您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >如何手写一个文件索引工具everything(第一章)网站首页学无止境
如何手写一个文件索引工具everything(第一章)
简介如何手写一个文件索引工具everything(第一章)
第一章(NTFS格式及USN日志)
背景介绍
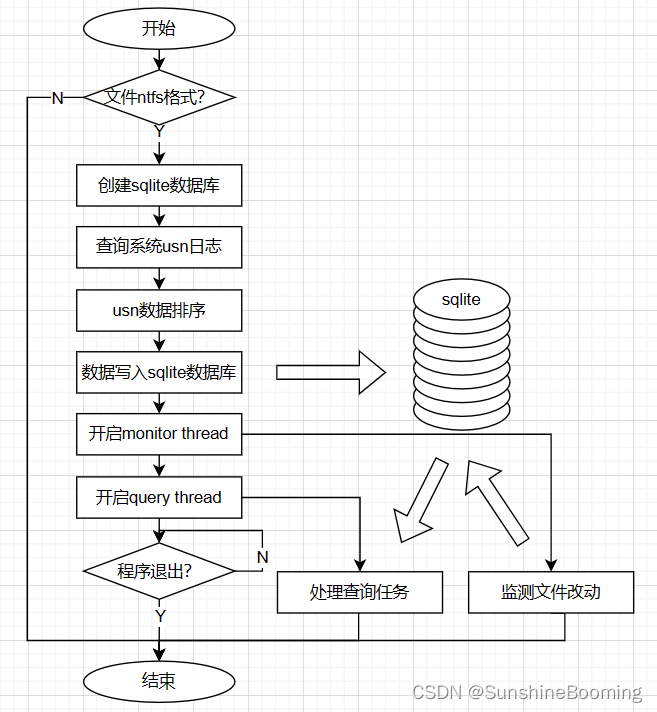
- Windows平台的Everything文件查找速度非常快,优势在于利用了NTFS的USN日志,以及Windows上的文件监测机制
- 我们也可以仿照类似原理,通过查询USN日志、监测Windows平台文件修改、使用SQLite数据库存储文件节点,并提供文件信息查询功能
项目仓库
- https://gitee.com/alanosong/MiniThing
NTFS格式
- NTFS(New Technology File System)是微软随Windows系统开发的一种文件格式,专门为网络和磁盘配额、文件加密等管理安全特性设计。比起FAT格式,NTFS属于一种较为新型的磁盘格式。
- 比起FAT格式,NTFS文件格式支持更大的分区,可以达到2TB。而FAT32可支持的最大分区只有32GB。
- NTFS可以更有效地管理磁盘空间,避免磁盘空间的浪费。NTFS采用了更小的簇组,利用率更高。
- NTFS更加安全稳定。NTFS拥有许多安全性能方面的选项,还提供文件加密支持,保障数据的安全性。同时,NTFS还能有效阻止没有授权的用户访问文件。
- NTFS可自动修复磁盘出错的信息。例如,在当Windows系统向NTFS分区写入文件时,会保留文件的一份拷贝,然后检查向磁盘中所写的文件是否与内存中的一致。如果出现不一致的情况,Windows就把相应的扇区标为坏扇区而不再使用它(簇重映射)。之后,Windows系统会通过内存中保留的文件重新拷贝写入磁盘。在磁盘读写发生错误时,NTFS会报告错误信息,并告知相应的应用程序数据已经丢失。
USN日志
- USN Journal 相当于 NTFS 的秘书,为磁盘记录下改动的一切,并储存为 USN_RECORD 的格式。
- 因此我们可以通过查询系统的USN日志,快速获取系统中的所有文件节点信息,并建立相应的数据库以供查询
相关代码
-
- 判断磁盘是否为NTFS格式,这是首要条件
BOOL MiniThing::IsNtfs(VOID)
{
BOOL isNtfs = FALSE;
char sysNameBuf[MAX_PATH] = { 0 };
int len = WstringToChar(m_volumeName + L"\", nullptr);
char* pVol = new char[len];
WstringToChar(m_volumeName + L"\", pVol);
BOOL status = GetVolumeInformationA(
pVol,
NULL,
0,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
sysNameBuf,
MAX_PATH);
if (FALSE != status)
{
std::cout << "File system name : " << sysNameBuf << std::endl;
if (0 == strcmp(sysNameBuf, "NTFS"))
{
isNtfs = true;
}
else
{
std::cout << "File system not NTFS format !!!" << std::endl;
GetSystemError();
}
}
return isNtfs;
}
-
- 控制系统生成USN记录,方便我们查询,这一步通过Win32的DeviceIoControl()接口来实现
HRESULT MiniThing::CreateUsn(VOID)
{
HRESULT ret = S_OK;
DWORD br;
CREATE_USN_JOURNAL_DATA cujd;
cujd.MaximumSize = 0;
cujd.AllocationDelta = 0;
BOOL status = DeviceIoControl(
m_hVol,
FSCTL_CREATE_USN_JOURNAL,
&cujd,
sizeof(cujd),
NULL,
0,
&br,
NULL);
if (FALSE != status)
{
std::cout << "Create usn file success" << std::endl;
ret = S_OK;
}
else
{
std::cout << "Create usn file failed" << std::endl;
GetSystemError();
ret = E_FAIL;
}
return ret;
}
-
- 查询系统生成的USN相关信息,为下一步获取具体的文件日志做准备
HRESULT MiniThing::QueryUsn(VOID)
{
HRESULT ret = S_OK;
DWORD br;
BOOL status = DeviceIoControl(m_hVol,
FSCTL_QUERY_USN_JOURNAL,
NULL,
0,
&m_usnInfo,
sizeof(m_usnInfo),
&br,
NULL);
if (FALSE != status)
{
std::cout << "Query usn info success" << std::endl;
}
else
{
ret = E_FAIL;
std::cout << "Query usn info failed" << std::endl;
GetSystemError();
}
return ret;
}
-
- 查询具体的USN日志,其中包含了所有文件的节点信息,包括了文件节点的Reference Number,Parent Reference Number等等,其类似于一个父子链表,通过Reference Number指定了文件之间的父子关系(目录和目录内的文件)。此处获取所有文件节点信息后,还需要我们手动为所有节点排序,获得文件的详细路径.
HRESULT MiniThing::RecordUsn(VOID)
{
MFT_ENUM_DATA med = { 0, 0, m_usnInfo.NextUsn };
med.MaxMajorVersion = 2;
// Used to record usn info, must big enough
char buffer[0x1000];
DWORD usnDataSize = 0;
PUSN_RECORD pUsnRecord;
// Find the first USN record
// return a USN followed by zero or more change journal records, each in a USN_RECORD structure
while (FALSE != DeviceIoControl(m_hVol,
FSCTL_ENUM_USN_DATA,
&med,
sizeof(med),
buffer,
_countof(buffer),
&usnDataSize,
NULL))
{
DWORD dwRetBytes = usnDataSize - sizeof(USN);
pUsnRecord = (PUSN_RECORD)(((PCHAR)buffer) + sizeof(USN));
DWORD cnt = 0;
while (dwRetBytes > 0)
{
// Here FileNameLength may count in bytes, and each wchar_t occupy 2 bytes
wchar_t* pWchar = new wchar_t[pUsnRecord->FileNameLength / 2 + 1];
memcpy(pWchar, pUsnRecord->FileName, pUsnRecord->FileNameLength);
pWchar[pUsnRecord->FileNameLength / 2] = 0x00;
// wcsncpy_s(pWchar, pUsnRecord->FileNameLength / 2, pUsnRecord->FileName, pUsnRecord->FileNameLength / 2);
std::wstring fileNameWstr = WcharToWstring(pWchar);
delete pWchar;
UsnInfo usnInfo = { 0 };
usnInfo.fileNameWstr = fileNameWstr;
usnInfo.pParentRef = pUsnRecord->ParentFileReferenceNumber;
usnInfo.pSelfRef = pUsnRecord->FileReferenceNumber;
usnInfo.timeStamp = pUsnRecord->TimeStamp;
m_usnRecordMap[usnInfo.pSelfRef] = usnInfo;
// Get the next USN record
DWORD recordLen = pUsnRecord->RecordLength;
dwRetBytes -= recordLen;
pUsnRecord = (PUSN_RECORD)(((PCHAR)pUsnRecord) + recordLen);
}
// Get next page USN record
// from MSDN(http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa365736%28v=VS.85%29.aspx ):
// The USN returned as the first item in the output buffer is the USN of the next record number to be retrieved.
// Use this value to continue reading records from the end boundary forward.
med.StartFileReferenceNumber = *(USN*)&buffer;
}
return S_OK;
}
-
- 至此,所有文件节点信息已经获取,需要对于信息进行排序,下一章再叙述。
风语者!平时喜欢研究各种技术,目前在从事后端开发工作,热爱生活、热爱工作。






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) SpringSecurity实现前后端分离认证授权
SpringSecurity实现前后端分离认证授权