您现在的位置是:首页 >其他 >linux部署k8s网站首页其他
linux部署k8s
简介linux部署k8s
linux部署k8s
0、k8s的前世今生
参考链接: https://kubernetes.io/blog/2015/04/borg-predecessor-to-kubernetes/
1、下载k8s
下载链接: https://kubernetes.io/releases/download/#binaries
2、k8s文档
k8s介绍: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/
k8s下载:https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/master/CHANGELOG/CHANGELOG-1.27.md#downloads-for-v1271
k8s安装:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl-linux/
2.1、容器化部署的优越性
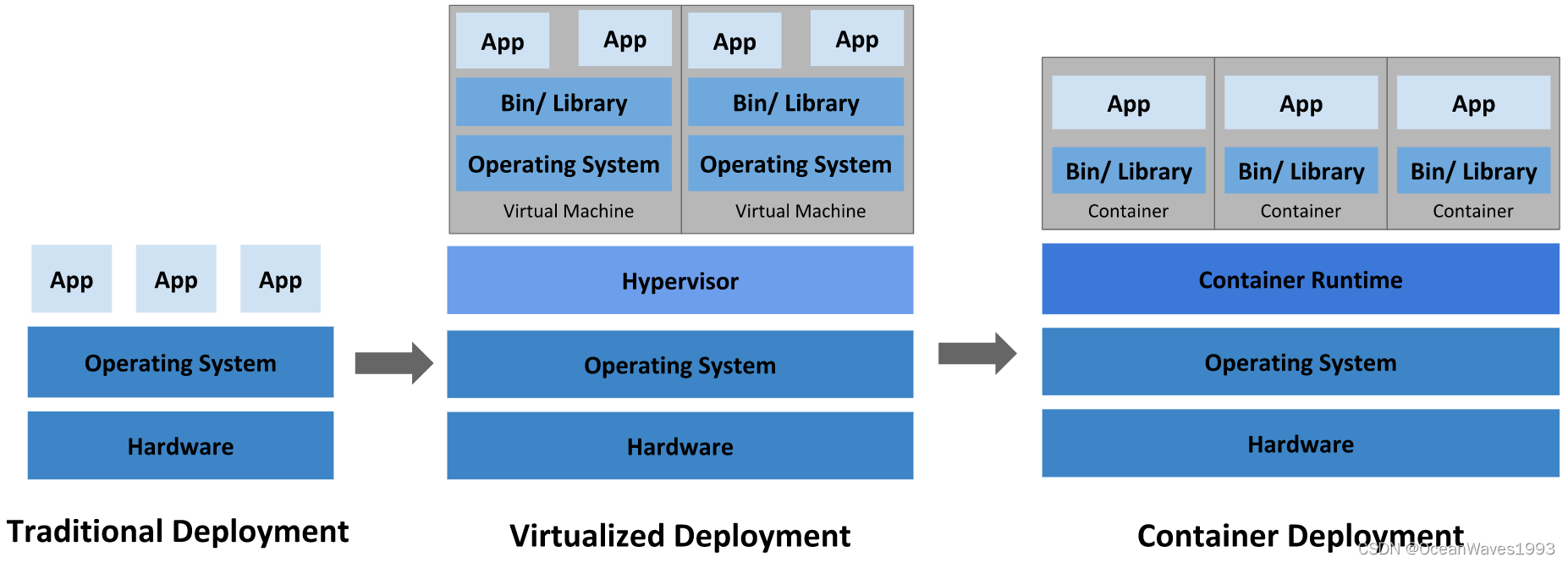
2.1.1、Traditional deployment era
Early on, organizations ran applications on physical servers.
There was no way to define resource boundaries for applications
in a physical server, and this caused resource allocation issues.
For example, if multiple applications run on a physical server,
there can be instances where one application would take up most
of the resources, and as a result, the other applications would
underperform. A solution for this would be to run each
application on a different physical server. But this did not
scale as resources were underutilized, and it was expensive for
organizations to maintain many physical servers.
2.1.2、Virtualized deployment era
As a solution, virtualization was introduced. It allows you to
run multiple Virtual Machines (VMs) on a single physical server's
CPU. Virtualization allows applications to be isolated between
VMs and provides a level of security as the information of one
application cannot be freely accessed by another application.
Virtualization allows better utilization of resources in a
physical server and allows better scalability because an
application can be added or updated easily, reduces hardware
costs, and much more. With virtualization you can present a set
of physical resources as a cluster of disposable virtual
machines.
Each VM is a full machine running all the components, including
its own operating system, on top of the virtualized hardware.
2.1.3、Container deployment era
Containers are similar to VMs, but they have relaxed isolation
properties to share the Operating System (OS) among the
applications. Therefore, containers are considered lightweight.
Similar to a VM, a container has its own filesystem, share of
CPU, memory, process space, and more. As they are decoupled from
the underlying infrastructure, they are portable across clouds
and OS distributions.
Containers have become popular because they provide extra benefits, such as:
- Agile application creation and deployment: increased ease and efficiency of container image creation compared to VM image use.
- Continuous development, integration, and deployment: provides for reliable and frequent container image build and deployment with quick and efficient rollbacks (due to image immutability).
- Dev and Ops separation of concerns: create application container images at build/release time rather than deployment time, thereby decoupling applications from infrastructure.
- Observability: not only surfaces OS-level information and metrics, but also application health and other signals.
- Environmental consistency across development, testing, and production: runs the same on a laptop as it does in the cloud.
- Cloud and OS distribution portability: runs on Ubuntu, RHEL, CoreOS, on-premises, on major public clouds, and anywhere else.
- Application-centric management: raises the level of abstraction from running an OS on virtual hardware to running an application on an OS using logical resources.
- Loosely coupled, distributed, elastic, liberated micro-services: applications are broken into smaller, independent pieces and can be deployed and managed dynamically – not a monolithic stack running on one big single-purpose machine.
- Resource isolation: predictable application performance.
- Resource utilization: high efficiency and density.
3、安装k8s
3.1、Install kubectl on Linux
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl-linux/#install-kubectl-on-linux
3.2、
风语者!平时喜欢研究各种技术,目前在从事后端开发工作,热爱生活、热爱工作。






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结