您现在的位置是:首页 >技术教程 >samba开发篇---顶级库下的General purpose库分析1网站首页技术教程
samba开发篇---顶级库下的General purpose库分析1
samba开发篇—general purpose库(top_level)
samba 是由source3,source4,top_level,Infrastructure components,Autogenerated code组成,本章主要是分析top_level下的General purpose库(lib)分析,由于samba下的虽然架构,层次清晰,但是很多库还是紧扣相连,一个库里伴随着另一个库里的调用。耦合性比较紧密。
文章目录
- samba开发篇---general purpose库(top_level)
- 前言
- 一、general purpose库介绍
- 二、general purpose 库(lib)源码分析
- 1.talloc库
- talloc 内存池介绍
- 性能
- 搭建环境
- talloc使用教程
- 1.零长度上下文
- 2.顶级上下文
- 3.释放上下文
- 4.talloc内存池的API函数
- 1.void* talloc_new (const void * ctx)
- 2.void* talloc(const void * ctx,#type)
- 3.char *talloc_strdup(const void * p , const char *t)
- 4.void *talloc_array(const void *ctx, #type, unsigned count)
- 5.char *talloc_asprintf(const void *t, const char *fmt, ...)
- 6.void *talloc_realloc(const void *ctx, void *ptr, #type, size_t count);
- 5.案例分析
- 上下文区别
- talloc 高级使用
- 2.smbconf库
- 总结
前言
本次讲解和开发,使用环境为ubuntu20.04,默认你已经用apt-get 安装了samba-413.17以及samba-dev,并且用git下载了samba源码。
一、general purpose库介绍
从框架篇讲解到,samba下的top_level 库下有很多库。
addns async_req compression dbwrap krb5_wrap ldb-samba mscat printer_driver README smbconf talloc tdb_wrap tevent torture util
afs audit_logging crypto fuzzing ldb messaging param pthreadpool replace socket tdb tdr texpect tsocket wscript_build
很多库其实对于普通开发者以及中小企业开发者来说基本用不到,很多目录里面代码其实也很久没有更新,当然其中一个原因是这套代码主打的就是oop思想,和内核代码开发方式相仿。
比较常用的目录如下:
- smbconf目录:主要还是提供了api,来管理创建删除共享等操作,当然还是有些貌似没开发,也许是没必要开发了。
- talloc目录:因为samba整体内存管理是以talloc内存池为主体,在官网有接口使用教程。
- util目录:一个通用的工具目录,封装了各种工具的api,相当实用,比如tevent事件的api的二次封装,talloc内存池的二次封装,还有一些字符串处理对比函数的封装,比如util下的charset目录,不过基本上代码可以参考,但是我本人是很少用到,但是这个目录也是为数不多比较重要的目录了,在samba里基本上很多解析和工具都是围绕这个工具库。
- param(?):这个目录说重要也重要,说不重要也不重要。很多里面的字符串处理函数都被注释了,很大一部分功能还是在source3下的param的目录的api。顶级库下的可能用处不是太大,不过目前还是解释一下关系,也有少部分函数在这里面也是有实现和展开的。
- tevent目录:这是个基于talloc内存池的一个事件的api,官网也有api接口说明,是为数不多的官方给出教程文档的,可恨可叹。有一些工具会用到,比如smbclient命令源码里就有。
- replace目录:我个人也用不到,但是samba源码里集成了封装了很多外部字符串处理工具,甚至一些线程调用的工具,时间处理的工具的封装。所以这是samba里比较重要的。调这里面库不如直接一个<time.h>来的实在?<strptime.h>等等。
剩下感觉也说不出来什么了,什么打印机驱动,线程池,tdb_wrap,tscocket,基本上很多都是用不到的。
二、general purpose 库(lib)源码分析
1.talloc库
talloc下其实在通过apt-get install 安装后,这个目录就已经移到标准库目录下了。
talloc 内存池介绍
Talloc 是一个分层的、引用计数的内存池系统,带有析构函数。它建立在 C 标准库之上,它定义了一组实用函数,这些函数完全简化了数据的分配和释放,特别是对于包含许多动态分配的元素(如字符串和数组)的复杂结构。
这个库的主要目标是:消除为每个复杂结构创建清理函数的需要,提供分配内存块的逻辑组织,并减少在长时间运行的应用程序中创建内存泄漏的可能性。所有这一切都是通过在 talloc 上下文的分层结构中分配内存来实现的,这样释放一个上下文就会递归地释放它的所有后代。
性能
talloc总体使用在性能方面和malloc差距百分8左右,但是在samba这里一些特殊的应用场景,甚至效率比malloc还要快很多。
搭建环境
ubuntu20.04下安装samba-dev,samba即可
sudo apt-get install samba samba-dev
talloc使用教程
talloc api教程在samba官网上有文档,使用方法很全面,我这里是介绍常用的使用方法以及整合官方的文档集合成一个使用说明。
talloc 上下文是这个库中最重要的部分,负责这个内存分配器的每一个特性。它是一个逻辑单元,表示由 talloc 管理的内存空间。
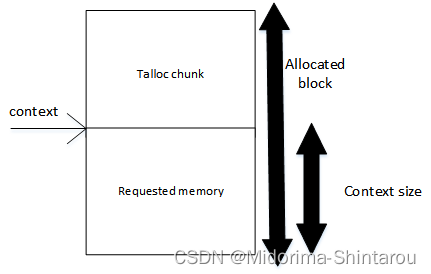
当我们为很多结构体,甚至结构体数组分配内存同时,malloc分配会导致一个弊端,只能一个个去释放,但是如果用了talloc内存池,通过这种分层的引用计数的方式,可以直接释放当前的talloc上下文,就能把整个基于当前talloc上下文分配的内存全部释放出去。
1.零长度上下文
如下是申请一个零长度的上下文:
//TALLOC_CTX 实际上是void类型
//这种类型只是一个别名,void仅出于语义原因而存在
TALLOC_CTX *tmp_ctx;
/* new zero-length top level context */
tmp_ctx = talloc_new(NULL);
if (tmp_ctx == NULL) {
return -1;
}
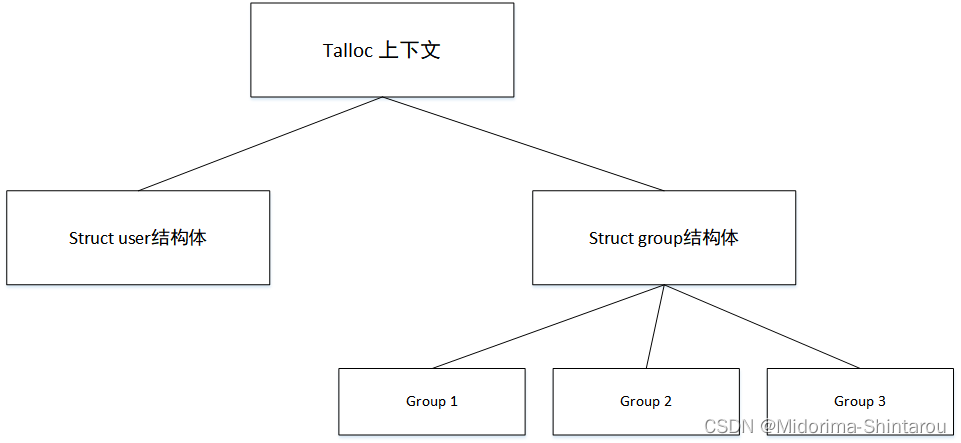
2.顶级上下文
如下是申请一个顶级上下文:
struct user {
uid_t uid;
char *username;
size_t num_groups;
char **groups;
};
/* create new top level context */
struct user *user = talloc(NULL, struct user);
3.释放上下文
释放上下文的操作如下:
TALLOC_FREE(tmp_ctx);
//也可以用talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
两者区别是TALLOC_FREE是封装了talloc_free的一个宏。
**
* @brief Free a talloc chunk and NULL out the pointer.
*
* TALLOC_FREE() frees a pointer and sets it to NULL. Use this if you want
* immediate feedback (i.e. crash) if you use a pointer after having free'ed
* it.
*
* @param[in] ctx The chunk to be freed.
*/
#define TALLOC_FREE(ctx) do { if (ctx != NULL) { talloc_free(ctx); ctx=NULL; } } while(0)
4.talloc内存池的API函数
配合上下文使用的内存分配API
1.void* talloc_new (const void * ctx)
分配一个新的 0 大小的 talloc 块。
这是一个实用程序宏,它创建一个新的内存上下文,挂在现有上下文之外,
自动将其命名为“talloc_new: location”,其中 location 是调用它的源代码行。
它对于创建新的临时工作环境特别有用。
Parameters:
[in] ctx The talloc parent context.
Returns:
A new talloc chunk, NULL on error.
TALLOC_CTX *tmp_ctx = talloc_new(NULL);
2.void* talloc(const void * ctx,#type)
创建一个新的 talloc 上下文。
talloc ()宏是 talloc 库的核心。
它需要一个内存上下文和一个类型,并返回一个指向给定类型的新内存区域的指针。
返回的指针本身就是一个 talloc 上下文,
因此如果愿意,可以将它用作对 talloc 的更多调用的上下文参数。
返回的指针是提供的上下文的“child”。
这意味着如果talloc_free()上下文那么新的child也会消失。或者,您可以只释放child。
TALLOC_CTX *tmp_ctx = talloc_new(NULL);
unsigned int *a, *b;
a = talloc(tmp_ctx, unsigned int);
b = talloc(a, unsigned int);
3.char *talloc_strdup(const void * p , const char *t)
将一个字符串复制到一个 talloc 块中。
这个函数其实和strdup函数类似,只不过talloc_strdup会多一个选项,让你填入一个
talloc分配的上下文。
TALLOC_CTX *tmp_ctx = talloc_new(NULL);
char *p;
p = talloc_strdup(tmp_ctx,"hello world");
4.void *talloc_array(const void *ctx, #type, unsigned count)
talloc_array函数用于在给定上下文中分配一个数组,并返回一个指向数组的指针;
TALLOC_CTX *tmp_ctx = talloc_new(NULL);
if (tmp_ctx == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.
");
return 1;
}
int *arr = talloc_array(tmp_ctx, int, 5);
if (arr == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.
");
talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
return 1;
}
5.char *talloc_asprintf(const void *t, const char *fmt, …)
talloc_asprintf函数是一个便捷函数,用于在给定上下文中分配一个缓冲区并格式化一个字符串,类似于标准C库中的asprintf函数
其中,t参数表示分配的缓冲区应该归属于哪个上下文;fmt参数是一个格式化字符串,支持与printf函数相同的格式说明符;…表示可变参数列表,用于传递给格式化字符串的参数。
TALLOC_CTX *tmp_ctx = talloc_new(NULL);
if (tmp_ctx == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.
");
return 1;
}
char *str = talloc_asprintf(tmp_ctx, "Hello, %s!", "world");
if (str == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.
");
talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
return 1;
}
6.void *talloc_realloc(const void *ctx, void *ptr, #type, size_t count);
talloc_realloc函数是用于在给定的上下文中重新分配先前分配的内存块的函数;
就是类似于realloc函数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <talloc.h>
int main(void) {
TALLOC_CTX *tmp_ctx = talloc_new(NULL);
if (tmp_ctx == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.
");
return 1;
}
void *ptr = talloc_realloc(tmp_ctx, NULL, char, 1);
if (ptr == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.
");
talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
return 1;
}
ptr = talloc_realloc(tmp_ctx, ptr, char, 2);
if (ptr == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to reallocate memory.
");
talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
return 1;
}
char *buf = ptr;
buf[0] = 'A';
buf[1] = 'B';
printf("%c%c
", buf[0], buf[1]);
talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
return 0;
}
编译
gcc xxx.c -ltalloc
5.案例分析
1.零长度上下文案例
如下图是一个使用零长度上下文来进行生产环境的测试代码
vim zero_length.c
将如下代码copy到zero_length.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <talloc.h>
struct person {
char *name;
int age;
};
int main(void) {
TALLOC_CTX *tmp_ctx = talloc_new(NULL);
if (tmp_ctx == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.
");
return 1;
}
struct person *p1 = talloc(tmp_ctx, struct person);
if (p1 == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.
");
talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
return 1;
}
p1->name = talloc_strdup(p1, "Alice");
p1->age = 30;
struct person *p2 = talloc(tmp_ctx, struct person);
if (p2 == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.
");
talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
return 1;
}
p2->name = talloc_strdup(p2, "Bob");
p2->age = 25;
printf("%s is %d years old.
", p1->name, p1->age);
printf("%s is %d years old.
", p2->name, p2->age);
talloc_free(tmp_ctx);
return 0;
}
编译
gcc zero_length.c -ltalloc
执行结果
Alice is 30 years old.
Bob is 25 years old.
案例内存分析
内存分析工具使用的是valgrind工具,可以通过apt自行下载
valgrind ./a.out
Alice is 30 years old.
Bob is 25 years old.
==5203==
==5203== HEAP SUMMARY:
==5203== in use at exit: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==5203== total heap usage: 6 allocs, 6 frees, 1,546 bytes allocated
==5203==
==5203== All heap blocks were freed -- no leaks are possible
==5203==
==5203== For lists of detected and suppressed errors, rerun with: -s
==5203== ERROR SUMMARY: 0 errors from 0 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)
可以看到,我们这里对tmp_ctx上下文直接释放内存,下面所有结构体的内存都被释放了。
2.顶级上下文案例
如下图是一个创建顶级上下文的案例:
vim top_ctx.c
将如下代码copy到top_ctx.c
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <talloc.h>
struct user {
int uid;
char *username;
int num_groups;
char **groups;
};
int main() {
struct user *user = talloc(NULL, struct user);
if (user == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory
");
return 1;
}
user->uid = 1000;
user->num_groups = 3;
user->username = talloc_strdup(user, "Test user");
if (user->username == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory
");
return 1;
}
user->groups = talloc_array(user, char *, user->num_groups);
if (user->groups == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory
");
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < user->num_groups; i++) {
user->groups[i] = talloc_asprintf(user->groups, "Test group %d", i+1);
if (user->groups[i] == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory
");
return 1;
}
}
printf("User ID: %d
", user->uid);
printf("Username: %s
", user->username);
printf("Number of groups: %d
", user->num_groups);
for (int i = 0; i < user->num_groups; i++) {
printf("Group %d: %s
", i+1, user->groups[i]);
}
talloc_free(user);
return 0;
}
编译
gcc top_ctx.c -ltalloc
执行结果
User ID: 1000
Username: Test user
Number of groups: 3
Group 1: Test group 1
Group 2: Test group 2
Group 3: Test group 3
案例内存分析
内存分析工具使用的是valgrind工具,可以通过apt自行下载
valgrind ./a.out
==5835== Memcheck, a memory error detector
==5835== Copyright (C) 2002-2017, and GNU GPL'd, by Julian Seward et al.
==5835== Using Valgrind-3.15.0 and LibVEX; rerun with -h for copyright info
==5835== Command: ./a.out
==5835==
User ID: 1000
Username: Test user
Number of groups: 3
Group 1: Test group 1
Group 2: Test group 2
Group 3: Test group 3
==5835==
==5835== HEAP SUMMARY:
==5835== in use at exit: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==5835== total heap usage: 7 allocs, 7 frees, 1,705 bytes allocated
==5835==
==5835== All heap blocks were freed -- no leaks are possible
==5835==
==5835== For lists of detected and suppressed errors, rerun with: -s
==5835== ERROR SUMMARY: 0 errors from 0 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)
可以看到我们仅仅释放顶级上下文,其我们在顶级上下文下申请的内存全部被释放。
上下文区别
零长度上下文和顶级上下文,通过官方api文档来看,看起来没有什么大的区别。一个是通过TALLOC_CTX *申请一个上下文tmp_ctx。然后通过调用函数来给这个tmp_ctx成为一个零长度上下文。顶级上下文则是用任何定义的指针,结构体指针,字符指针等等,通过放入一个NULL类型的上下文,然后让这个指针成为一个顶级上下文。
当然现在我们看看上下文是怎么分配内存的
struct user *user = talloc(NULL, struct user);
TALLOC_CTX *tmp_ctx = talloc_new(NULL);
这两个调用一个是创建顶级上下文,一个是创建零长度上下文。通过追代码得知
#define talloc_new(ctx) talloc_named_const(ctx, 0, "talloc_new: " __location__)
#define talloc(ctx, type) (type *)talloc_named_const(ctx, sizeof(type), #type)
从这里可以看出,只不过talloc_named_const时候第二个参数是传入了一个是0的大小,一个是sizeof(type)的大小,第三个参数则是传入了个字符串。
talloc_named_const 原型
tatic inline void *_talloc_named_const(const void *context, size_t size, const char *name)
{
void *ptr;
struct talloc_chunk *tc;
ptr = __talloc(context, size, &tc);
if (unlikely(ptr == NULL)) {
return NULL;
}
_tc_set_name_const(tc, name);
return ptr;
}
可以看到name这个并不会影响到talloc申请内存,则是调用了 _tc_set_name_const(tc, name);
具体 _tc_set_name_const(tc, name);这个函数原型我这里貌似追不到,可能这个函数用了类似的##这种方法来命令函数,也就是传入一个标识符然后来隐示的声明函数。当然这个我后面也会涉及到。
接下来我们看看__talloc原型
__talloc原型
static inline void *__talloc(const void *context,
size_t size,
struct talloc_chunk **tc)
{
return __talloc_with_prefix(context, size, 0, tc);
}
__talloc也是返回了一个__talloc_with_prefix(context, size, 0, tc);
__talloc_with_prefix原型
static inline void *__talloc_with_prefix(const void *context,
size_t size,
size_t prefix_len,
struct talloc_chunk **tc_ret)
{
struct talloc_chunk *tc = NULL;
struct talloc_memlimit *limit = NULL;
size_t total_len = TC_HDR_SIZE + size + prefix_len;
struct talloc_chunk *parent = NULL;
if (unlikely(context == NULL)) {
context = null_context;
}
if (unlikely(size >= MAX_TALLOC_SIZE)) {
return NULL;
}
if (unlikely(total_len < TC_HDR_SIZE)) {
return NULL;
}
if (likely(context != NULL)) {
parent = talloc_chunk_from_ptr(context);
if (parent->limit != NULL) {
limit = parent->limit;
}
tc = tc_alloc_pool(parent, TC_HDR_SIZE+size, prefix_len);
}
if (tc == NULL) {
uint8_t *ptr = NULL;
union talloc_chunk_cast_u tcc;
/*
* Only do the memlimit check/update on actual allocation.
*/
if (!talloc_memlimit_check(limit, total_len)) {
errno = ENOMEM;
return NULL;
}
ptr = malloc(total_len);
if (unlikely(ptr == NULL)) {
return NULL;
}
tcc = (union talloc_chunk_cast_u) { .ptr = ptr + prefix_len };
tc = tcc.chunk;
tc->flags = talloc_magic;
tc->pool = NULL;
talloc_memlimit_grow(limit, total_len);
}
tc->limit = limit;
tc->size = size;
tc->destructor = NULL;
tc->child = NULL;
tc->name = NULL;
tc->refs = NULL;
if (likely(context != NULL)) {
if (parent->child) {
parent->child->parent = NULL;
tc->next = parent->child;
tc->next->prev = tc;
} else {
tc->next = NULL;
}
tc->parent = parent;
tc->prev = NULL;
parent->child = tc;
} else {
tc->next = tc->prev = tc->parent = NULL;
}
*tc_ret = tc;
return TC_PTR_FROM_CHUNK(tc);
}
- 首先判断上下文是否为NULL,如果为NULL则将上下文指向全局的NULL context。
- 判断请求分配的内存大小是否超过了talloc的最大限制。
- 计算talloc chunk需要的总内存大小,其中包括chunk头部大小、请求分配的内存大小以及前缀(如果有的话)。
- 如果上下文非NULL,则将其转换为talloc chunk,并获取其相应的内存限制。
- 调用tc_alloc_pool()函数从上下文的内存池中获取内存,如果内存池中没有足够的内存,则需要调用malloc()函数从系统中获取内存。
- 如果调用malloc()分配内存,则需要检查内存限制并更新内存使用情况。
- 初始化新的talloc chunk的各个成员,并将其添加到相应的上下文中。
- 返回新的talloc chunk的指针。
上下文区别总结
其实从这里分析下来可以看出来,顶级上下文和零长度上下文区别就在于_talloc_named_const(context, size, name);传入的size大小,以及name的字符串
_tc_set_name_const(tc, name);这里则是传入name字符串,进行一个标记。所以可以得知为什么零长度上下文会放入一个 "talloc_new: " __location__这个字符串。我猜测这里可能是用于某些魔数操作有关和debug方面。因为我也追了一些类似调用这个函数的应用。
talloc 高级使用
talloc除了申请上下文使用,还有很多其他功能,比如
- 窃取上下文
- 动态类型系统
- 使用析构函数
- 内存池
- 调试
- 使用带有 talloc 的线程
剩下我会专门开一个talloc内存池的专栏的教程来展示。
2.smbconf库
smbconf库介绍
smb.conf是Samba的主要配置文件,它描述了Samba服务器的配置和共享资源的配置信息。Samba提供了一个smbconf库,可以用来读取和修改smb.conf文件。该库提供了一系列的API,可以方便地读取、解析和修改smb.conf配置文件的参数。可以说它是一个方便管理Samba服务器的工具,可以让管理员更加容易地管理Samba服务器并且定制化自己的配置。
环境搭建
smbconf安装如下
使用ubuntu20.04
sudo apt-get install samba samba-dev
安装完成后,include头文件路径如下
/usr/include/samba-4.0
charset.h credentials.h dcerpc.h dcesrv_core.h gen_ndr lookup_sid.h ndr netapi.h passdb.h rpc_common.h share.h smbconf.h smbldap.h time.h tsocket_internal.h util_ldb.h
core data_blob.h dcerpc_server.h domain_credentials.h ldb_wrap.h machine_sid.h ndr.h param.h policy.h samba smb2_lease_struct.h smb_ldap.h tdr.h tsocket.h util wbclient.h
安装时候自然也是自动链接了需要的动态库,动态库路径如下
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 25 Jan 26 22:03 libsamba-passdb.so -> libsamba-passdb.so.0.28.0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 22 Jan 26 22:03 libsamba-util.so -> libsamba-util.so.0.0.1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 15 Jan 26 22:03 libsmbconf.so -> libsmbconf.so.0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 18 Nov 2 2021 libtalloc.so -> libtalloc.so.2.3.1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 18 Nov 2 2021 libtalloc.so -> libtalloc.so.2.3.1
当然只要关注这个目录下的smbconf.h就可以了,因为里面的文件除了一些安装后的头文件,还有我本人自己放进去的一些头文件,至于为什么这么做,后续会说明。
smbconf库分析
我们是调用smbconf.h里面的库文件来使用,既然又是调库操作,为什么不看文档呢。首先再次为samba团队感到心痛,以及感谢。samba团队官方给的开发资料寥寥无几,就算特别重要的开发,也没有相关文档,据我所知,我只了解到vfs模块的开发是给了教程,以及tevent事件的api教程和talloc内存池教程。
smbconf.h文件(如何调用smbconf_create_share)
从这个文件里可以可以看到,有很多smbconf_xxx的函数名字,这边不用猜也知道了是修改smb.conf文件的api,通过这些api我们来用C语言实现配置文件的增删改查。
我列举如下一些
/**
* @brief Add a service if it does not already exist.
* @param[in] ctx The smbconf context to use.
* @param[in] servicename The name of the service to add.
* @return SBC_ERR_OK on success, a corresponding sbcErr if an
* error occurred.
*/
sbcErr smbconf_create_share(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx, const char *servicename);
这个是一个创建共享的api。但是光靠一个smbconf.h貌似是做不了什么,因为怎么操作都是报段错误。这时候就是需要分析其原理了,我们来看samba 根目录下的lib目录里面的smbconf目录。
samba 下的lib下的smbconf目录
在lib/smbconf/目录下有如下几个文件
smbconf.c smbconf.h smbconf_private.h smbconf_txt.c smbconf_txt.h smbconf_util.c wscript_build
现在就可以从smbconf.c文件一个个开始分析.
smbconf.c
从smbconf.c里面可以看出一些类似oop模块思想。
从如下图可以看出是通过ctx指向ops然后ops调用了create_share。那此情此前可以看出这个一定是一个用结构体封装了一些函数指针进行模块化封装
/**
* Add a service if it does not already exist.
*/
sbcErr smbconf_create_share(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx,
const char *servicename)
{
if ((servicename != NULL) && smbconf_share_exists(ctx, servicename)) {
return SBC_ERR_FILE_EXISTS;
}
return ctx->ops->create_share(ctx, servicename);
}
smbconf_private.h
通过追这个 struct smbconf_ctx结构体可以追到在smbconf_private.h里面有这个结构体的声明。
struct smbconf_ops {
sbcErr (*init)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx, const char *path);
int (*shutdown)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx);
bool (*requires_messaging)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx);
bool (*is_writeable)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx);
sbcErr (*open_conf)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx);
int (*close_conf)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx);
void (*get_csn)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx, struct smbconf_csn *csn,
const char *service, const char *param);
sbcErr (*drop)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx);
sbcErr (*get_share_names)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx,
TALLOC_CTX *mem_ctx,
uint32_t *num_shares,
char ***share_names);
bool (*share_exists)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx, const char *service);
sbcErr (*create_share)(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx, const char *service);
...省略
};
那既然这样,代码逻辑就清晰可见了。我们只需要找到这个使用这个结构体的地方就能很快分析代码如何使用了。
smbconf_txt.c
从这里我们可以看到封装了一些函数模块,并且使用struct smbconf_ops来定义。
static struct smbconf_ops smbconf_ops_txt = {
.init = smbconf_txt_init,
.shutdown = smbconf_txt_shutdown,
.requires_messaging = smbconf_txt_requires_messaging,
.is_writeable = smbconf_txt_is_writeable,
.open_conf = smbconf_txt_open,
.close_conf = smbconf_txt_close,
.get_csn = smbconf_txt_get_csn,
.drop = smbconf_txt_drop,
.get_share_names = smbconf_txt_get_share_names,
.share_exists = smbconf_txt_share_exists,
.create_share = smbconf_txt_create_share,
省略...
};
接着看看函数实现原型,如下图,函数原型里只有一个return,以return SBC_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED;通过这返回值字面意思可以看出是不支持的意思,除了下面的展示的,大家可自行查看其他函数原型。
/**
* Add a service if it does not already exist
*/
static sbcErr smbconf_txt_create_share(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx,
const char *servicename)
{
return SBC_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED;
}
既然现在陷入死胡同了,从这里应该是得不到结论了。那现在看来这个实现可能在内部source3下的通用lib库下的smbconf目录
source3下的lib下的smbconf目录
可以看到如下几个文件
smbconf_init.c smbconf_init.h smbconf_reg.c smbconf_reg.h testsuite.c
从这里可以看出如何使用smbconf.h使用大概要从这里入手了,因为我们可以看到有一个init.c。
smbconf_init.c
这个文件里面只有一个函数实现,就是smbconf_init函数,为了整体看起来简短精要,我复制了重要的部分,从如下可以看出,有两个init函数,一个是smbconf_init_reg,一个是smbconf_init_txt。
sbcErr smbconf_init(TALLOC_CTX *mem_ctx, struct smbconf_ctx **conf_ctx,
const char *source)
{
省略.....
if (strequal(backend, "registry") || strequal(backend, "reg")) {
err = smbconf_init_reg(mem_ctx, conf_ctx, path);
} else if (strequal(backend, "file") || strequal(backend, "txt")) {
err = smbconf_init_txt(mem_ctx, conf_ctx, path);
} else if (sep == NULL) {
err = smbconf_init_txt(mem_ctx, conf_ctx, backend);
} else {
err = smbconf_init_txt(mem_ctx, conf_ctx, source);
省略.....
smbconf_init_txt原型
实现可以看出,对smbconf_ops_txt结构体变量进行了取址,也就是我们一开始的顶级库下的lib库下的smbconf里面的smbconf_txt.c的函数,那么另外一个就显而易见了。所以从这里,我们需要调用source3下lib下smbconf下的init函数来初始化
static struct smbconf_ops smbconf_ops_txt = {
函数指针声明,这部分省略
};
sbcErr smbconf_init_txt(TALLOC_CTX *mem_ctx,
struct smbconf_ctx **conf_ctx,
const char *path)
{
sbcErr err;
err = smbconf_init_internal(mem_ctx, conf_ctx, path, &smbconf_ops_txt);
if (!SBC_ERROR_IS_OK(err)) {
return err;
}
smbconf_init_reg原型
通过smbconf_init_reg函数可以看到,用smbconf_ops结构体初始化了一个smbconf_ops_reg。然后init调用时候对这个结构体进行取址。通过结构体也可以了解,这个create_share调用了smbconf_reg_create_share
struct smbconf_ops smbconf_ops_reg = {
.init = smbconf_reg_init,
.shutdown = smbconf_reg_shutdown,
省略..复制时候留下我们需要的使用的函数案例
.create_share = smbconf_reg_create_share
以下省略..
};
/**
* initialize the smbconf registry backend
* the only function that is exported from this module
*/
sbcErr smbconf_init_reg(TALLOC_CTX *mem_ctx, struct smbconf_ctx **conf_ctx,
const char *path)
{
return smbconf_init_internal(mem_ctx, conf_ctx, path, &smbconf_ops_reg);
}
smbconf_reg_create_share原型
现在逻辑就清晰可见,我们需要调用的函数在samba/source3/lib/smbconf下的smbconf_reg.c文件里面,这里有很明确的创建共享的函数实现
/**
* Add a service if it does not already exist - registry version
*/
static sbcErr smbconf_reg_create_share(struct smbconf_ctx *ctx,
const char *servicename)
{
sbcErr err;
struct registry_key *key = NULL;
if (servicename == NULL) {
return SBC_ERR_OK;
}
err = smbconf_reg_create_service_key(talloc_tos(), ctx,
servicename, &key);
talloc_free(key);
return err;
}
调用smbconf_create_share总结
具体如何使用请看smbconf使用章节,也就是下一节
看到这里,可以得出一个结论,调用smbconf_create_share,则需要调用smbconf_init函数,通过这个init函数分配上下文。看使用方式,应该是要用registry的方式,也就是这个库的初衷就不是给用txt文本方式提供的接口。如果对registry和txt两种配置方式不明确可以去看samba的两种管理方式
sbcErr smbconf_init(TALLOC_CTX *mem_ctx, struct smbconf_ctx **conf_ctx,
const char *source)
同时这个函数调用需要用到talloc内存池,因为有一个传入的参数是TALLOC_CTX *mem_ctx;那同时介绍一个samba内部自己二次封装talloc api 的函数,也就是在通用库下util目录下的talloc_stack.c
这个文件在如下这个目录下
samba/lib/util/talloc_stack.c
扩展 分析:talloc_stack.c/h
这里面有两个函数提及一个是talloc_stackframe(),一个是talloc_tos()
talloc_stackframe();
函数意义是创建一个新的堆栈帧上下文,创建一个新的talloc堆栈框架。
当被释放时,它会释放在此之后创建的所有堆栈帧
未显式释放
函数原型如下:
TALLOC_CTX *_talloc_stackframe(const char *location);
使用方法如下:
TALLOC_CTX* tmp_ctx = talloc_stackframe();
talloc_tos();
talloc_tos() 函数用于获取当前线程中的栈顶上下文。它返回的是一个 TALLOC_CTX 类型的指针,指向当前线程栈中的顶级上下文。
在多线程环境中,每个线程都有自己的栈帧,因此每个线程都可以有自己的栈顶上下文。talloc_tos() 函数获取的是当前线程的栈顶上下文,因此可以用于在当前线程中分配内存。
TALLOC_CTX *_talloc_tos(const char *location);
使用方法如下:
TALLOC_CTX* tmp_ctx = talloc_tos();
可以这样理解,talloc_tos会获取当前线程最近的一个上下文来使用,也就是包括全局变量,如果你申请了一个全局变量上下文,调用这个函数会自动把tmp_ctx分配到全局上下文的下面一级,所以如果一定要调用talloc_tos,必须在当前模块函数内创建一个零长度上下文或者顶级上下文,这样调用的talloc_tos会自动使用当前函数内的上下文作为它第一级上下文。
smbconf库调用(smbconf_create_share的案例)
本节主要实现使用smbconf.h文件里面的创建共享功能。
搭建samba 注册表配置环境
如果不懂什么是注册表请看这里,注册表配置
不过步骤这里也再教一遍
sudo vim /etc/samba/smb.conf
把下面配置放到smb.conf里面
[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP
server string = %h server (Samba, Ubuntu)
security = user
unix charset = utf8
dos charset = cp850
log file = /var/log/samba/%m.log
max log size = 1000
logging = file
log level = 1
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
server role = standalone server
obey pam restrictions = yes
unix password sync = yes
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
passwd chat = *Entersnews*spassword:* %n
*Retypesnews*spassword:* %n
*passwordsupdatedssuccessfully* .
pam password change = yes
map to guest = bad user
config backend = registry
sudo vim test
将下面文本放进去
[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP
server string = %h server (Samba, Ubuntu)
security = user
unix charset = utf8
dos charset = cp850
log file = /var/log/samba/%m.log
max log size = 1000
logging = file
log level = 1
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
server role = standalone server
obey pam restrictions = yes
unix password sync = yes
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
passwd chat = *Entersnews*spassword:* %n
*Retypesnews*spassword:* %n
*passwordsupdatedssuccessfully* .
pam password change = yes
map to guest = bad user
执行,导入全局配置到注册表里面
sudo net conf import test
调用smbconf.h的api
代码如下:
#include <talloc.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <samba-4.0/smbconf.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define talloc_stackframe() _talloc_stackframe(__location__)
TALLOC_CTX *_talloc_stackframe(const char *location);
bool lp_load_global(const char *file_name);
const char *get_dyn_CONFIGFILE();
sbcErr smbconf_init(TALLOC_CTX *mem_ctx, struct smbconf_ctx **conf_ctx,
const char *source);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret = 0;
struct smbconf_ctx *conf_ctx = NULL;
TALLOC_CTX *mem_ctx = talloc_stackframe();
ret = lp_load_global(get_dyn_CONFIGFILE());
if (!ret) {
printf("Failed to load smb.conf
");
talloc_free(mem_ctx);
return 1;
}
ret = smbconf_init(mem_ctx, &conf_ctx, "reg:");
if (ret != 0) {
printf("Failed to initialize smbconf_ctx
");
talloc_free(mem_ctx);
return 1;
}
ret = smbconf_create_share(conf_ctx, "home");
if (ret != 0) {
printf("Failed to create share
");
talloc_free(mem_ctx);
return 1;
}
talloc_free(mem_ctx);
return 0;
}
这里我就不过多说明,为什么要声明这么多函数在test.c里面了
vim ./test.c
将上面代码copy进去。
编译
gcc test.c -ltalloc -lsmbconf -lsamba-util
sudo net conf list
可以看到现在只有一个global全局配置
[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP
server string = %h server (Samba, Ubuntu)
security = user
unix charset = utf8
dos charset = cp850
log file = /var/log/samba/%m.log
max log size = 1000
logging = file
log level = 1
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
server role = standalone server
obey pam restrictions = yes
unix password sync = yes
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
passwd chat = *Entersnews*spassword:* %n
*Retypesnews*spassword:* %n
*passwordsupdatedssuccessfully* .
pam password change = yes
map to guest = bad user
然后执行sudo ./a.out
接下来可以看到这里创建了一个空白的共享
[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP
server string = %h server (Samba, Ubuntu)
security = user
unix charset = utf8
dos charset = cp850
log file = /var/log/samba/%m.log
max log size = 1000
logging = file
log level = 1
panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d
server role = standalone server
obey pam restrictions = yes
unix password sync = yes
passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u
passwd chat = *Entersnews*spassword:* %n
*Retypesnews*spassword:* %n
*passwordsupdatedssuccessfully* .
pam password change = yes
map to guest = bad user
[home]
这时候就代表程序完美执行了,现在测试下内存泄漏。
内存泄漏检测
执行如下:
valgrind ./a.out
lp_load_ex: changing to config backend registry
Failed to create share
==8575==
==8575== HEAP SUMMARY:
==8575== in use at exit: 66,595 bytes in 146 blocks
==8575== total heap usage: 2,907 allocs, 2,761 frees, 579,929 bytes allocated
==8575==
==8575== LEAK SUMMARY:
==8575== definitely lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==8575== indirectly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==8575== possibly lost: 66,331 bytes in 142 blocks
==8575== still reachable: 264 bytes in 4 blocks
==8575== suppressed: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==8575== Rerun with --leak-check=full to see details of leaked memory
==8575==
==8575== For lists of detected and suppressed errors, rerun with: -s
==8575== ERROR SUMMARY: 0 errors from 0 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)
从这里可以看出,为什么会出现少量内存没有释放呢,那继续再次深度检测
执行
valgrind --leak-check=full ./a.out
其余部分就省略了,因为问题所在就在这个lp_load_global函数上
==8821== 4,030 bytes in 38 blocks are possibly lost in loss record 62 of 63
==8821== at 0x483B7F3: malloc (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/valgrind/vgpreload_memcheck-amd64-linux.so)
==8821== by 0x4876FC3: talloc_strdup (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libtalloc.so.2.3.1)
==8821== by 0x4DDFFB1: debug_add_class (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/samba/libsamba-debug.so.0)
==8821== by 0x4DDFE7B: ??? (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/samba/libsamba-debug.so.0)
==8821== by 0x4DE16C4: debug_parse_levels (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/samba/libsamba-debug.so.0)
==8821== by 0x4D9F024: lpcfg_do_global_parameter (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libsamba-hostconfig.so.0.0.1)
==8821== by 0x493F18D: tini_parse (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libsamba-util.so.0.0.1)
==8821== by 0x493903E: pm_process (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libsamba-util.so.0.0.1)
==8821== by 0x48E6EEC: ??? (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libsmbconf.so.0)
==8821== by 0x48E7873: lp_load_global (in /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libsmbconf.so.0)
==8821== by 0x10929B: main (in /fy/project/linux/project/test/samba_api/smbconf/a.out)
lp_load_global是加载当前注册表的配置,这样才能执行剩下的smbconf的api函数。这个函数目前博主也没有分析到位,不过也就只有这一个函数会出现内存没有释放。至于具体内存分析,博主会在smbconf.h库的整体调用和使用的时候会继续说明。
使用总结
目前本节介绍了如何使用smbconf.h的接口库的代码案例,因为讲解的实在是太长了,所以给了一个体验论证的代码来使用及测试。具体为什么要声明一堆没有用过的函数,会在后面专门讲解smbconf库的使用。
总结
本章讲解了samba开发篇,顶级库下的general purpose库的分析。






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结