您现在的位置是:首页 >技术交流 >feign远程调用原理网站首页技术交流
feign远程调用原理
目录
2.2 @Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class),
一、简介
feign是springCloud全家桶中的远程调用组件,其底层主要依赖于Java的动态代理机制,然后基于http client进行http请求,同时它还能配合其它组件实现Loadbalance(负载均衡)、Hystrix(熔断)、fallback(降级)等功能。
二、调用流程分析
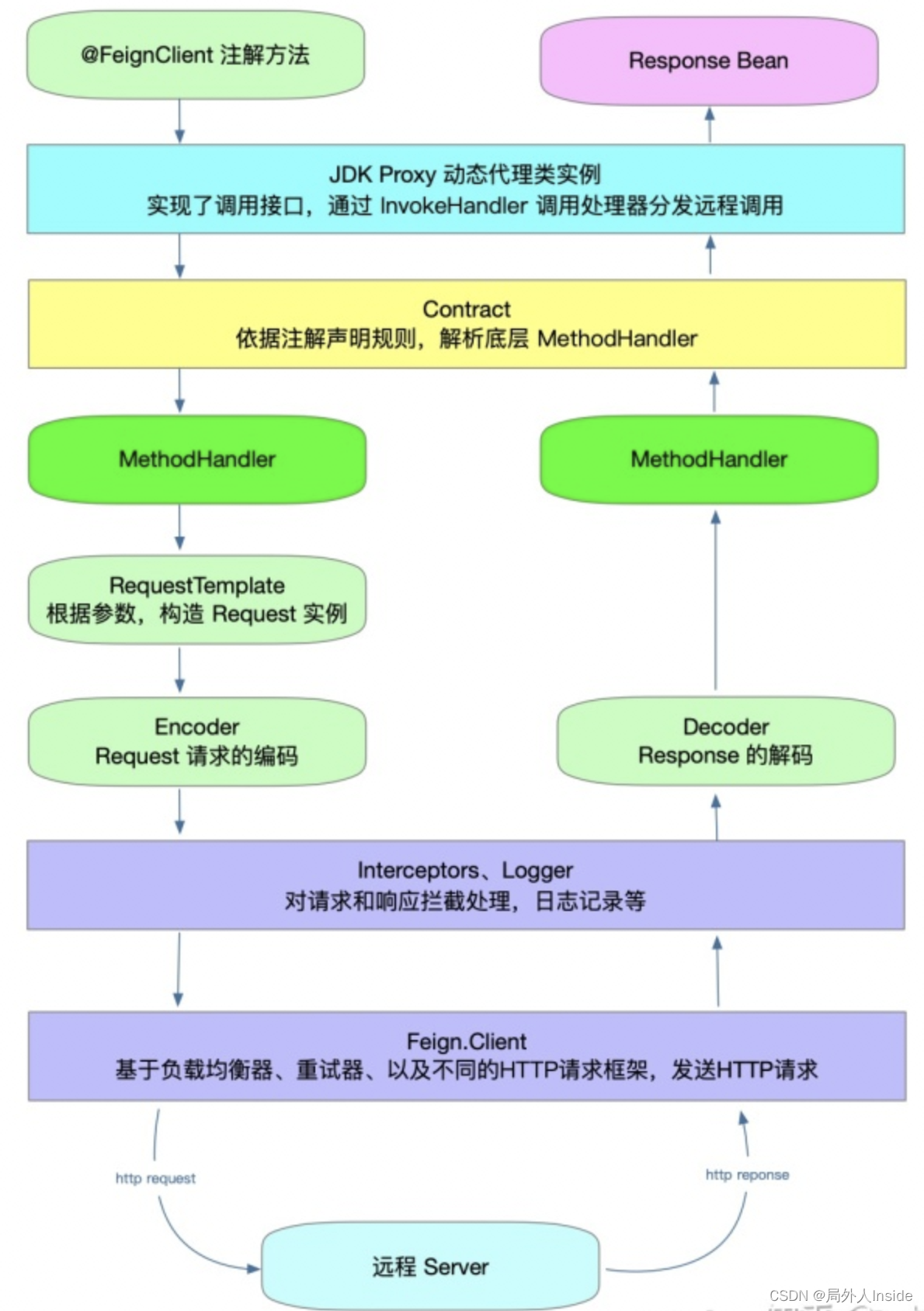
2.1 添加注解
在application启动类上添加@EnableFeignClients注解,并在basePackages属性中添加FeignClient所在的包,使Spring容器能够扫描到所有的FeignClient对象,这样就可以开始使用feign的远程调用功能了,EnableFeignClients包含以下属性,常用的是basePackages。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableFeignClients {
/**
* basePackages() 属性的别名
*/
String[] value() default {};
/**
* 注解扫描包路径集
*/
String[] basePackages() default {};
/**
* basePackages的替代值,注解扫描类所在的每个包,
* 若使用此属性,会在每个feign类所在包下建立一个特殊意义的空类
*/
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
/**
* 针对所有client生效的注解类集
*/
Class<?>[] defaultConfiguration() default {};
/**
* 标注有@FeignClient注解的类集合,若不为空,则禁止路径扫描
* @return
*/
Class<?>[] clients() default {};
}
2.2 @Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class),
将feign相关对象注入到容器中,导入了 FeignClientsRegistrar注册器,该类实现了spring提供的ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,能够在registerBeanDefinitions方法中注册自定义的bean。同时也实现了ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware等钩子接口,能够持有spring的环境、资源等变量,方便进行包扫描。
class FeignClientsRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private Environment environment;
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//从@EnableFeignClients注解中提取defaultConfiguration属性配置的key和value,并将配置类注册至spring容器
registerDefaultConfiguration(metadata, registry);
//扫描所有的feignclient类,注册进spring容器
registerFeignClients(metadata, registry);
}
}registerFeignClients方法:注册所有feign逻辑
public void registerFeignClients(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider scanner = getScanner();
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
Set<String> basePackages;
Map<String, Object> attrs = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName());
AnnotationTypeFilter annotationTypeFilter = new AnnotationTypeFilter(
FeignClient.class);
final Class<?>[] clients = attrs == null ? null
: (Class<?>[]) attrs.get("clients");
//若clients为空,则进行包扫描
if (clients == null || clients.length == 0) {
//添加注解过滤条件
scanner.addIncludeFilter(annotationTypeFilter);
basePackages = getBasePackages(metadata);
}else {
//不为空直接注入
final Set<String> clientClasses = new HashSet<>();
basePackages = new HashSet<>();
for (Class<?> clazz : clients) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
clientClasses.add(clazz.getCanonicalName());
}
AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter filter = new AbstractClassTestingTypeFilter() {
@Override
protected boolean match(ClassMetadata metadata) {
String cleaned = metadata.getClassName().replaceAll("\$", ".");
return clientClasses.contains(cleaned);
}
};
scanner.addIncludeFilter(
new AllTypeFilter(Arrays.asList(filter, annotationTypeFilter)));
}
//遍历包路径集
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
//scanner扫描所有符合要求的bean
Set<BeanDefinition> candidateComponents = scanner
.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidateComponent : candidateComponents) {
if (candidateComponent instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// verify annotated class is an interface
AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidateComponent;
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata();
//校验是否为接口,若不为则抛异常,@FeignClient只能在接口上使用
Assert.isTrue(annotationMetadata.isInterface(),
"@FeignClient can only be specified on an interface");
Map<String, Object> attributes = annotationMetadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(
FeignClient.class.getCanonicalName());
String name = getClientName(attributes);
//添加独有配置
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attributes.get("configuration"));
//注册FeignClient
registerFeignClient(registry, annotationMetadata, attributes);
}
}
}
}registerFeignClient方法:实际注册单个FeignClient的逻辑
private void registerFeignClient(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
String className = annotationMetadata.getClassName();
//获取FeignClientFactoryBean的BeanDefinitionBuilder
BeanDefinitionBuilder definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientFactoryBean.class);
//属性校验
validate(attributes);
//bean属性添加
definition.addPropertyValue("url", getUrl(attributes));
definition.addPropertyValue("path", getPath(attributes));
String name = getName(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("name", name);
//class类型
definition.addPropertyValue("type", className);
definition.addPropertyValue("decode404", attributes.get("decode404"));
definition.addPropertyValue("fallback", attributes.get("fallback"));
//设置降级工厂
definition.addPropertyValue("fallbackFactory", attributes.get("fallbackFactory"));
//设置自动注入类型
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
String alias = name + "FeignClient";
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition();
boolean primary = (Boolean)attributes.get("primary"); // has a default, won't be null
beanDefinition.setPrimary(primary);
//设置别名
String qualifier = getQualifier(attributes);
if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) {
alias = qualifier;
}
BeanDefinitionHolder holder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, className,
new String[] { alias });
//注册BeanDefinition
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(holder, registry);
}到这里,我们所有的feignClient bean对象就已经被注入到spring容器中了,就可以正常使用feignClient接口去远程调用了。
2.3 代理创建流程
FeignClientFactoryBean工厂类,用于提供FeignClient实例,其关键方法如下:
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
//获取feign的上下文
FeignContext context = applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);
//若未指定url,则根据名称去构建feignClient,且具备负载均衡能力
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) {
String url;
if (!this.name.startsWith("http")) {
url = "http://" + this.name;
}
else {
url = this.name;
}
url += cleanPath();
return loadBalance(builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type,
this.name, url));
}
//若url不为空,代表指定了某台机器,不需要负载均衡
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.url) && !this.url.startsWith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.url;
}
String url = this.url + cleanPath();
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
if (client instanceof LoadBalancerFeignClient) {
// not lod balancing because we have a url,
// but ribbon is on the classpath, so unwrap
// 解除负载均衡能力
client = ((LoadBalancerFeignClient)client).getDelegate();
}
builder.client(client);
}
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
//真正的获取方法
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(
this.type, this.name, url));
}真正的获取方法其实是targeter.target()方法,targeter包含两个实现:
- DefaultTargeter:默认实现,直接调用Feign.Builder的target方法;
- HystrixTargeter:具备限流熔断机制,若builder不属于HystrixFeign类型,则直接调用Feign.Builder的target方法。若属于,则将builder强转为feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder类型,然后按顺序调用factory.getFallback()或factory.getFallbackFactory(),根据fallback或fallbackFactory是否为void.class,则调用targetWithFallback或targetWithFallbackFactory构建对象。若都为void.class,则直接调用Feign.Builder的target方法。
@Override
public <T> T target(FeignClientFactoryBean factory, Feign.Builder feign, FeignContext context,
Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
if (!(feign instanceof feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder)) {
return feign.target(target);
}
feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder builder = (feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign.Builder) feign;
SetterFactory setterFactory = getOptional(factory.getName(), context,
SetterFactory.class);
if (setterFactory != null) {
builder.setterFactory(setterFactory);
}
Class<?> fallback = factory.getFallback();
if (fallback != void.class) {
return targetWithFallback(factory.getName(), context, target, builder, fallback);
}
Class<?> fallbackFactory = factory.getFallbackFactory();
if (fallbackFactory != void.class) {
return targetWithFallbackFactory(factory.getName(), context, target, builder, fallbackFactory);
}
return feign.target(target);
}
private <T> T targetWithFallbackFactory(String feignClientName, FeignContext context,
Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target,
HystrixFeign.Builder builder,
Class<?> fallbackFactoryClass) {
FallbackFactory<? extends T> fallbackFactory = (FallbackFactory<? extends T>)
getFromContext("fallbackFactory", feignClientName, context, fallbackFactoryClass, FallbackFactory.class);
/* We take a sample fallback from the fallback factory to check if it returns a fallback
that is compatible with the annotated feign interface. */
Object exampleFallback = fallbackFactory.create(new RuntimeException());
Assert.notNull(exampleFallback,
String.format(
"Incompatible fallbackFactory instance for feign client %s. Factory may not produce null!",
feignClientName));
if (!target.type().isAssignableFrom(exampleFallback.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
String.format(
"Incompatible fallbackFactory instance for feign client %s. Factory produces instances of '%s', but should produce instances of '%s'",
feignClientName, exampleFallback.getClass(), target.type()));
}
return builder.target(target, fallbackFactory);
}
private <T> T targetWithFallback(String feignClientName, FeignContext context,
Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target,
HystrixFeign.Builder builder, Class<?> fallback) {
T fallbackInstance = getFromContext("fallback", feignClientName, context, fallback, target.type());
return builder.target(target, fallbackInstance);
}翻看源码调用链,会发现不管是HystrixFeign.Builder的target方法还是Feign.Builder的target方法,最终都会调用Feign接口的newInstance方法,该方法默认实现在ReflectiveFeign类中,这个里面就能看到熟悉的Proxy,也就是jdk动态代理
/**
* 创建绑定到目标的 API。由于这会调用反射,因此应注意缓存结果。
*/
@Override
public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) {
//创建configKey→SynchronousMethodHandler的映射,基本上是SynchronousMethodHandler,主要用于处理用户自定义的方法
Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
//存储处理用户定义的FeignClient接口中的default方法的handler
Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>();
List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>();
//遍历代理对象中的所有方法
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {
//如果是Object中的方法,跳过不处理
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
continue;
} else if(Util.isDefault(method)) {
//如果是default方法,则创建DefaultMethodHandler处理
DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);
defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);
methodToHandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
//用户自定义的方法了,此时从nameToHandler中拿出SynchronousMethodHandler进行映射
methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
//创建InvocationHandler 核心代理对象,代理逻辑都封装在该对象中
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
//jdk动态代理
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{target.type()}, handler);
for(DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}2.4 代理调用
远程代理调用核心逻辑在FeignInvocationHandler类的invoke方法中,首先判断是否为equals、hashcode或toString方法,是则直接调用target对象的这些方法。若不是,则根据创建过程中的configKey→MethodHandler的映射获取MethodHandler进行处理。
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if ("equals".equals(method.getName())) {
try {
Object
otherHandler =
args.length > 0 && args[0] != null ? Proxy.getInvocationHandler(args[0]) : null;
return equals(otherHandler);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
return false;
}
} else if ("hashCode".equals(method.getName())) {
return hashCode();
} else if ("toString".equals(method.getName())) {
return toString();
}
return dispatch.get(method).invoke(args);
}default方法:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable {
if(handle == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Default method handler invoked before proxy has been bound.");
}
return handle.invokeWithArguments(argv);
}自定义方法:核心逻辑,包含远程调用及重试机制。其中executeAndDecode会执行远程的http调用,同时也会进行http报文的解析,而catch块中会利用retryer进行重试。
@Override
public Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable {
RequestTemplate template = buildTemplateFromArgs.create(argv);
Retryer retryer = this.retryer.clone();
while (true) {
try {
return executeAndDecode(template);
} catch (RetryableException e) {
retryer.continueOrPropagate(e);
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRetry(metadata.configKey(), logLevel);
}
continue;
}
}
} Object executeAndDecode(RequestTemplate template) throws Throwable {
//构造请求对象
Request request = targetRequest(template);
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRequest(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, request);
}
Response response;
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
//client执行http远程调用,client可以是Apache HttpClient或者Feign封装的具有负载均衡能力的FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient
//或者RetryableFeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient,
//但这两个client的execute()方法底层最终会调用其中的delegate(即Apache HttpClient)执行http远程调用
response = client.execute(request, options);
// ensure the request is set. TODO: remove in Feign 10
response.toBuilder().request(request).build();
} catch (IOException e) {
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logIOException(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, e, elapsedTime(start));
}
throw errorExecuting(request, e);
}
//执行时长
long elapsedTime = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - start);
//解码
boolean shouldClose = true;
try {
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
response =
logger.logAndRebufferResponse(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, response, elapsedTime);
// ensure the request is set. TODO: remove in Feign 10
response.toBuilder().request(request).build();
}
if (Response.class == metadata.returnType()) {
if (response.body() == null) {
return response;
}
if (response.body().length() == null ||
response.body().length() > MAX_RESPONSE_BUFFER_SIZE) {
shouldClose = false;
return response;
}
// Ensure the response body is disconnected
byte[] bodyData = Util.toByteArray(response.body().asInputStream());
return response.toBuilder().body(bodyData).build();
}
if (response.status() >= 200 && response.status() < 300) {
if (void.class == metadata.returnType()) {
return null;
} else {
return decode(response);
}
} else if (decode404 && response.status() == 404 && void.class != metadata.returnType()) {
return decode(response);
} else {
throw errorDecoder.decode(metadata.configKey(), response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logIOException(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, e, elapsedTime);
}
throw errorReading(request, response, e);
} finally {
if (shouldClose) {
ensureClosed(response.body());
}
}
}重试机制:retryer.continueOrPropagate(e)
public void continueOrPropagate(RetryableException e) {
//重试次数
if (attempt++ >= maxAttempts) {
throw e;
}
//计算等待时间间隔
long interval;
if (e.retryAfter() != null) {
interval = e.retryAfter().getTime() - currentTimeMillis();
if (interval > maxPeriod) {
interval = maxPeriod;
}
if (interval < 0) {
return;
}
} else {
interval = nextMaxInterval();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(interval);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
//总等待时长
sleptForMillis += interval;
}





 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结