您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >神经网络实验---梯度下降法网站首页学无止境
神经网络实验---梯度下降法
本次实验主要目的是掌握梯度下降法的基本原理,能够使用梯度下降法求解一元和多元线性回归问题。
1. 实验目的
① 掌握深度学习框架中的自动求导机制;
② 掌握梯度下降法的基本原理,能够使用梯度下降法求解一元和多元线性回归问题。
2. 实验内容
① 使用TensorFlow的可训练变量和自动求导机制实现梯度下降法;
② 使用梯度下降法训练线性回归模型,测试模型性能;
3. 实验过程
题目一:
下载波士顿房价数据集,编写程序实现下述功能:
⑴使用波士顿房价数据集中的“低收入人口比例”属性,训练一元线性回归模型,并测试其性能,以可视化的形式展现训练测试的过程。
⑵使用波士顿房价数据集中的所有属性,训练多元线性回归模型,并测试其性能,以可视化的形式展现训练和测试的过程及结果。
⑶尝试调试学习率、迭代次数等超参数,使模型达到最优的性能,请记录超参数的调试过程及结果,并简要分析和总结;
⑷在第⑴和第⑵小题中,分别选择了单一属性和全部属性建立和训练模型,比较两者的学习率、迭代次数等超参数、在训练集和测试集上的均方差损失、以及模型训练时间,以表格或其他合适的图表形式展示。分析以上结果,可以得到什么结论,或对你有什么启发。
① 代码(一元线性回归模型)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
import time
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = "SimHei" #设置中文黑体为默认字体
boston_housing = tf.keras.datasets.boston_housing
(train_x, train_y), (test_x, test_y) = boston_housing.load_data() #导入训练集和测试集数据
x_train = train_x[:, 12] #使用低收入人口比例
y_train = train_y
x_test = test_x[:, 12]
y_test = test_y
#设置超参数
learn_rate = 0.009
iter = 2000
display_step = 50
#设置模型参数初始值
np.random.seed(612)
w = tf.Variable(np.random.randn())
b = tf.Variable(np.random.randn())
mse_train = [] #记录训练集上的损失
mse_test = [] #记录测试集上的损失
start = time.perf_counter() # 返回系统当时时间
for i in range(0, iter + 1):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: #梯度带对象的with语句,实现对w和b的自动监视
pred_train = w * x_train + b
loss_train = 0.5 * tf.reduce_mean(
tf.square(y_train - pred_train)) #计算训练集上的误差
pred_test = w * x_test + b
loss_test = 0.5 * tf.reduce_mean(
tf.square(y_test - pred_test)) #计算测试集上的误差
mse_train.append(loss_train)
mse_test.append(loss_test)
dL_dw, dL_db = tape.gradient(loss_train, [w, b]) #使用训练集中的数据更新模型参数,梯度下降,自动求导
w.assign_sub(learn_rate * dL_dw)
b.assign_sub(learn_rate * dL_db)
if i % display_step == 0:
print('i: %-5i,Train Loss:%-10f,Test Loss: %-10f' %
(i, loss_train, loss_test)) #输出训练误差和测试误差
end = time.perf_counter()
print("训练模型所耗时长:", end - start)
plt.figure(figsize=(15,10))
#第一个图
plt.subplot(221)
plt.scatter(x_train,y_train,color = "b",label = "data") #散点图
plt.plot(x_train,pred_train,color = "r",label = "model")
plt.title("波士顿房价与低收入人口的比例关系",fontsize = 14)
plt.legend(loc = "upper right") #图例
#第二个图
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(mse_train,color = "r",linewidth = 3,label = "train loss")
plt.plot(mse_test,color = "b",linewidth = 1.5,label = "test loss")
plt.title("损失值随迭代次数变化的曲线",fontsize = 14)
plt.legend(loc = "upper right") #图例
#第三个图
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(y_train,color = "b",marker = "o",label = "true_price")
plt.plot(pred_train,color = "r",marker = '.',label = "predict")
plt.title("训练集中的实际房价与预测的对比",fontsize = 14)
plt.legend(loc = "upper right") #图例
#第四个图
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(y_test,color = "b",marker = "o",label = "true_price")
plt.plot(pred_test,color = "r",marker = '.',label = "predict")
plt.title("测试集中的实际房价与预测的对比",fontsize = 14)
plt.legend(loc = "upper right") #图例
plt.show()② 结果记录

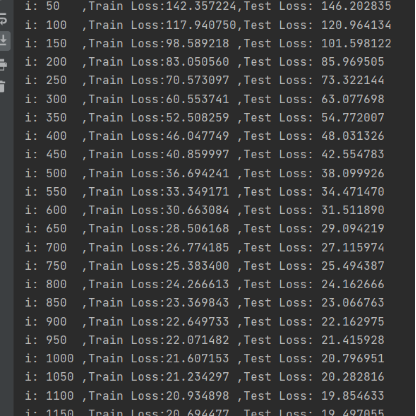
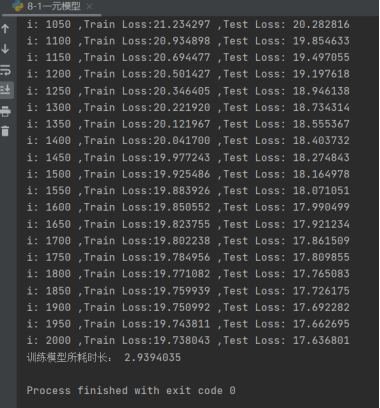
③ 实验总结
| 学习率 | 训练轮数 | 测试损失值 | 所花时间 | |
| 1 | 1e-2 | 2000 | 17.636801 | 2.9394035s |
| 2 | 1e-3 | 10000 | 19.777699 | 13.5335091s |
| 3 | 1e-3 | 20000 | 17.555531 | 27.0643188s |
① 代码(多元线性回归模型)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
#下载波士顿数据集
boston_housing = tf.keras.datasets.boston_housing
(train_x,train_y),(test_x,test_y) = boston_housing.load_data()
num_train = len(train_x)
num_test = len(test_x)
#运用广播运算进行归一化操作
x_train = (train_x - test_x.min(axis = 0)) / (train_x.max(axis = 0) - train_x.min(axis = 0))
y_train = train_y
x_test = (test_x - test_x.min(axis = 0)) / (test_x.max(axis = 0) - test_x.min(axis = 0))
y_test = test_y
x0_train = np.ones(num_train).reshape(-1,1)
x0_test = np.ones(num_test).reshape(-1,1)
X_train = tf.cast(tf.concat([x0_train,x_train],axis = 1),tf.float32)
X_test = tf.cast(tf.concat([x0_test,x_test],axis=1),tf.float32)
#将房价转换为列向量
Y_train = tf.constant(y_train.reshape(-1,1),tf.float32)
Y_test = tf.constant(y_test.reshape(-1,1),tf.float32)
#设置超参数
learn_rate = 0.01 #学习率
iter = 2000 #迭代次数
display_step = 200 #显示间隔
#设置模型变量初值
np.random.seed(612)
W = tf.Variable(np.random.randn(14,1),dtype=tf.float32)
mse_train = []
mse_test = []
for i in range(iter + 1):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
PRED_train = tf.matmul(X_train,W)
Loss_train = 0.5 * tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y_train - PRED_train))
PRED_test = tf.matmul(X_test,W)
Loss_test = 0.5 * tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y_test - PRED_test))
mse_train.append(Loss_train)
mse_test.append(Loss_test)
dL_dW = tape.gradient(Loss_train,W)
W.assign_sub(learn_rate * dL_dW)
if i % display_step == 0:
print("i:%d,Train Loss:%f,Test Loss:%f"%(i,Loss_train,Loss_test))
#画图
plt.figure(figsize=(15,4))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.ylabel("MSE")
plt.plot(mse_train,color = "b",linewidth = 3,label = "train loss")
plt.plot(mse_test,color = "r",linewidth = 1.5,label = "test loss")
plt.title("损失值随迭代次数变化的曲线",fontsize = 14)
plt.legend(loc = "upper right")
plt.subplot(132)
plt.plot(Y_train,color = "b",marker = "o",label = "true_price")
plt.plot(PRED_train,color = "r",marker = ".",label = "predict")
plt.legend()
plt.ylabel("Price")
plt.title("训练集中实际房价与预测的对比",fontsize = 14)
plt.legend(loc = "upper right")
plt.subplot(133)
plt.plot(Y_test,color = "b",marker = "o",label = "true_price")
plt.plot(PRED_test,color = "r",marker = '.',label = "predict")
plt.ylabel("Price")
plt.title("测试集中的实际房价与预测的对比",fontsize = 14)
plt.legend(loc = "upper right")
plt.show()② 结果记录


③ 实验总结
| 学习率 | 训练轮数 | 测试损失值 | |
| 1 | 1e-3 | 5000 | 26.834869 |
| 2 | 1e-2 | 5000 | 20.631872 |
| 3 | 1e-2 | 2800 | 19.298813 |
题目二:
观察6.4小节中给出的波士顿房价数据集中各个属性与房价关系的可视化结果(如图1所示),编写代码实现下述功能:

图1 波士顿房价数据集各个属性与房价关系
要求:
⑴观察图1,分析各个属性对房价的影响,从中选择你认为对房价影响最明显的属性并说明理由;
⑵使用第(1)问中选择的属性,编写代码建立并训练多元线性回归模型预测房价,并测试模型性能;
⑶尝试调试学习率、迭代次数等超参数,使模型达到最优性能,请记录超参数的调试过程以及训练和测试的结果,并简要分析和总结;
⑷分析和总结:
比较分别使用单一属性、全部属性和你自己选择的属性组合训练模型时,学习率、迭代次数等参数,以及在训练集和测试集上的均方差损失和模型训练时间等结果,以表格或其他合适的图表形式展示。通过以上结果,可以得到什么结论,或对你有什么启发。
① 代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = "SimHei" #设置中文黑体为默认字体
# 加载数据集
boston_housing = tf.keras.datasets.boston_housing
(train_x, train_y), (test_x, test_y) = boston_housing.load_data()
train_X = train_x[:,[5,12]]
test_X = test_x[:,[5,12]]
num_train = len(train_X)
num_test = len(test_X)
#运用广播运算对数据进行归一化处理
x_train = (train_X - train_X.min(axis=0)) / (train_X.max(axis=0) -
train_X.min(axis=0))
y_train = train_y
x_test = (test_X - test_X.min(axis=0)) / (test_X.max(axis=0) -
test_X.min(axis=0))
y_test = test_y
x0_train = np.ones(num_train).reshape(-1, 1)
x0_test = np.ones(num_test).reshape(-1, 1)
X_train = tf.cast(tf.concat([x0_train, x_train], axis=1), tf.float32) #数组堆叠
X_test = tf.cast(tf.concat([x0_test, x_test], axis=1), tf.float32) #指定为32位浮点数
#把房价转化为列向量
Y_train = tf.constant(y_train.reshape(-1, 1), tf.float32)
Y_test = tf.constant(y_test.reshape(-1, 1), tf.float32)
#设置超参数
learn_rate = 0.01 #学习率
iter = 2000 #迭代次数
display_step = 200 #显示间隔
#设置模型变量初值
np.random.seed(612)
W = tf.Variable(np.random.randn(3, 1), dtype=tf.float32)
mse_train = []
mse_test = []
for i in range(0, iter + 1):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
PRED_train = tf.matmul(X_train, W)
Loss_train = 0.5 * tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y_train - PRED_train))
PRED_test = tf.matmul(X_test, W)
Loss_test = 0.5 * tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(Y_test - PRED_test))
mse_train.append(Loss_train)
mse_test.append(Loss_test)
dL_dW = tape.gradient(Loss_train, W)
W.assign_sub(learn_rate * dL_dW)
if i % display_step == 0:
print('i: %-5i,Train Loss:%-10f,Test Loss: %-10f' %
(i, Loss_train, Loss_test))
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
plt.subplot(131)
plt.ylabel('MSE')
plt.plot(mse_train, color='blue', linewidth=3)
plt.plot(mse_test, color='red', linewidth=1.5)
plt.title("损失值随迭代次数变化的曲线", fontsize=14)
plt.subplot(132)
plt.plot(Y_train, color='blue', marker='o', label='true_price')
plt.plot(PRED_train, color='red', marker='.', label='predict')
plt.legend()
plt.ylabel('Price')
plt.title("训练集中的实际房价与预测的对比", fontsize=14)
plt.subplot(133)
plt.plot(Y_test, color='blue', marker='o', label='true_price')
plt.plot(PRED_test, color='red', marker='.', label='predict')
plt.legend()
plt.ylabel('Price')
plt.title("测试集中的实际房价与预测的对比", fontsize=14)
plt.show()② 结果记录

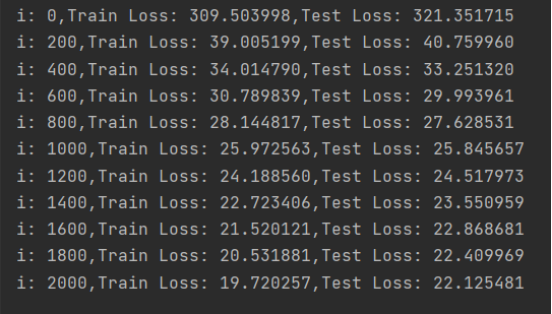
③ 实验总结
使用了第6和13个属性,低收入人口及平均房间数
| 学习率 | 训练轮数 | 测试损失值 | |
| 1 | 1e-3 | 5000 | 31.471260 |
| 2 | 1e-2 | 4000 | 23.086786 |
| 3 | 1e-2 | 8000 | 25.460329 |
题目三:
Advertising数据集(见附件1)记录了200件产品在3个媒体平台的广告投入与销售总额。数据集结构如图1所示(只列举了前19行数据),其中共有200条数据,每条数据中有3个属性,是产品分别在TV、radio、newspaper平台的广告投入额度,标签是产品的销售总额。
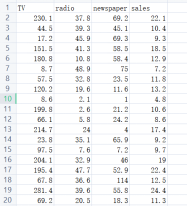
图1 Advertising数据集
要求:
⑴下载Advertising数据集,并采用适当的形式对数据集进行可视化,要求清晰美观;
⑵将数据集划分为训练集和测试集,寻找恰当的属性训练多元线性回归模型,测试模型,并将结果以可视化的形式展示;
⑶记录超参数的调试过程,综合考虑模型训练时间和均方差损失,寻找使模型达到最佳性能的超参数。
提示:
① 划分数据集前应首先打乱数据集,打乱数据集的相关函数:
| 序号 | 函数 | 函数功能 | 函数相关库 |
| (1) | np.random.permutation(seq) | 随机排列序列seq | Numpy库 |
| (2) | 对象名.iloc() | 基于行、列索引序号进行查询 | Pandas库 |
① 代码
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 加载数据集
data = pd.read_csv('c:\users\yy\desktop\Advertising.CSV')
# 查看数据集属性和前5行数据
print(data.info())
print(data.head())
# 绘制属性与销售额的关系图
sns.pairplot(data, x_vars=['TV', 'radio', 'newspaper'], y_vars='sales', height=7, aspect=0.7, kind='reg')
plt.show()
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# 将数据集划分为训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data[['TV', 'radio', 'newspaper']], data['sales'], test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 训练多元线性回归模型
lin_reg = LinearRegression()
lin_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 在测试集上测试模型
y_pred = lin_reg.predict(X_test)
# 计算均方差损失
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print('MSE:', mse)
# 绘制预测值与实际值的散点图
plt.scatter(y_test, y_pred)
plt.xlabel('Actual Values')
plt.ylabel('Predictions')
plt.show()
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
# 定义超参数的取值范围
param_grid = {'fit_intercept': [True, False], 'normalize': [True, False], 'copy_X': [True, False]}
# 使用网格搜索寻找最佳超参数
lin_reg = LinearRegression()
grid_search = GridSearchCV(lin_reg, param_grid, cv=5, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 输出最佳超参数和对应的均方差损失
print('Best Params:', grid_search.best_params_)
print('Best Score:', -grid_search.best_score_)
# 使用最佳超参数训练模型
lin_reg = LinearRegression(copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, normalize=False)
lin_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 在测试集上测试模型
y_pred = lin_reg.predict(X_test)
# 计算均方差损失
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print('MSE:', mse)
# 绘制预测值与实际值的散点图
plt.scatter(y_test, y_pred)
plt.xlabel('Actual Values')
plt.ylabel('Predictions')
plt.show()② 结果记录


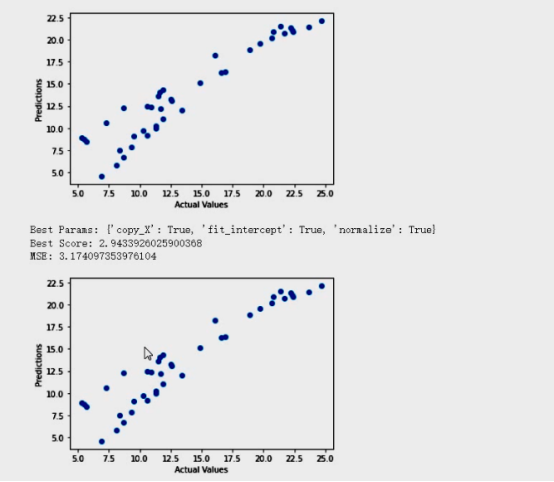
实验小结&讨论题
① 为什么要对数据归一化?除了课程中介绍的方法,查阅资料,看看还有哪些归一化方法?各有什么特点?分别适用于什么类型的数据。
答:归一化后加快了梯度下降求最优解的速度、归一化有可能提高精度。
(1)Decimal place normalization,小数位归一化
小数位归一化发生在具有数字类型的数据表中。如果你使用过 Excel,你就会知道这是如何发生的。默认情况下,Excel 会保留小数点后两位数字,也可以设定小数的位数,并在整个表格中进行统一。
(2)Data type normalization,数据类型归一化
另一种常见是对数据类型的归一化。在 Excel 或 SQL 查询数据库中构建数据表时,可能会发现自己查看的数字数据有时被识别为货币,有时被识别为文本,有时被识别为数字,有时被识别为逗号分割的字符串。
(3)Formatting normalization,格式的归一化
这对于字符串(文本)是很常见的,并且在印刷和打印上出现的更多。虽然这些问题不会对分析产生影响,但是他可能会分散我们的注意力和现实的效果,例如斜体、粗体或下划线或者字体与其他的文字显示不一样。
(4)Z-Score normalization
Z-Score 将数据按比例缩放,使之落入一个特定区间
(5)Linear normalization (“Max-Min”)
它允许分析人员获取集合中最大 x 值和最小 x 值之间的差值,并建立一个基数。
(6)Clipping normalization,剪裁归一化
裁剪并不完全是一种归一化技术,他其实是在使用归一化技术之前或之后使用的一个操作。简而言之,裁剪包括为数据集建立最大值和最小值,并将异常值重新限定为这个新的最大值或最小值。需要注意的是,裁剪不会从数据集中删除点,它只是重新计算数据中的统计值。
(7)Standard Deviation Normalization,标准差归一化
② 在使用梯度下降法对波士顿房价数据集进行模型训练时,怎样设置超参数能够使得模型快速收敛?怎样能够找到合适的超参数?想一想,并查阅资料,总结寻找合适的超参数都有哪些方法。
答:对训练集和测试集归一化,可以采用以下3种方式:①先把测试集和训练集放在一起,进行属性归一化,然后再分开。②先划分训练集和测试集,然后分别归一化。③先划分训练集和测试集,归一化训练集,记录训练集的归一化参数(最大值,最小值),然后再使用训练集的参数去归一化测试集。
③ 解析法和梯度下降法都能求解线性回归问题,它们的区别在哪?
答:在线性回归算法求解中,常用的是解析法与梯度下降法,其中梯度下降法是解析法求解方法的优化,但这并不说明梯度下降法好于解析法,实际应用过程中,二者各有特点,需结合实际案例具体分析。相对于解析法来说,梯度下降法须要归一化处理以及选取学习速率,且需多次迭代更新来求得最终结果,而解析法则不需要。
相对于梯度下降法来说,解析法须要求解(XTX)-1,其计算量为o(n3),当训练数据集过于庞大的话,其求解过程非常耗时,而梯度下降法耗时相对较小。
所以,当模型相对简单,训练数据集相对较小,用解析法较好;对于更复杂的学习算法或者更庞大的训练数据集,用梯度下降法较好,一般当特征变量小于10的四次方时,使用解析法较稳妥,而大于10的四次方时,则应该使用梯度下降法来降低计算量。






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结