您现在的位置是:首页 >技术教程 >算法Day01网站首页技术教程
算法Day01
DAY01
704-二分查找
不考虑边界==target的方法
我的while循环里不考虑边界=target的情况,最后注意考虑nums[left]==target、nums[right]==target的情况
class Solution
{
public:
int search(vector<int> &nums, int target)
{
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
int now = (right - left) / 2 + left;
while (nums[now] != target && left + 1 < right)
{
if (nums[now] > target)
{
right = now;
}
else if (nums[now] < target)
{
left = now;
}
now = ((right - left) >> 1) + left;
//表达式(right - left) >> 1表示将(right - left)这个数向右移动1位,也就是除以2。
}
if (nums[now] == target)
{
return now;
}
else if (nums[left] == target)
{
return left;
}
else if (nums[right] == target)
{
return right;
}
return -1;
}
};
左闭右开区间方法二
左闭右开区间,判断的时候不考虑right==target的情况。
-
如果middle>target,在左区间找,right=middle,不考虑right==target的情况;
-
如果middle<target,右区间找,left=+1,考虑left==target的情况
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size(); // 定义target在左闭右开的区间里,即:[left, right)
while (left < right) { // 因为left == right的时候,在[left, right)是无效的空间,所以使用 <
int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (nums[middle] > target) {
right = middle; // target 在左区间,在[left, middle)中
} else if (nums[middle] < target) {
left = middle + 1; // target 在右区间,在[middle + 1, right)中
} else { // nums[middle] == target
return middle; // 数组中找到目标值,直接返回下标
}
}
// 未找到目标值
return -1;
}
};
二分查找——左闭右开区间
int right = nums.size(); // 定义target在左闭右开的区间里,即:[left, right)
while (left < right) {
int middle = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
//在左区间
right = middle;
//在右区间
left = middle + 1;
}
27-移除元素
快慢指针
把数组中不等于val的元素nums[fastindex]放到nums[slowindex]的位置
// 时间复杂度:O(n)
// 空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int slowIndex = 0;
for (int fastIndex = 0; fastIndex < nums.size(); fastIndex++) {
if (val != nums[fastIndex]) {
nums[slowIndex++] = nums[fastIndex];
}
}
return slowIndex;
}
};
最少移动次数
从左边找**=val的元素nums[left],从右边找!=val**的元素nums[right],让nums[left]=nums[right],一直到left=right。
注意循环条件是while(leftIndex <= rightIndex)
// 时间复杂度:O(n)
// 空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int leftIndex = 0;
int rightIndex = nums.size() - 1;
while (leftIndex <= rightIndex) {
// 找左边等于val的元素
while (leftIndex <= rightIndex && nums[leftIndex] != val){
leftIndex++;
}
// 找右边不等于val的元素
while (leftIndex <= rightIndex && nums[rightIndex] == val) {
rightIndex--;
}
// 将右边不等于val的元素覆盖左边等于val的元素
if (leftIndex < rightIndex) {
nums[leftIndex] = nums[rightIndex];
leftIndex++;
rightIndex--;
}
}
return leftIndex; // leftIndex一定指向了最终数组末尾的下一个元素
}
};
D - Count Subtractions

思路
辗转相除法:若不相等,先使A>B,要通过A/B次A=A-B操作,使A=A%B,这个时候A<B,swap(A,B)使A>B,重复上述操作,直到A=A%B=0,因为我要求的是使A、B相等的操作次数,不需要让A=0,所以最后sum–。
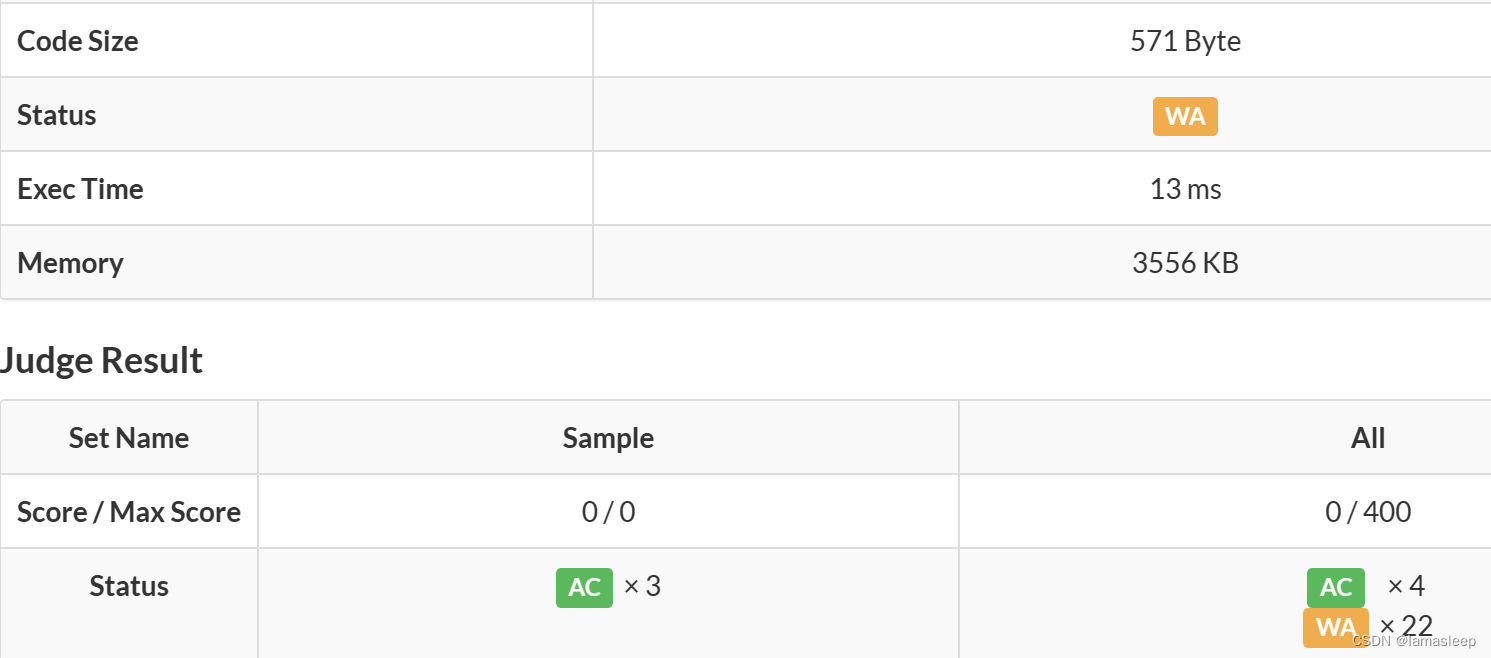
WAcode1
没注意到A,B的范围,用的int类型。A了4个
#include <iostream> // include the iostream library for input/output operations
using namespace std; // use the standard namespace
void swap(int &a, int &b) {
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int main() { // main function
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int sum = 0;
if (a < b)//保证a>=b
{
swap(a, b);
}
do{
sum += (a / b);
a %= b;
swap(a, b);
}while (b!=0);
cout << sum - 1;
return 0; // return 0 to indicate successful program termination
}
ACCode-改成long long类型之后
#include <iostream> // include the iostream library for input/output operations
using namespace std; // use the standard namespace
void swap(long long &a, long long &b) {
long long temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
int main() { // main function
long long a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
long long sum = 0;
if (a < b)//保证a>=b
{
swap(a, b);
} do{
sum += (a / b);
a %= b;
swap(a, b);
}while (b!=0);
cout << sum - 1;
return 0; // return 0 to indicate successful program termination
}
E - Kth Takoyaki Set
问题描述
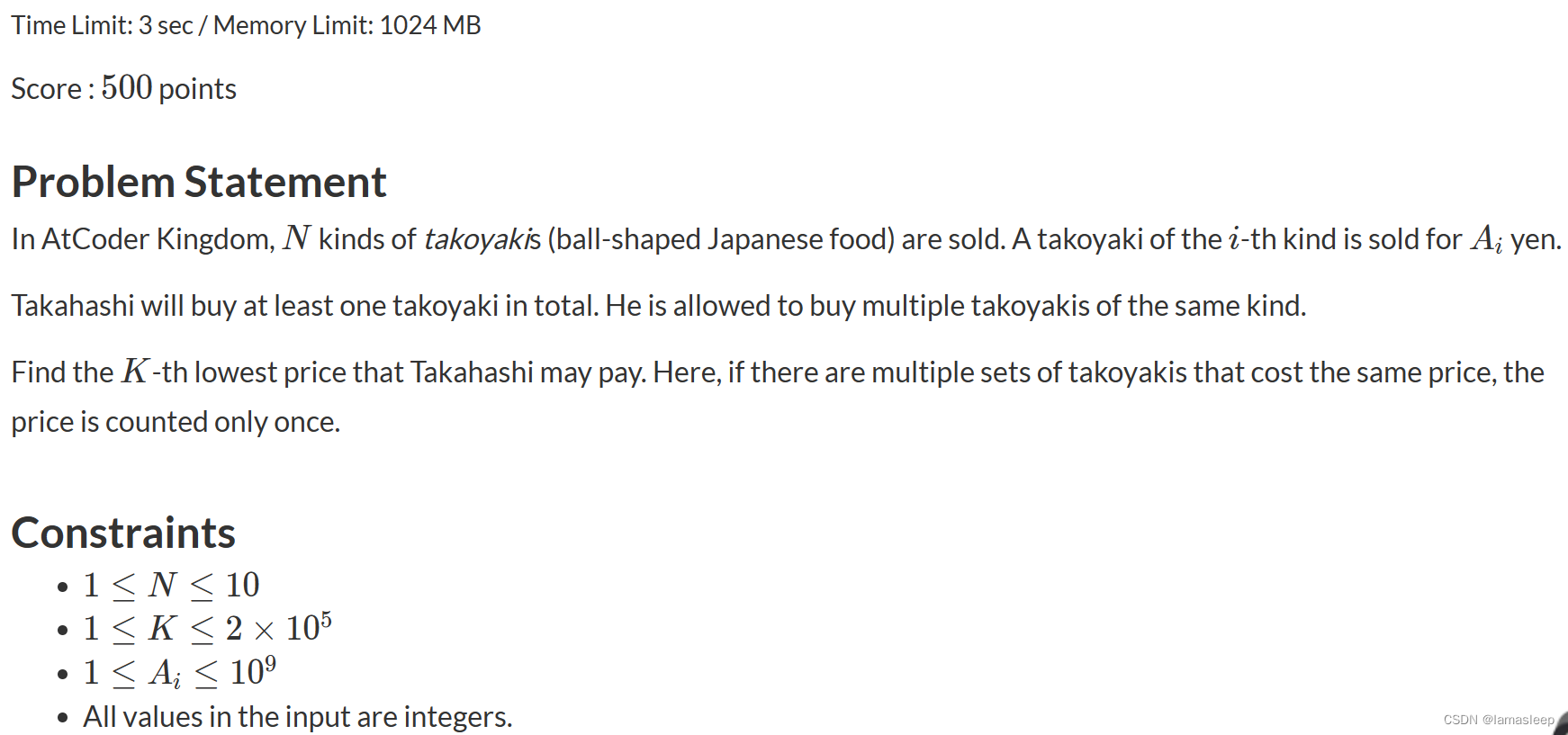
思路
Ai价格用vector存储,使用优先队列存储不同买法的价格之和,每次while循环pop出最小的数first,在first基础上依次加上vector中的价格,分别push进优先队列,用map<LL, bool> visited来确保不会将相同的数值push进优先队列中。再进行下一次while循环,弹出当前最小的数first,将first加上价格Ai的值push进优先队列,直到pop出第K小的数。
code
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL n, k;
vector<LL> a;
map<LL, bool> visited;
priority_queue<LL, vector<LL>, greater<LL> > pq;
int main() { // main function
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//输入价格到vector
LL temp;
cin >> temp;
a.push_back(temp);
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());//价格排序
pq.push(0);
visited[0] = true;//优先队列填充一个0
LL order = -1;
while (!pq.empty()) {
LL first = pq.top();//first是最小的
pq.pop();
order++;//已经pop出去了order个最小的数
if (order == k) {
cout << first << endl;
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {
LL now = a[i];
LL next = first + now;//每次for循环都是在pb中最小的数的基础上加上vector a中的价格
if (visited[next]) {
continue;
}
visited[next] = true;
pq.push(next);
}
}
return 0;
}
知识点-优先队列
定义:priority_queue<Type, Container, Functional>
Type 就是数据类型,Container 就是容器类型(Container必须是用数组实现的容器,比如vector,deque等等,但不能用 list。STL里面默认用的是vector),Functional 就是比较的方式,当需要用自定义的数据类型时才需要传入这三个参数,使用基本数据类型时,只需要传入数据类型,默认是大顶堆
//升序队列
priority_queue <int,vector<int>,greater<int> > pq;
//降序队列
priority_queue <int,vector<int>,less<int> >pq;
top 访问队头元素
empty 队列是否为空
size 返回队列内元素个数
push 插入元素到队尾 (并排序)
emplace 原地构造一个元素并插入队列
pop 弹出队头元素
swap 交换内容
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
priority_queue<pair<int, int> > a;
pair<int, int> b(1, 2);
pair<int, int> c(1, 3);
pair<int, int> d(2, 5);
//pari的比较,先比较第一个元素,第一个相等比较第二个
a.push(d);
a.push(c);
a.push(b);
while (!a.empty())
{
cout << a.top().first << ' ' << a.top().second << '
';
a.pop();
}
}
输出:
2 5
1 3
1 2






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结