您现在的位置是:首页 >技术交流 >快速上手Pytorch实现BERT,以及BERT后接CNN/LSTM网站首页技术交流
快速上手Pytorch实现BERT,以及BERT后接CNN/LSTM
快速上手Pytorch实现BERT,以及BERT后接CNN/LSTM
本项目采用HuggingFace提供的工具实现BERT模型案例,并在BERT后接CNN、LSTM等
HuggingFace官网
一、实现BERT(后接线性层)
1.引用案例源码:
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel
import torch
model_name = 'bert-base-uncased'
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="pt" , padding='max_length',max_length=10)
outputs = model(**inputs)
# print(inputs) # 字典类型的input_ids必选字段 101CLS 102SEP
last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state # last_hidden_state 最后一层的输出 pooler_output / hidden_states
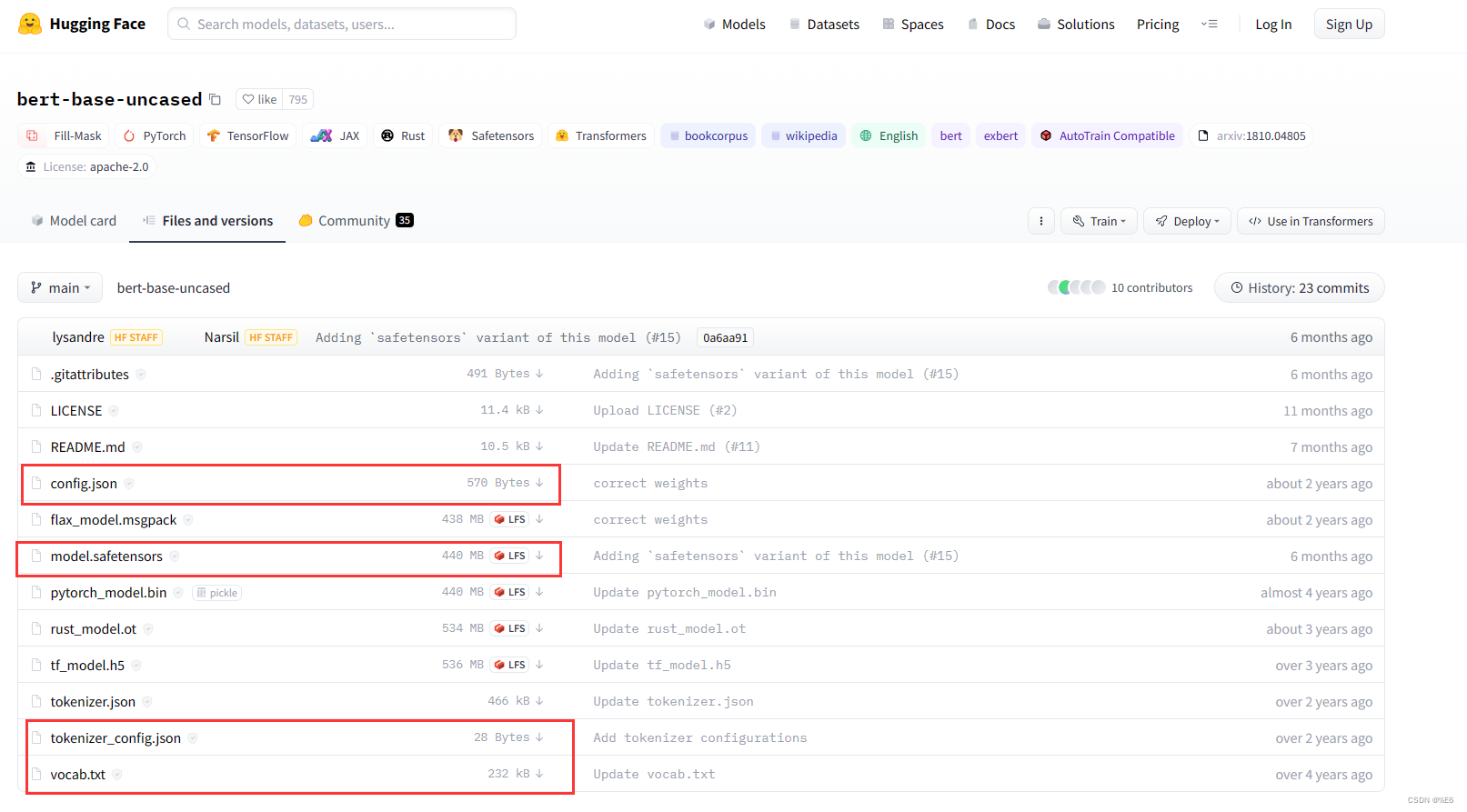
程序会自行下载模型和配置文件,也可自行在官网上手动下载
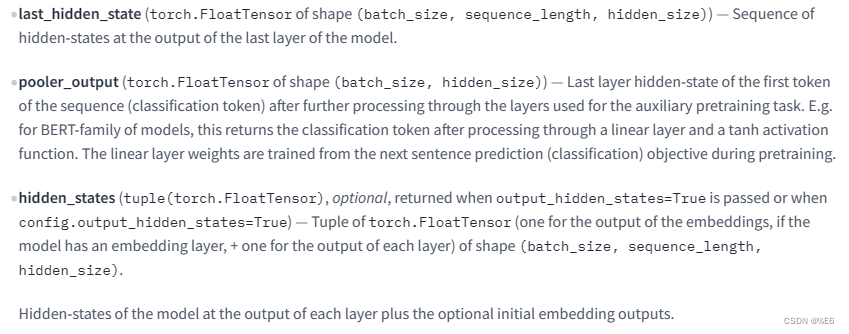
模型返回的参数
2. 自定义类调用数据集
class MyDataSet(Data.Dataset) :
def __init__(self , data ,label):
self.data = data # ['今天天气很好', 'xxxx' , ……]
self.label = label # [1 , 2 , 0]
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
def __getitem__(self , idx):
text = self.data[idx] # str
label = self.label[idx]
inputs = self.tokenizer(text , return_tensors="pt" , padding='max_length',max_length=10 , truncation = True) # truncation = True 是否进行截断操作
input_ids = inputs.input_ids.squeeze(0) # squeeze(0) 对张量进行降维操作 为啥降维:输入的data是一句话(一维)但生成的input_ids默认是二维,因此需要降维
token_type_ids = inputs.token_type_ids.squeeze(0)
attention_mask = inputs.attention_mask.squeeze(0)
return input_ids , token_type_ids , attention_mask,label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
squeeze(0)的作用: 举个栗子
input_ids: tensor([[ 101, 7592, 1010, 2026, 3899, 2003, 10140, 102, 0, 0]])
b = input_ids.squeeze(0)
b: tensor([ 101, 7592, 1010, 2026, 3899, 2003, 10140, 102, 0, 0])
当张量是一个1 * n 维度的张量时,input_ids的维度是 1 * 10,调用squeeze(0) 将张量降成1维。
若不是1 * n的这种2维张量,如本就是1维的,或者m * n(其中m和n都是大于1的),调用这个函数没有效果。
squeeze(1)和squeeze(-1)作用相同 ,与squeeze(0)类似
将一个n*1维度的张量降成1维
3. 将数据集传入模型
data , label = [] , []
with open('./dataset/data.txt') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
a, b = line.strip().split(' ')
data.append(a)
label.append(int(b))
dataset = MyDataSet(data,label)
dataloader = Data.DataLoader(dataset , batch_size = 2,shuffle =True)
4.自定义模型
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel,self).__init__()
self.bert = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.liner = nn.Linear(768, 3) # "hidden_size": 768
def forward(self , input_ids , token_type_ids , attention_mask) :
output = self.bert(input_ids , token_type_ids ,attention_mask).pooler_output # [batch_size , hidden_size]
# print(output.shape)
output = self.linnear(output)
return output
5.配置运行环境
device = torch.device('cuda')
model = MyModel().to(device)
loss_fun = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters() , lr = 1e-5)
6.训练模型,计算损失
for epoch in range(10):
for input_ids,token_type_ids,attention_mask ,label in dataloader:
input_ids,token_type_ids,attention_mask ,label = input_ids.to(device),token_type_ids.to(device),attention_mask.to(device) ,label.to(device)
pred = model(input_ids,token_type_ids,attention_mask)
loss = loss_fn(pred , label)
print(loss.item())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
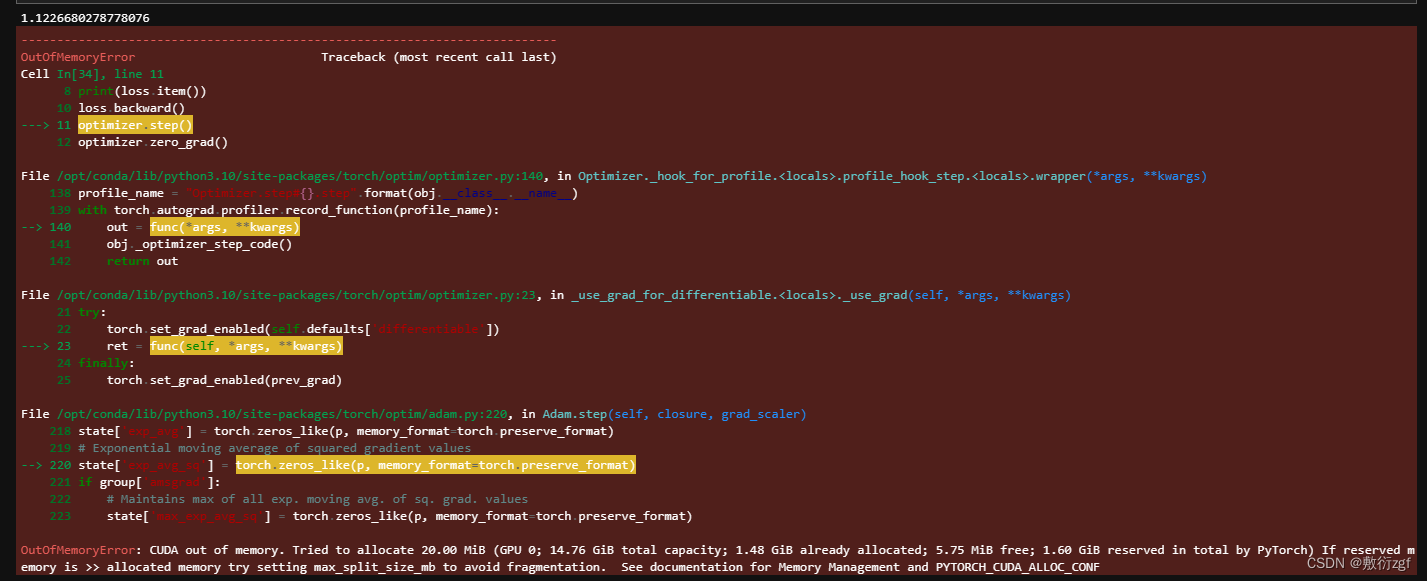
易出现显存不够的错误,可以在服务器控制台中输入nvidia-smi //查看所有进程信息
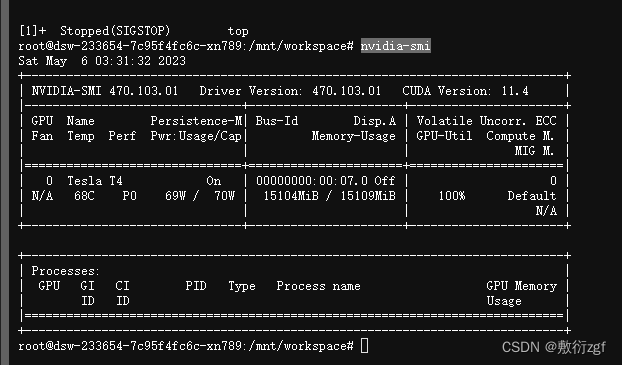
选择需要杀死的进程taskkill /PID PTD号 /F //使用taskkill 进程id,杀死进程
二、BERT+CNN
添加卷积层,查看需要的参数

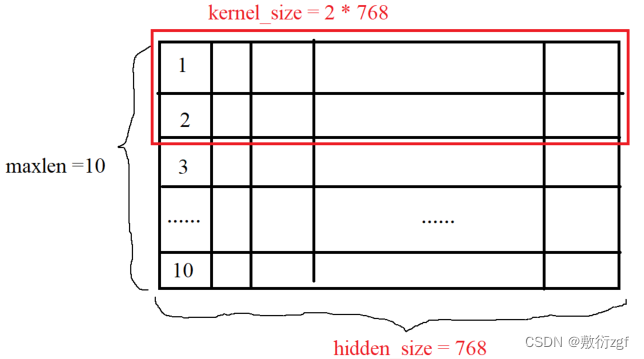
输入层和输出层之间的参数关系为:Wout = (Win + 2p - w)/ s +1 ; Hout = (Hin + 2p - w)/ s +1
其中Win = maxlen,Hin = hidden_size,卷积核大小为 w * h ,p表示padding(默认为0),s表示卷积步长(默认为1)
因此输出为 (10 + 2 * 0 - 2)/ 1 + 1 = 9 ,(768 + 2 * 0 - 768)/ 1 + 1 = 1
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.bert = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
'''
BERT后接CNN
'''
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(1 ,3 ,kernel_size=(2,768)) # in_channels 输入的通道数 out_channels 经过卷积之后的通道数 kernel_size 卷积核大小
self.linear = nn.Linear(27, 3) # "hidden_size": 768
def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids, attention_mask):
'''
x : [batch , channel , width , height]
'''
batch = input_ids.size(0)
output = self.bert(input_ids, token_type_ids, attention_mask).last_hidden_state # [batch_size , seq , hidden_size]
output = output.unsqueeze(1) # [batch , 1, seq , hidden_size] 三维扩展成四维
# print(output.shape)
output = self.conv(output) # [batch , 3, 9 ,1]
print(output.shape)
# 为了进行分类,希望将四维转换成二维 # [batch , 3]
output = output.view(batch , -1) # [batch , 3*9*1]
output = self.linear(output)
return output
输出结果
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
1.0467640161514282
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
1.6651103496551514
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
1.1516715288162231
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
1.0645687580108643
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
1.0910512208938599
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
0.9897172451019287
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
1.0313527584075928
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
1.0067516565322876
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
0.9847115278244019
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
1.01240873336792
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
0.9597381353378296
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
0.9435619115829468
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
0.9591015577316284
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
0.8384571075439453
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
0.9722234010696411
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
0.7264331579208374
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
0.9841375350952148
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
0.6240622997283936
torch.Size([2, 3, 9, 1])
0.7659112811088562
torch.Size([1, 3, 9, 1])
1.0371975898742676
三、BERT+LSTM
添加LSTM,查看需要哪些参数


class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.bert = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
'''
BERT后接LSTM
'''
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=768, hidden_size= 512 ,num_layers= 1 , batch_first= True , bidirectional=True) # batch_first = True 表示输入输出顺序(batch,seq,feature) LSTM默认(seq,batch,feature)
self.linear = nn.Linear(1024, 3) # "hidden_size": 768
def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids, attention_mask):
'''
x : [batch , seq]
'''
batch = input_ids.size(0)
output = self.bert(input_ids, token_type_ids, attention_mask).last_hidden_state # [batch_size , seq , hidden_size]
output , _ = self.lstm(output)
print(output.shape) # [2 , seq ,2*hidden_size]
# 使用LSTM最后一层的输出做分类
output = output[: ,-1,:] # [batch , 1024]
print('最后一层' ,output.shape)
output = self.linear(output)
return output
输出结果
{‘input_ids’: tensor([[ 101, 7592, 1010, 2026, 3899, 2003,
10140, 102, 0, 0]]), ‘token_type_ids’: tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]), ‘attention_mask’: tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 0, 0]])} [‘今天天气很好’, ‘今天天气很不好’, ‘明天天气非常好’] [1, 0, 2]torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
1.0788244009017944 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
1.3834939002990723 torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
1.155088186264038 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
1.0809415578842163 torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
1.061639666557312 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
1.1302376985549927 torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
1.0572789907455444 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
1.086378812789917 torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
1.0700803995132446 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
1.0184061527252197 torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
0.9948051571846008 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
1.203598976135254 torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
1.1068116426467896 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
0.9117098450660706 torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
0.9891176223754883 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
1.1974778175354004 torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
1.0810655355453491 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
0.8861477375030518 torch.Size([2, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([2, 1024])
0.9180283546447754 torch.Size([1, 10, 1024]) 最后一层 torch.Size([1, 1024])
1.2292695045471191
要实现BERT后接各种模型,最重要的是需要知道模型经过每一层后的维度是多少,最粗暴的方式可以通过print输出维度。






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结