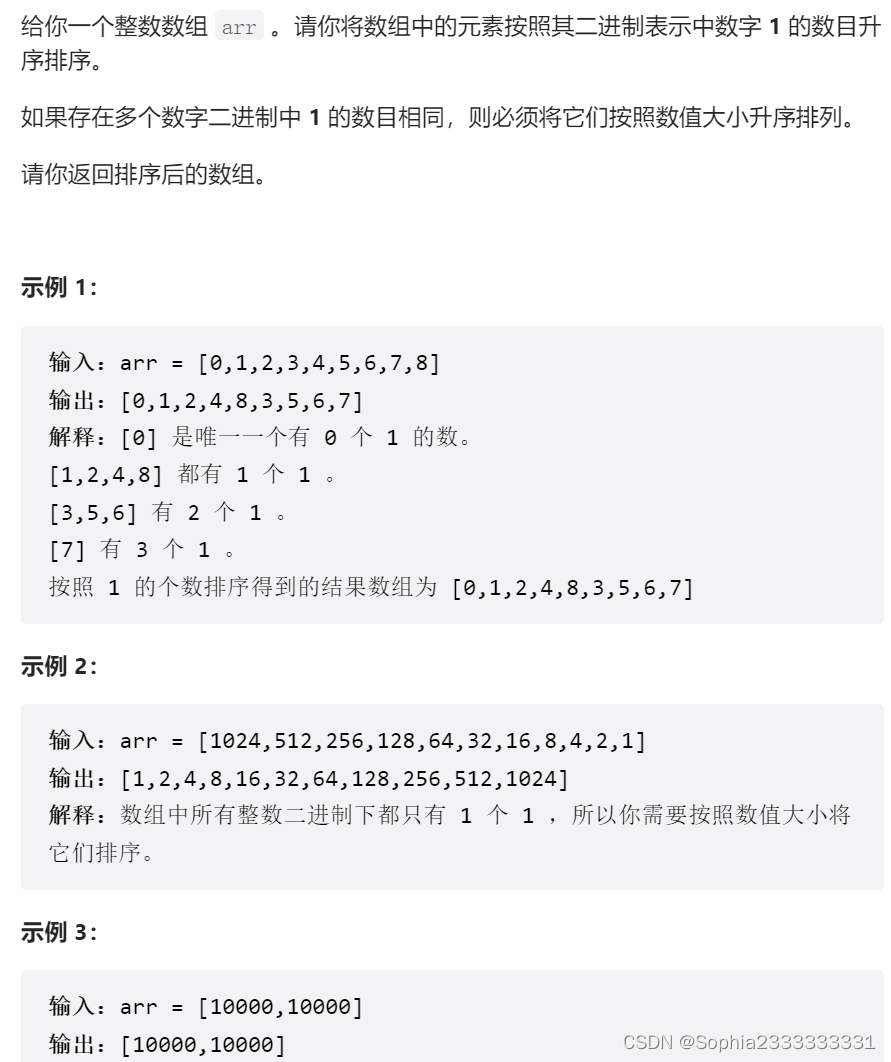
1356
class Solution {
public int[] sortByBits(int[] arr) {
//13-23
int[][] a = new int[arr.length][2];//第一维是arr 第二维是1的个数
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
a[i][0] = arr[i];
int t = arr[i];
int count = 0;//1的个数
while(t!=0){
if((t&1)==1){ //或者t%2==1
count++;
}
// t /=2;
t>>=1;
}
a[i][1] = count;
}
Arrays.sort(a,(o1,o2)->o1[1]-o2[1]!=0?o1[1]-o2[1]:o1[0]-o2[0]);
int[] res = new int[arr.length];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
res[i] = a[i][0];
}
return res;
}
}






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结