您现在的位置是:首页 >技术杂谈 >Spring IoC 深度学习网站首页技术杂谈
Spring IoC 深度学习
Io回顾
IoC 是 Inversion of Control 的简写,译为“控制反转”,它不是一门技术,而是一种设计思想,是一个重要的面向对象编程法则,能够指导我们如何设计出松耦合、更优良的程序。
Spring 通过 IoC 容器来管理所有 Java 对象的实例化和初始化,控制对象与对象之间的依赖关系。我们将由 IoC 容器管理的 Java 对象称为 Spring Bean,它与使用关键字 new 创建的 Java 对象没有任何区别。
IoC 容器是 Spring 框架中最重要的核心组件之一,它贯穿了 Spring 从诞生到成长的整个过程。
基础知识可以参考:
IoC引用外部属性文件
引入context的名称空间:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
</beans>引入jdbc的依赖:
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>在resources中创建jdbc的配置文件。(写一些测试数据)
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=atguigu
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm?serverTimezone=UTC
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver创建bean-jdbc.xml,开始测试。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 引入外部的数据源配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 通过数据源的文件将数据注入bean中-->
<!-- 通过${}在数据源的配置文件中进行取值-->
<bean id="jdbcDriver" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
创建测试类进行测试。
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@Test
void test7() throws SQLException {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-jdbc.xml");
DataSource bean = context.getBean(DataSource.class);
Connection connection = bean.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}测试结果:
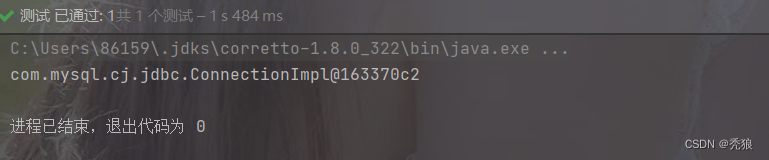
bean的作用域
单例&多例
在bean中使用scope属性设置单例和多例,使用singleton/prototype。(默认使用单例)
生命周期
-
bean对象创建(调用无参构造器)
-
给bean对象设置属性
-
bean的后置处理器(初始化之前)
-
bean对象初始化(需在配置bean时指定初始化方法)
-
bean的后置处理器(初始化之后)
-
bean对象就绪可以使用
-
bean对象销毁(需在配置bean时指定销毁方法)
-
IOC容器关闭
进行测试 :
创建一个life类
public class Life {
String name;
//创建无参构造
public Life() {
System.out.println("1.创建一个空的实体类");
}
//初始化方法
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("4.使用了初始化函数");
}
//销毁方法
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("7.使用了摧毁函数");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("2.给属性进行赋值");
this.name = name;
}
}
创建Spring的配置文件bean-life.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="life" class="com.huang.Life" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod" scope="singleton">
<property name="name" value="hfw"></property>
</bean>
</beans>编写测试代码
@Test
void test1() {
//ApplicationContext接口没有close方法,要使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext实现类进行CLose操作
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-life.xml");
Life life = (Life) context.getBean("life");
System.out.println("6.获取到了完整的实体类");
context.close();
}测试结果
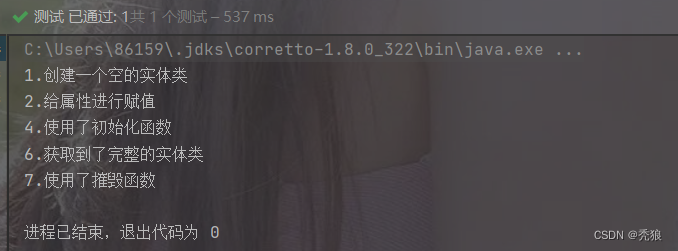
编写后置处理器
bean的后置处理器会在生命周期的初始化前后添加额外的操作,需要实现BeanPostProcessor接口,且配置到IOC容器中,需要注意的是,bean后置处理器不是单独针对某一个bean生效,而是针对IOC容器中所有bean都会执行。(默认使用BeanPostProcessor)
在BeanPostProcessor接口中存在俩个方法,就是对应初始化前后的方法。
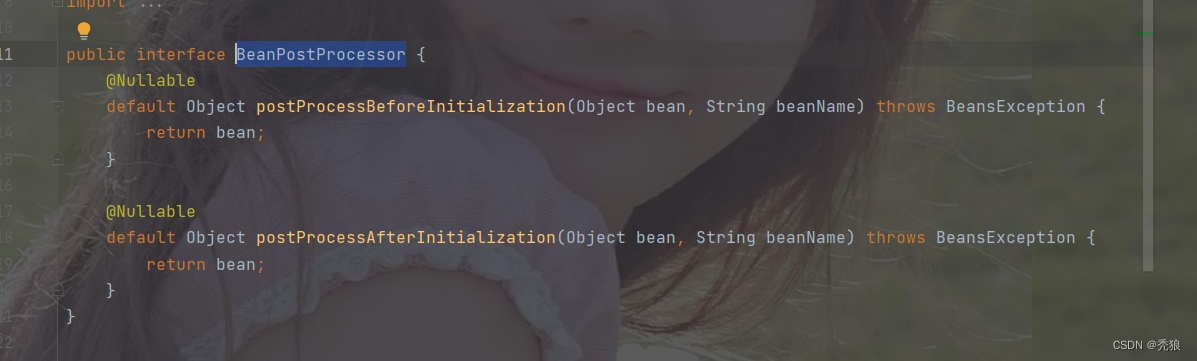
所以我们创建自己的后置处理器时就是去实现这两个方法。
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("3.在初始化之前的后置处理器");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("5.在初始化之后的后置处理器");
return bean;
}
}
将MyBeanprocessor在bean-life.xml中进行配置。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="life" class="com.huang.Life" init-method="initMethod" destroy-method="destroyMethod" scope="singleton">
<property name="name" value="hfw"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="myBeanProcessor" class="com.huang.MyBeanProcessor"></bean>
</beans>进行测试,结果为下
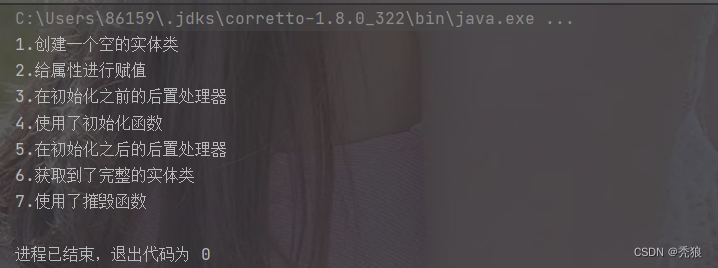
FactoryBean(不是BeanFactory)
FactoryBean是Spring提供的一种整合第三方框架的常用机制。和普通的bean不同,配置一个FactoryBean类型的bean,在获取bean的时候得到的并不是class属性中配置的这个类的对象,而是getObject()方法的返回值。通过这种机制,Spring可以帮我们把复杂组件创建的详细过程和繁琐细节都屏蔽起来,只把最简洁的使用界面展示给我们。
配置factoryBean类
package com.huang.factoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
public class factoryBean implements FactoryBean<User> {
@Override
public User getObject() throws Exception {
//可以在这类中完成实体类的操作,将具体的操作封装在该方法中
User user = new User();
user.setName("hfw");
return user;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return User.class;
}
}
将该类在bean-factoryBean.xml配置文件中进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="factoryBean" class="com.huang.factoryBean.factoryBean"></bean>
</beans>进行测试,最终我们会发现在获取该bean时会返回User对象,完成封装。
Spring 开启自动扫描的方法
在bean.xml中配置扫描注解的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--开启组件扫描功能-->
<!-- base-package对应的就是要扫描注解的包路径-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.huang">
<!-- 要排除的扫描注解的如路径-->
<!-- <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="xxx.xxx.xxx"/>-->
<!--要排除扫描注解的类-->
<!--<context:exclude-filter type="assignable" expression="xxx.xxx.xxx"/>-->
<!-- 仅扫描的包路径-->
<!-- <context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="xxx.xxx.xxx"/>-->
<!-- 仅扫描的类-->
<!--<context:include-filter type="assignable" expression="xxx.xxx.xxx"/>-->
</context:component-scan>
</beansspring中的@Autowired可以使用在 属性上,set方法上,构造方法上,构造方法的形参上,注解上。
如果类中只存在一个构造方法时,可以省略@Autowired。
如果在使用@Autowired的属性是接口且存在多个实现类的话,我们就需要使用@Qualifier(value="bean中对应的id"),我们可以将@Autowired当作ByType,@Resource当作ByName,如果Autowired要达到ByNam的效果就要配合@Qualifier使用 。
实现全注解开发
创建配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@ComponentScan
public class Configuration {
}使用ApplicationContext的实现类AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
@org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Configuration.class);
}手写IoC
Java反射回顾测试例子
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class reflectTest {
@Test
public void Test1() throws Exception {
//直接通过.class获取该类的class
Class clazz1 = User.class;
//通过new出来的对象调用getClass方法
Class clazz2 = new User().getClass();
//通过class.forName获取Class对象
Class clazz3 = Class.forName("com.huang.User");
//创建一个实体类后续需要使用
User user = new User();
System.out.println("############通过反射获取构造器############");
//通过反射获取公共的构造器
Constructor[] constructors = clazz1.getConstructors();
for (Constructor item : constructors
) {
System.out.println(item.getName());
//使用构造器的newInstance()创建实例
}
// System.out.println("############=############");
System.out.println("############获取所有的构造器############");
//通过反射获取私有和公有的构造器
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = clazz1.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor item : declaredConstructors
) {
System.out.println(item.getName());
}
System.out.println("############获取类的属性############");
Field[] fields = clazz1.getFields();
System.out.println("因为属性全部为私有,所以打印为空");
for (Field item : fields
) {
System.out.println(item.getName());
}
System.out.println("############获取类的私有和公共的属性############");
Field[] declaredFields = clazz1.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field item : declaredFields
) {
System.out.println(item.getName());
if(item.getName().equals("name")) {
//设置访问权限为true,这样我们才可以设置对应的属性
item.setAccessible(true);
item.set(user, "秃狼");
System.out.println("设置的新值为:" + user.getName());
}
if(item.getName().equals("age")) {
//设置访问权限为true,这样我们才可以设置对应的属性
item.setAccessible(true);
item.set(user, 21);
System.out.println("设置的新值为:" + user.getAge());
}
}
System.out.println("############获取类的方法############");
Method[] methods = clazz1.getMethods();
for (Method item : methods
) {
System.out.println(item);
}
System.out.println("############获取类的私有和公共的方法############");
Method[] declaredMethods = clazz1.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method item : declaredMethods
) {
System.out.println(item.getName());
if(item.getName().equals("tostring")) {
//因为该方法是私有类型的,所以需要设置权限
//这里使用了私有方法
item.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println("============");
item.invoke(user);
System.out.println("=============");
}
}
System.out.println("############=############");
}
}
这里的User为简单的类,可以自行创建
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public User() {
}
private User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
private void tostring() {
System.out.println("Name:" + this.name + ";" + "age:" + this.age);
}
}
测试结果为下

开始手写IoC
手写例子
这里设置的情况为每个类最多只有可以实现的接口,IoC为单例的情况。
创建两个注释:
Bean(转载注释)
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//设置作用域:作用在类上
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Bean {
}
rush(注入注释)
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//设置作用域:设置为作用在属性上
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface rush {
}
在包中创建三层架构:Dao,Service,Controller,分别创建一个接口和对应的Impl实现类。
这里的ApplicationContext就是包含一个getBean的接口,就是模仿Spring中ApplicationContext。
import com.huang.Annotation.Bean;
import com.huang.Annotation.rush;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class AnnotationApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext{
//bean的本质就是将对应的class和实例对象存放在map中,放和取就是通过对应的注解完成
private Map<Class, Object> beanFactory = new HashMap<>();
//绝对路径的头路径
private String rootPath;
@Override
public Object getBean(Class clazz) {
return beanFactory.get(clazz);
}
public AnnotationApplicationContext(String basePackage) {
/*basePackage中的路径为指定类的当前路径,
并且要进行格式转换后获取绝对路径
*/
String packageDirName = basePackage.replaceAll("\.", "\\");
try {
//通过当前线程获取对应的绝对路径
Enumeration<URL> dirs = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(packageDirName);
while (dirs.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = dirs.nextElement();
/*因为获取的绝对路径中的""会被打印成"%",
需要通过Decoder将绝对路径转为UTF-8的格式*/
String filePath = URLDecoder.decode(url.getFile(), "utf-8");
/*获取绝对路径头路径,方便后续的拆分,
filePath.length() - packageDirName.length() - 1,
正好就取到头路径部分*/
rootPath = filePath.substring(0, filePath.length() - packageDirName.length() - 1);
//装载bean
this.loadBean(new File(filePath));
//注入属性
this.loadRush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void loadBean(File file) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
//进行判断插入的文件是否为文件夹
if(file.isDirectory()) {
//获取去子文件,如果没有就说明文件夹为空,直接返回空值
File[] files = file.listFiles();
if(files.length == 0 || files == null) {
return ;
}
for (File child : files) {
if(child.isDirectory()) {
//如果子文件还是文件夹的话,就直接使用递归调用loadBean函数
loadBean(child);
} else {
//将子文件的绝对路径设置截取为类路径
String pathWithClass = child.getAbsolutePath().substring(rootPath.length());
//获取类的路径后,需要判断是否为.class文件再进行操作
if(pathWithClass.endsWith(".class")) {
//如果是,就再将类路径进行格式转化
String fullName = pathWithClass.replaceAll("\\", ".").
replace(".class", "");
//通过类路径获取反射
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(fullName);
//判断该反射是否为接口的反射类,如果不是我们才进行判断类上是否有指定的注解
if(!aClass.isInterface()) {
//获取类上的注解,判断这些注解是否有指定的注解
Bean annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(Bean.class);
if(annotation != null) {
//instance作为beanFactory的值
Object instance = aClass.newInstance();
//如果该类存在实现的接口就用接口作为键,这里就不考虑存在多个接口了
if(aClass.getInterfaces().length > 0) {
Class<?>[] interfaces = aClass.getInterfaces();
//这里就考虑存在一个接口
beanFactory.put(aClass.getInterfaces()[0], instance);
} else {
//如果不存在就之家用本类
beanFactory.put(aClass, instance);
}
}
}
}
}
}
} else {
System.out.println("不是文件夹,输入有误");
return ;
}
}
private void loadRush() throws IllegalAccessException {
//遍历map
Set<Map.Entry<Class, Object>> entries = beanFactory.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Class, Object> entry : entries) {
//获取实体类(这里就只考虑单例)
Object obj = entry.getValue();
Class key = obj.getClass();
//获取所有的属性
Field[] declaredFields = key.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
//设置访问权限
field.setAccessible(true);
//判断该属性是否有对应的注解
rush annotation = field.getAnnotation(rush.class);
if(annotation != null) {
//就对实体类的属性进行赋值
field.set(obj, beanFactory.get(field.getType()));
//完成注入
}
}
}
}
}
在代码中 String filePath = URLDecoder.decode(url.getFile(), "utf-8")的作用是格式化路径,如果不加将会出现下面的情况。(/被%替代)
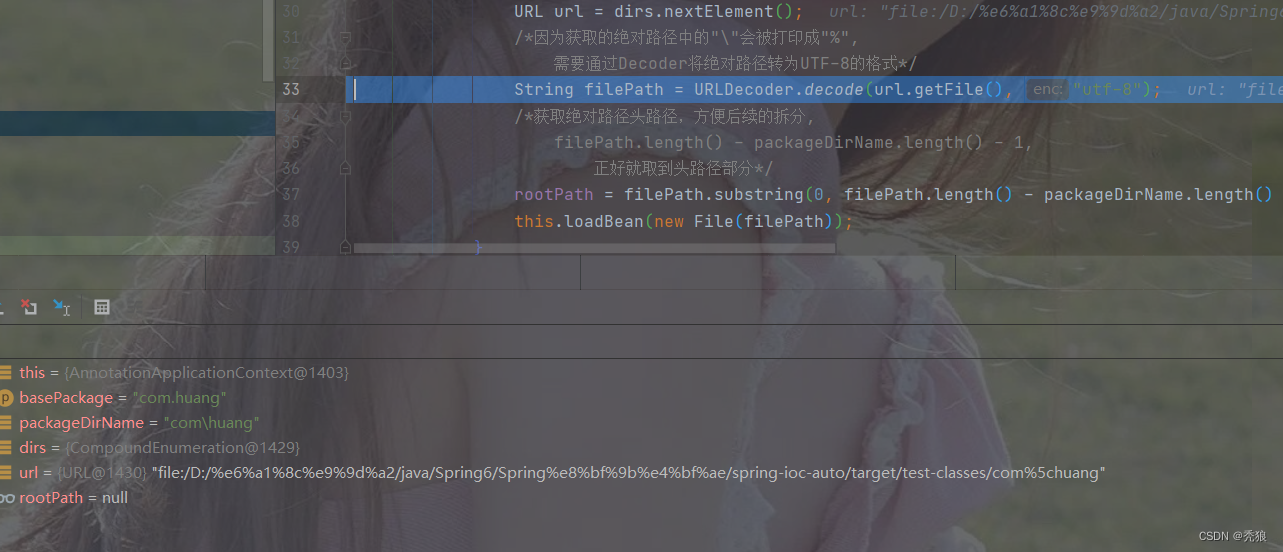
测试代码
//要到对自己写的包
import com.huang.ApplicationContext.AnnotationApplicationContext;
import com.huang.ApplicationContext.ApplicationContext;
import com.huang.Controller.UserController;
public class TestUser {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationApplicationContext("com.huang");
UserController userController = (UserController) context.getBean(UserController.class);
userController.run();
}
}测试结果为下:
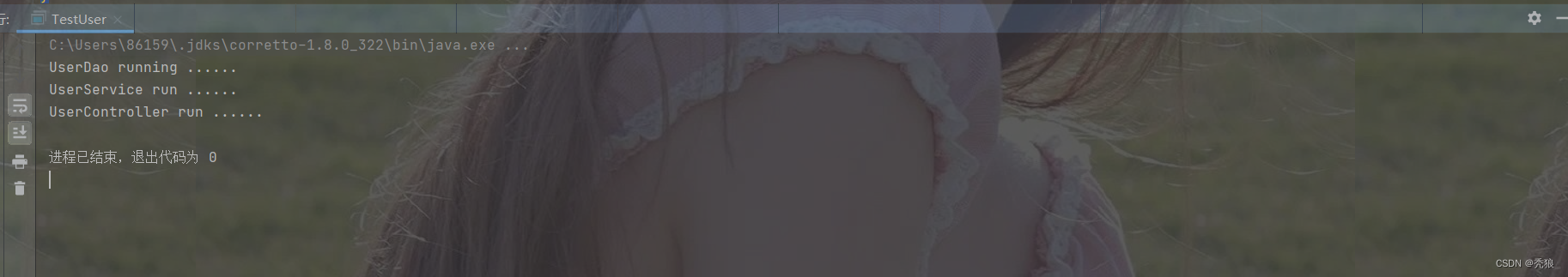
最终完成手写IoC。






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结