您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >nginx实战,nginx高可用, nginx负载配置, nginx正向,反向代理,nginx各种配置, 及其配置问题网站首页学无止境
nginx实战,nginx高可用, nginx负载配置, nginx正向,反向代理,nginx各种配置, 及其配置问题
简介nginx实战,nginx高可用, nginx负载配置, nginx正向,反向代理,nginx各种配置, 及其配置问题
nginx配置实战, nginx负载, nginx正向,反向代理,nginx路由配置
nginx
简介:Nginx是一款轻量级的Web 服务器/反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器,在BSD-like 协议下发行。其特点是占有内存少,并发能力强,事实上nginx的并发能力在同类型的网页服务器中表现较好。
场景: 因此我们有这样的一个业务场景, 我们系统会收录公司所有的api接口, 每个api都会有自己的preview 页面,有的api提供者会提供preview的共能, 有的需要重新开发ui,那当我们系统访问不同的preview时, 都会存在问题, 例如跨域, 前端, 后端等会有, 对于api提供者非常不友好, 那我就想使用nginx做代理服务, 统计管理请求。
业务设计如下:
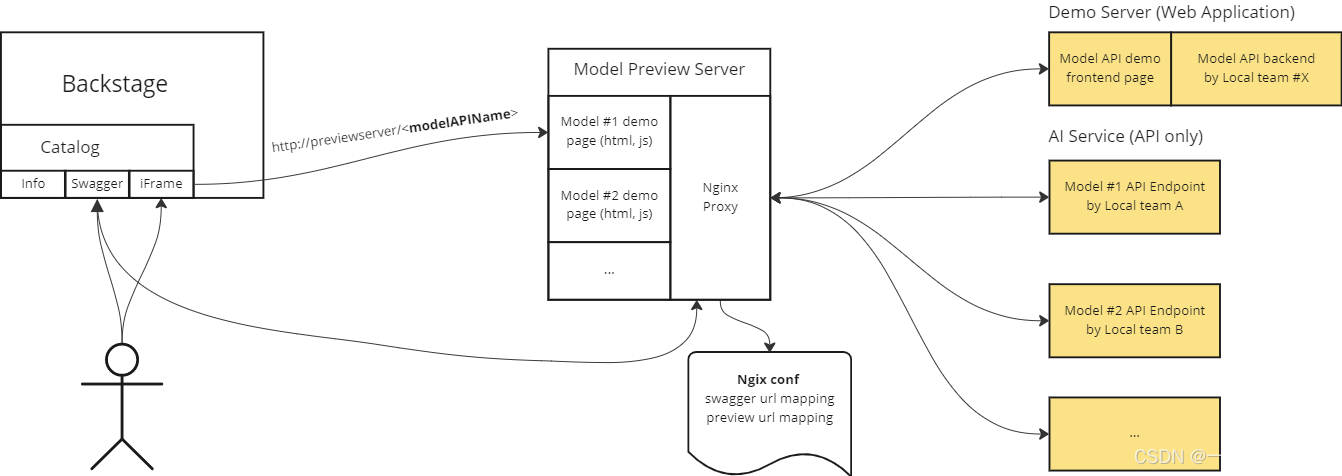
- nginx集中部署preview 前端代码,或者正向代理到preview
- nginx集中反向代理preview对应的apiserver
基于以上业务场景, 接着全面熟悉nginx知识。
如果英文够好, 可以详细了解: nginx官方文档
nginx基础
nginx 配置
1.首先来看看nginx配置的结构
# 全局配置
...
# events 配置
events {
...
}
# http配置
http
{
# http 全局配置
...
# server 配置
server
{
#server 全局配置
...
#location配置
location /xxx
{
...
}
}
}
# 全局配置: 配置影响全局, 包括运行nginx的用户组, 进程存放, 日志, 配置文件等
# events: 配置影响nginx 的服务器与客户端的网络连接, 包括进程最大连接数, 数据驱动模型, 序列化等
# http: 配置代理, 缓存, 日志, 第三方模块等, 可嵌套多个server
# server : 配置虚拟主机的参数, 可以配置多个location
# location: 配置请求路由, 页面处理
- 全局配置
# 全局配置
# nginx的用户组, 默认noboby
# user noboby noboby;
# 开启进程的线程数, 根据机器的cpu核数确定
# worker_processes 1;
# 定义错误日志位置 参数log level (notice, debug, info, warn, error, crit)debug输出最多, crit最少
# error_log logs/error.log debug;
#指定进程id的存储位置
#pid logs/nginx.pid
#指定一个nginx进程打开的最多文件描述符数目,受系统进程的最大打开文件数量限制
#worker_rlimit_nofile 65535
#envents 配置
events {
#设置工作模式为epoll,除此之外还有select,poll,kqueue,rtsig和/dev/poll模式
use epoll;
#定义每个进程的最大连接数,受系统进程的最大打开文件数量限制
worker_connections 1024;
}
#http 配置
http {
#主模块指令,实现对配置文件所包含的文件的设定,可以减少主配置文件的复杂度
include mime.types;
#核心模块指令,默认设置为二进制流,也就是当文件类型未定义时使用这种方式
default_type application/octet-stream;
#下面代码为日志格式的设定,main为日志格式的名称,可自行设置,后面引用
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#引用日志main格式
access_log logs/access.log main;
#设置允许客户端请求的最大的单个文件字节数
client_max_body_size 20M;
#指定来自客户端请求头的headebuffer大小
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
#指定连接请求试图写入缓存文件的目录路径
client_body_temp_path /dev/shm/client_body_temp;
#指定客户端请求中较大的消息头的缓存最大数量和大小,目前设置为4个32KB
large client_header_buffers 4 32k;
#开启高效文件传输模式
sendfile on;
#开启防止网络阻塞
tcp_nopush on;
#开启防止网络阻塞
tcp_nodelay on;
#设置客户端连接保存活动的超时时间
#keepalive_timeout 0; # 无限时间
keepalive_timeout 65;
#设置客户端请求读取header超时时间
client_header_timeout 10;
#设置客户端请求body读取超时时间
client_body_timeout 10;
#HttpGZip模块配置
#开启gzip压缩
gzip on;
#设置允许压缩的页面最小字节数
gzip_min_length 1k;
#申请4个单位为16K的内存作为压缩结果流缓存
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
#设置识别http协议的版本,默认为1.1
gzip_http_version 1.1;
#指定gzip压缩比,1-9数字越小,压缩比越小,速度越快
gzip_comp_level 2;
#指定压缩的类型
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascript text/css application/xml;
#让前端的缓存服务器进过gzip压缩的页面
gzip_vary on;
}
# server 配置:
server {
#单连接请求上限次数
keepalive_requests 120;
#监听端口
listen 88;
#监听地址,可以是ip,最好是域名
server_name 111.222.333.123;
#server_name www.123.com;
#设置访问的语言编码
charset utf-8;
#设置虚拟主机访问日志的存放路径及日志的格式为main
access_log /info/respones.log main; #响应日志
error_log /error/erro.log main; #错误日志
# includes
include xxx.conf;
#REWRITE URL重写规则引用
include /nginx/conf/xxx.conf;
#REWRITE-END
#设置主机基本信息
#请求的url过滤,正则匹配,~为区分大小写,~*为不区分大小写。
location ~*^.+$ {
#根目录
root html;
#设置默认页
index index.html index.htm;
#拒绝的ip,黑名单
deny 127.0.0.1;
#允许的ip,白名单
allow 172.111.111.111;
}
#禁止访问的文件或目录
location ~ ^/(.user.ini|.htaccess|.git|.svn|.project|LICENSE|README.md)
{
return 404;
}
#SSL证书验证目录相关设置
location ~ .well-known{
allow all;
}
#图片资源配置
location ~ .*.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$
{
expires 30d;
error_log /dev/null;
access_log off;
}
#网站js与css资源配置
location ~ .*.(js|css)?$
{
expires 12h;
error_log /dev/null;
access_log off;
}
#访问异常页面配置
error_page 404 /404.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
- location + proxy_pass
server {
listen 8081;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#情景1:proxy_pass后有/ ,表绝对路径,不把匹配部分加入最终代理路径(location 和proxy_pass结尾一致)
#访问地址:http://localhost:8081/wcp/a2/download/asc.shtml
#最终代理:http://127.0.0.1:8082/a2/download/asc.shtml
location /wcp/a2/download/ {
proxy_pass http://10.194.171.7:13082/a2/download/;
}
#访问地址:http://localhost:8081/model/asc.shtml
#最终代理:http://127.0.0.1:8082/model/asc.shtml
location /model/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8082/model/;
}
#情景2:proxy_pass后有/ ,表绝对路径,不把匹配部分加入最终代理路径(location 和proxy_pass结尾不一致)
#访问地址:http://localhost:8081/model/asc.shtml
#最终代理:http://127.0.0.1:8082/asc.shtml
location /model/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8082/;
}
#情景3:proxy_pass后没有 / ,Nginx会把匹配部分带到代理的url
#访问地址:http://localhost:8081/model/asc.shtml
#最终代理:http://127.0.0.1:8082/model/asc.shtml
location /model/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8082;
}
#情景4
#访问地址:http://localhost:8081/model/asc.shtml
#最终代理:http://127.0.0.1:8082/aaamodel/asc.shtml
location /model/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8082/aaa;
}
#情景5
#访问地址:http://localhost:8081/model/asc.shtml
#最终代理:http://127.0.0.1:8082/asc.shtml
location /model {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8082/;
}
#情景6
#访问地址:http://localhost:8081/modelXxxxx/asc.shtml
#最终代理:http://127.0.0.1:8082/asc.shtml
location /model {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8082/;
}
location /opus-front-sso {
proxy_pass http://10.194.170.94/opus-front-sso;
}
location /awater {
proxy_pass http://10.194.170.94/awater;
}
}
- rewrite
server {
listen 6677;
server_name 10.212.38.39;
# 情景1: http://127.0.0.1:6677/aa -> http://127.0.0.1:6688
location /aa{
proxy_http_version 1.1;
##rewrite ^/js/(.*)$ /$1/$2 break;
rewrite ^/aa http://127.0.0.1:6688/ break;
}
# 情景2: http://127.0.0.1:6677/cc -> https://xxx.xxxxx.com/
location /cc {
proxy_http_version 1.1;
##rewrite ^/js/(.*)$ /$1/$2 break;
rewrite ^/cc https://xxx.xxxxx.com/ break;
}
#情景3: http://127.0.0.1:6677/dd/docs -> https://xxx.xxxxx.com/docs 参数: (.*) = $1=docs
location /dd {
rewrite ^/dd/(.*)$ https://xxx.xxxxx.com/$1 break;
}
}
- try_files
# try_files 解释:
# 首先:按照指定的顺序检查文件是否存在,并使用第一个找到的文件进行请求处理
# 其次:处理是在当前上下文中执行的。根据 root 和 alias 指令从 file 参数构造文件路径。
# 然后:可以通过在名称末尾指定一个斜杠来检查目录的存在,例如“ $uri/”。
# 最后:如果没有找到任何文件,则进行内部重定向到最后一个参数中指定的 uri。
server {
listen 6688;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location /{
root /home/bieber/backstage/dist1/;
index index.html;
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
}
# 配置解释:
# root:设置静态根目录为 /home/bieber/backstage/dist1/
# index:设置目录的默认文件为 index.html 、index.htm
# try_files:设置文件查找规则为 $uri $uri/ /index.html。即3个规则,先从 $uri 查找,再从 $uri/ 目录中查找,最后查找 /index.html
# 注意: try_files 必须有一个存在, 不然一直死循环找, 最终抛出500
- includes
includes 可以使用在多个位置, 在http里面,与server并列, 在server 里面,与location 并列
// 情景1: http includes: conf1
http {
.....
include /usr/local/nginx/conf/*default.conf;
}
// default.conf
server {
listen 5566;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location / {
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_pass https://xx.xxx.com/ssds/ssss;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
//情景2: http server: conf2
server {
listen 6677;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
include /usr/local/nginx/conf/*conf3.conf;
include /usr/local/nginx/conf/*conf4.conf;
}
// conf3
location /aa{
proxy_http_version 1.1;
##rewrite ^/js/(.*)$ /$1/$2 break;
rewrite ^/aa http://127.0.0.1:6688/ break;
}
// conf4
location /dd {
rewrite ^/dd/(.*)$ https://xxx.xxxx.com/$1 break;
}
nginx正向代理
何为正向代理?
正向代理就是前端对前端, 即客户端对客户端, 比如我们的backstage前端页面要访问preview的前端, 直接访问受防火墙, 跨域等限制, 通过nginx正向代理解决了这个问题
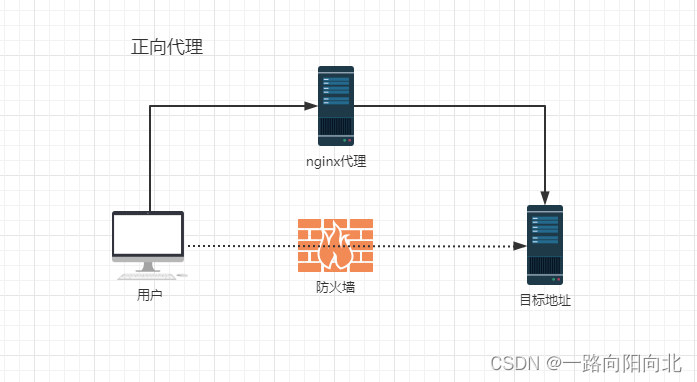
# nginx 配置 比如公司只能用内网, 但是10.110.111.1上可以访问外网
server {
listen 4433;
server_name 10.110.111.1;
location / {
proxy_pass http://www.baidu.com
}
}
# 重启nginx(nginx -s reload)
# 访问http://10.110.111.1:4433/ 就能访问到百度
nginx 反向代理
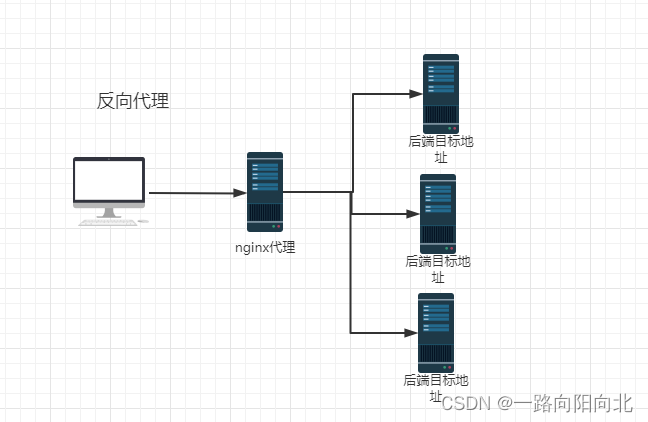
location /opus-front-sso {
proxy_pass http://10.194.170.94/opus-front-sso;
}
nginx 负载
- nginx 负载均衡配置, 默认负载(轮询)
http {
upstream myapp1 {
server srv1.example.com;
server srv2.example.com;
server srv3.example.com;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://myapp1;
}
}
}
- 最少连接的负载
upstream myapp1 {
least_conn;
server srv1.example.com down; // down 永久下线
server srv2.example.com;
server srv3.example.com;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://myapp1;
}
}
- ip哈希负载
upstream myapp1 {
ip_hash;
server srv1.example.com;
server srv2.example.com;
server srv3.example.com;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://myapp1;
}
}
- 加权重负载平衡
# 每 5 个新请求将分布在 应用程序实例如下:将定向 3 个请求 对于 SRV1,一个请求将转到 SRV2,另一个请求将转到 SRV3
upstream myapp1 {
server srv1.example.com weight=3;
server srv2.example.com;
server srv3.example.com;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://myapp1;
}
}
nginx高可用
nginx的使用场景非常多了, 那nginx做到高可用就非常的重要, 下来我们借助第三方插件Keepalived 完成nginx的负载, 如下图:
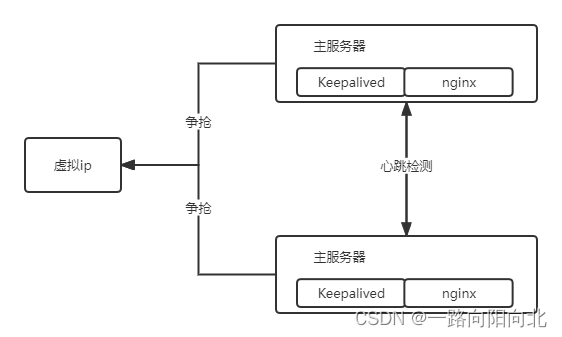
- 首先可以用一个域名代理这个虚拟ip
- 这个虚拟ip负载到两台机器上
- 每台机器装Keepalived:
yum install keepalived -y #安装
rpm -q -a keepalived # 查看安装情况
# 修改两台配置
cd /etc/keepalived vi keepalived.conf
global_defs {
notification_email {
acassen@firewall.loc
failover@firewall.loc
sysadmin@firewall.loc
}
notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc
smtp_server 127.0.0.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id LVS_DEVEL #唯一
}
vrrp_script chk_http_port {
script "/usr/local/src/nginx_check.sh"
interval 2 #(检测脚本执行的间隔)2 s执行一次
weight 2 # 脚本成立 权重增加2。
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP # 备份服务器上将 MASTER(主) 改为 BACKUP
interface ens33 # 网卡
virtual_router_id 51 # 主、备机的 virtual_router_id 必须相同
priority 100 # 主、备机取不同的优先级,主机值较大,备份机值较小
advert_int 1 # 进行心跳检测 每隔一秒 发送检测信息 查看是否存活
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.110.111.01 # 虚拟地址
}
}
# 注意: Keepalived 必须在nginx的实力存活的情况下启动
systemctl start keepalived
# 结果: 访问10.110.111.01 然后两个keepalived会抢占这个虚拟ip,同时将服务请求发送到不同对应的nginx服务器上,这样就保证了在一个服务器出现故障时候,另外一个还能够正常的工作。
nginx 配置常见问题
反向代理报426错误
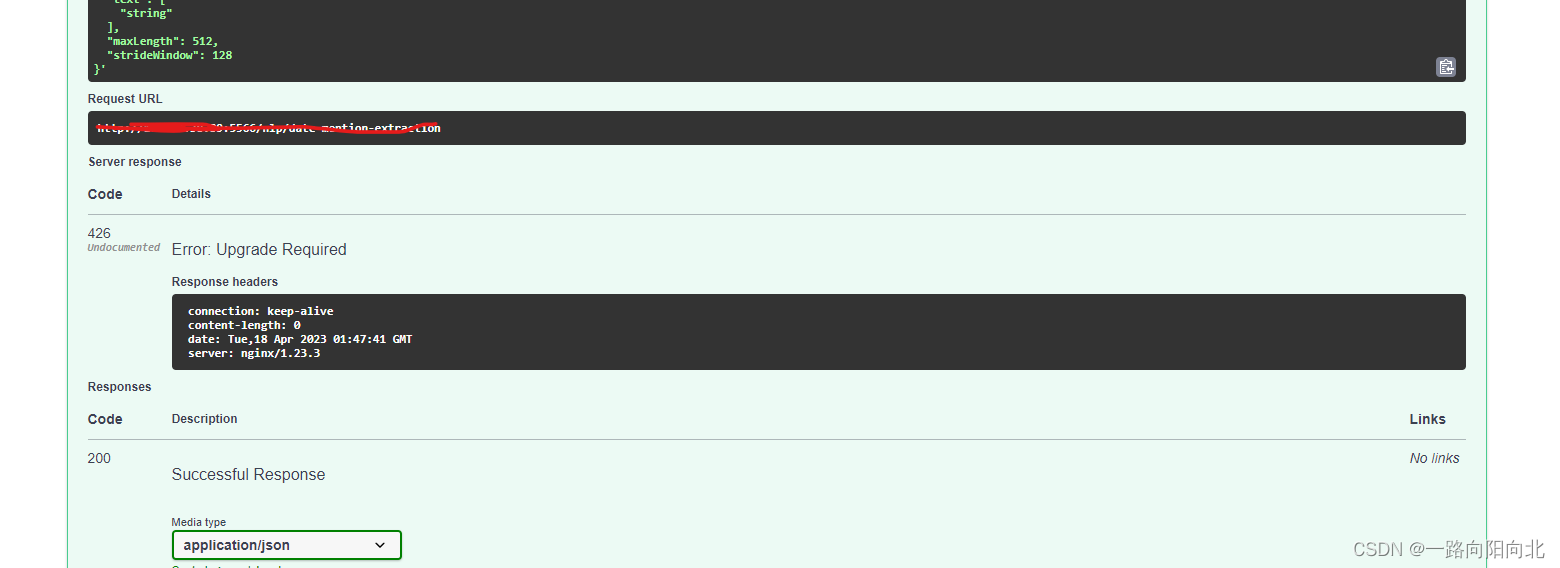
server {
listen 5566;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location / {
proxy_pass https://xx.xxx.com/ssds/ssss;
}
}
// 修改如下:
server {
listen 5566;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location / {
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_pass https://xx.xxx.com/ssds/ssss;
}
}
post请求变get请求
问题: 使用nginx转发请求,但是明明是post请求,打到服务上确实get请求,body中的参数都没了
原因: post转get其实不是Nginx导致的!而是重定向导致, 可以关闭重定向。
server {
listen 5566;
server_name 10.212.38.39;
location / {
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_pass https://xx.xxx.com/ssds/ssss;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
nginx 配置前端代理, 会出现js, css找不到
可以使用rewrite 重定向, 或者处理js, css的再次代理
location /aa{
proxy_http_version 1.1;
##rewrite ^/js/(.*)$ /$1/$2 break;
rewrite ^/aa http://10.212.38.39:6688/ break;
}
风语者!平时喜欢研究各种技术,目前在从事后端开发工作,热爱生活、热爱工作。






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结