您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >( “树” 之 BST) 109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树 ——【Leetcode每日一题】网站首页学无止境
( “树” 之 BST) 109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树 ——【Leetcode每日一题】
简介( “树” 之 BST) 109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树 ——【Leetcode每日一题】
二叉查找树(BST):根节点大于等于左子树所有节点,小于等于右子树所有节点。
二叉查找树中序遍历有序。
109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
给定一个单链表的头节点 head ,其中的元素 按升序排序 ,将其转换为高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差不超过 1。
示例 1:
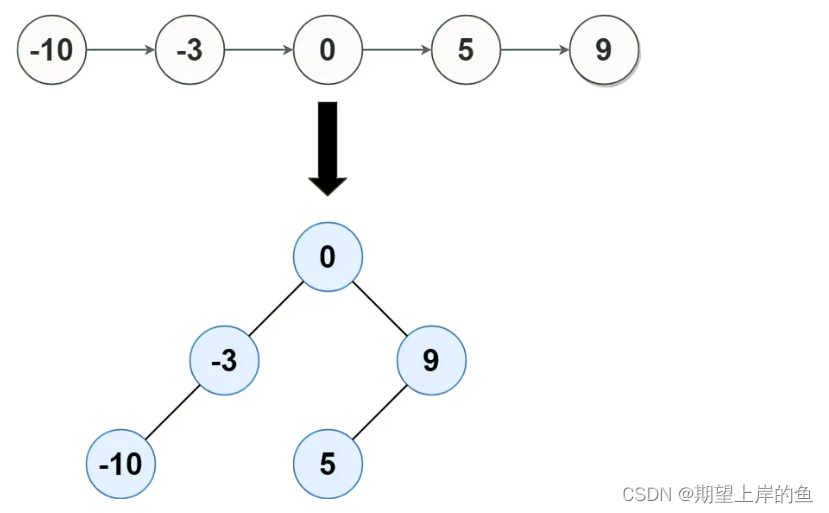
输入: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
解释: 一个可能的答案是[0,-3,9,-10,null,5],它表示所示的高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
示例 2:
输入: head = []
输出: []
提示:
- head 中的节点数在 [ 0 , 2 ∗ 1 0 4 ] [0, 2 * 10^4] [0,2∗104] 范围内
- − 1 0 5 < = N o d e . v a l < = 1 0 5 -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5 −105<=Node.val<=105
思路:分治 + 递归
法一:
先将链表转化为数组,具体思路为:108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
法二:快慢指针
和法一类似,我们使用快慢指针要找到有序链表的中位数,以该中位数为根节点,并将该中位数左右两边分成两个子有序链表,再在子有序链表找中位数,以此类推递归。
代码:(Java、C++)
法一:
Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
while(head != null){
nums.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
TreeNode root = toBST(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
return root;
}
public TreeNode toBST(List<Integer> nums, int be, int ed){
if(be > ed) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums.get(be + (ed - be) / 2));
root.left = toBST(nums, be, be + (ed - be) / 2 - 1);
root.right = toBST(nums, be + (ed - be) / 2 + 1, ed);
return root;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> nums;
while(head != nullptr){
nums.push_back(head->val);
head = head->next;
}
TreeNode* root = toBST(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* toBST(vector<int>& nums, int be, int ed){
if(be > ed) return nullptr;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[be + (ed - be) / 2]);
root->left = toBST(nums, be, be + (ed - be) / 2 - 1);
root->right = toBST(nums, be + (ed - be) / 2 + 1, ed);
return root;
}
};
法二:快慢指针
Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
if(head.next == null) return new TreeNode(head.val);
ListNode preMid = getPreMid(head);
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preMid.next.val);
root.right = sortedListToBST(preMid.next.next);
preMid.next = null;
root.left = sortedListToBST(head);
return root;
}
public ListNode getPreMid(ListNode head){
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return pre;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;
if(head->next == nullptr) return new TreeNode(head->val);
ListNode* preMid = getPreMid(head);
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preMid->next->val);
root->right = sortedListToBST(preMid->next->next);
preMid->next = nullptr;
root->left = sortedListToBST(head);
return root;
}
ListNode* getPreMid(ListNode* head){
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* pre = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr){
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return pre;
}
};
运行结果:
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n),其中
n是链表的长度。 - 空间复杂度:
O
(
l
o
g
n
)
O(logn)
O(logn),法一为
O
(
n
)
O(n)
O(n),需要长度为
n的数组;法二为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),这里只计算除了返回答案之外的空间。平衡二叉树的高度为 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn),即为递归过程中栈的最大深度,也就是需要的空间。
题目来源:力扣。
放弃一件事很容易,每天能坚持一件事一定很酷,一起每日一题吧!
关注我 leetCode专栏,每日更新!
注: 如有不足,欢迎指正!
风语者!平时喜欢研究各种技术,目前在从事后端开发工作,热爱生活、热爱工作。






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结