您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >搜索算法(四) 广度优先搜素算法网站首页学无止境
搜索算法(四) 广度优先搜素算法
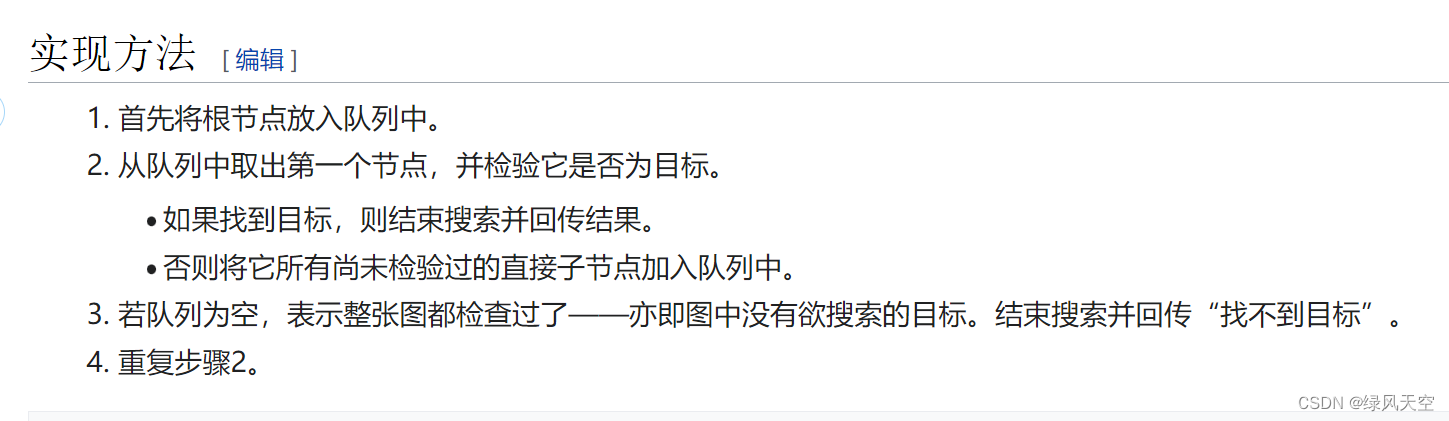
一、BFS
bfs一层一层地遍历图或树,一般用队列实现,可以计算距离目标的步数。

二、例题
1)
力扣![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-bridge/ 这道题实际是计算两个岛屿之间的最短距离,可以先用dfs搜索到第一个岛屿并且记录第一个岛屿的每对坐标,接着以这些坐标作为bfs的起始节点集合,一层一层地向外遍历,寻找第二个岛屿,当找到第二个岛屿时,当前遍历的层数减一就是两个岛屿之间的最短路径。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-bridge/ 这道题实际是计算两个岛屿之间的最短距离,可以先用dfs搜索到第一个岛屿并且记录第一个岛屿的每对坐标,接着以这些坐标作为bfs的起始节点集合,一层一层地向外遍历,寻找第二个岛屿,当找到第二个岛屿时,当前遍历的层数减一就是两个岛屿之间的最短路径。
tips: 将第一个岛屿的坐标值标为2,方便区分两个岛屿
bfs遍历过程中,将0标为2,表示已加入了第一个岛屿
class Solution {
public:
int shortestBridge(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1){
dfs(grid,i,j);
return bfs(grid);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int bfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid){
int level = 0;
int m;
int n = grid.size();
while(!first.empty()){
level++;
m = first.size();
while(m--){
auto[a,b] = first.front();
first.pop();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int x = a + path[i];
int y = b + path[i+1];
if(x>=0 && y>=0 && x<n && y<n){
if(grid[x][y]==0){
grid[x][y] = 2;
first.push({x,y});
}else if(grid[x][y]==1){
return level-1;
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int a, int b){
grid[a][b] = 2;
first.push({a,b});
int n = grid.size();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int x = a + path[i];
int y = b + path[i+1];
if(x>=0 && y>=0 && x<n && y<n && grid[x][y]==1){
dfs(grid, x, y);
}
}
}
private:
queue<pair<int,int>> first;
vector<int> path{-1,0,1,0,-1};
};2)
力扣![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-ladder-ii/单词接龙可以理解成寻找两个单词之间的最短路径,当两个单词之间只有一个字母不相同时可以认为两个单词之间有一条双向边,这道题就是寻找起始单词到目标单词的最短路径。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-ladder-ii/单词接龙可以理解成寻找两个单词之间的最短路径,当两个单词之间只有一个字母不相同时可以认为两个单词之间有一条双向边,这道题就是寻找起始单词到目标单词的最短路径。
用BFS从起始单词开始,变换一个字母,代表走了一步,变换两个字母,代表走了两步了,一层一层变换,一直遍历到达目标单词。
在一层一层遍历的过程中,需要记录下每一层变换所得到的单词,这样BFS结束后,可以用DFS找到最短路径。
我一开始用的是双向BFS+DFS,基于正向的逻辑,在第34个测试用例时超时了。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> findLadders(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
vector<vector<string>> ans;
unordered_set<string> dict;
for(auto w:wordList){
dict.insert(w);
}
if(dict.count(endWord)==0){
return ans;
}
dict.erase(beginWord);
dict.erase(endWord);
unordered_set<string> q1{beginWord}, q2{endWord};
unordered_map<string,vector<string>> next;
bool reversed = false, found = false;
while(!q1.empty()){
unordered_set<string> q;
for(const auto& w:q1){
string s = w;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
char ch = s[i];
for(int j=0;j<26;j++){
s[i] = 'a' + j;
if(q2.count(s)){
reversed?next[s].push_back(w):next[w].push_back(s);
found = true;
}
if(dict.count(s)){
reversed?next[s].push_back(w):next[w].push_back(s);
q.insert(s);
}
}
s[i] = ch;
}
}
if(found){
break;
}
for(const auto& w:q){
dict.erase(w);
}
if(q.size()<q2.size()){
q1 = q;
}else{
reversed = !reversed;
q1 = q2;
q2 = q;
}
}
if(found){
vector<string> path;
path.push_back(beginWord);
dfs(beginWord,endWord,next,path,ans);
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(string beginWord, string endWord, unordered_map<string,vector<string>>& next, vector<string>& path, vector<vector<string>>& ans ){
if(beginWord==endWord){
ans.push_back(path);
}
for(const auto& w:next[beginWord]){
path.push_back(w);
dfs(w,endWord,next,path,ans);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};结果:
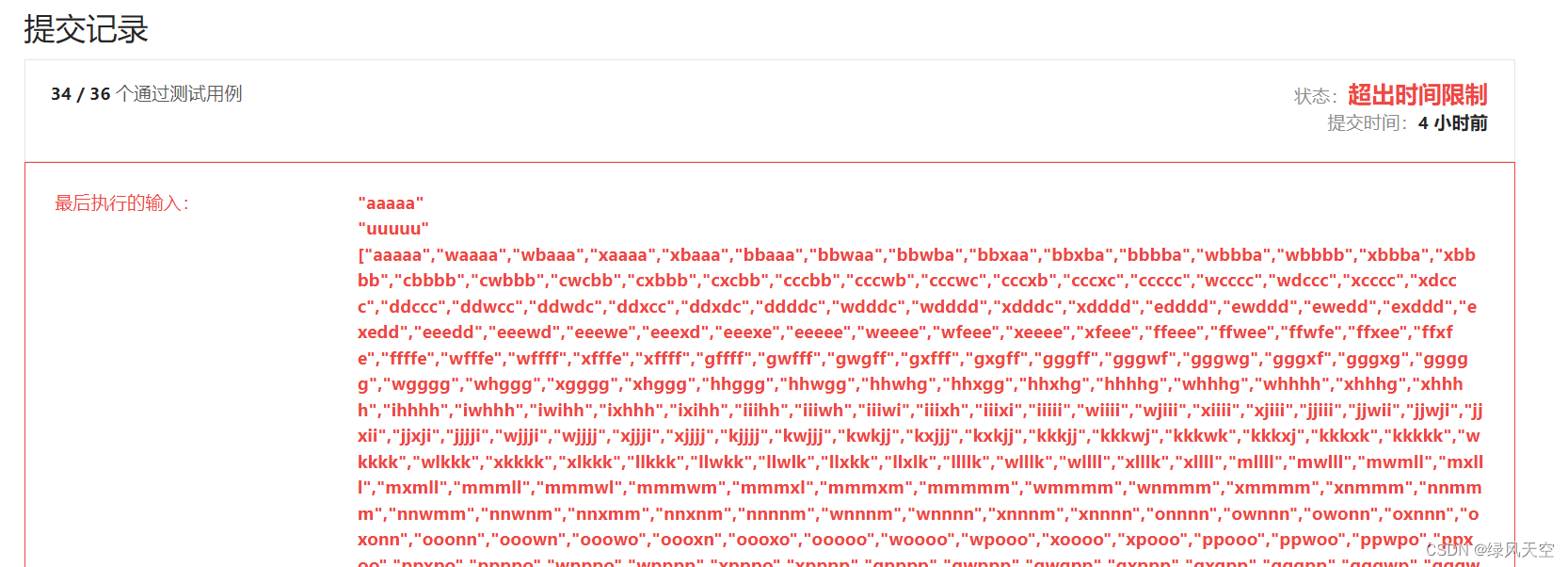
看了一下大家的讨论,发现错误在于DFS搜索是正向搜索的(从起始单词向目标单词搜索),这样会导致指数级别的可能路径。
为了不超时,正确做法是从目标单词反向向起始单词搜索,这样可能路径会少很多。
将前面的代码简单修改:记录每一层原单词变换所得到的所有单词,改为记录单词可由哪些单词得到。DFS从目标单词开始搜索,反转最终路径。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> findLadders(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
vector<vector<string>> ans;
unordered_set<string> dict;
for(auto w:wordList){
dict.insert(w);
}
if(dict.count(endWord)==0){
return ans;
}
dict.erase(beginWord);
dict.erase(endWord);
unordered_set<string> q1{beginWord}, q2{endWord};
unordered_map<string,vector<string>> next;
bool reversed = false, found = false;
while(!q1.empty()){
unordered_set<string> q;
for(const auto& w:q1){
string s = w;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
char ch = s[i];
for(int j=0;j<26;j++){
s[i] = 'a' + j;
if(q2.count(s)){
reversed?next[w].push_back(s):next[s].push_back(w);
found = true;
}
if(dict.count(s)){
reversed?next[w].push_back(s):next[s].push_back(w);
q.insert(s);
}
}
s[i] = ch;
}
}
if(found){
break;
}
for(const auto& w:q){
dict.erase(w);
}
if(q.size()<q2.size()){
q1 = q;
}else{
reversed = !reversed;
q1 = q2;
q2 = q;
}
}
if(found){
vector<string> path;
path.push_back(endWord);
dfs(endWord, beginWord,next,path,ans);
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(string beginWord, string endWord, unordered_map<string,vector<string>>& next, vector<string>& path, vector<vector<string>>& ans ){
if(beginWord==endWord){
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
ans.push_back(path);
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
}
for(const auto& w:next[beginWord]){
path.push_back(w);
dfs(w,endWord,next,path,ans);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};结果:
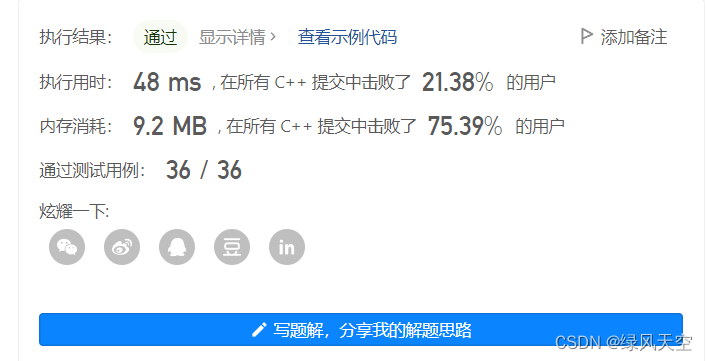
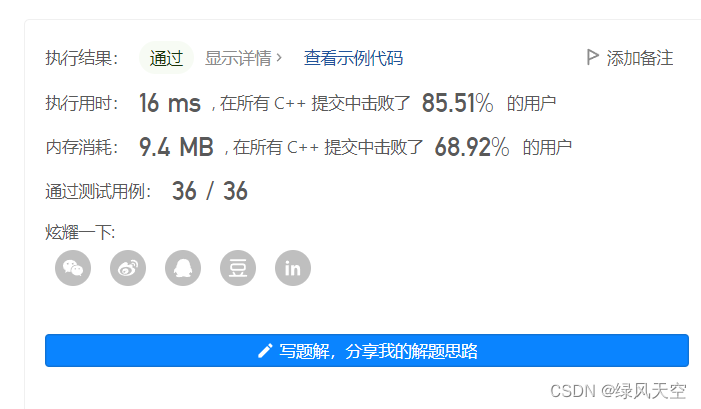
这个结果不算好,我就把双向BFS改成单向了,执行时间明显变快了,说明双向BFS属实没必要。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> findLadders(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
vector<vector<string>> ans;
unordered_set<string> dict;
for(auto w:wordList){
dict.insert(w);
}
if(dict.count(endWord)==0){
return ans;
}
dict.erase(beginWord);
unordered_set<string> q1{beginWord};
unordered_map<string,vector<string>> next;
bool found = false;
while(!q1.empty()){
unordered_set<string> q;
for(const auto& w:q1){
string s = w;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
char ch = s[i];
for(int j=0;j<26;j++){
s[i] = 'a' + j;
if(s==endWord){
next[s].push_back(w);
found = true;
break;
}
if(dict.count(s)){
next[s].push_back(w);
q.insert(s);
}
}
s[i] = ch;
}
}
if(found){
break;
}
for(const auto& w:q){
dict.erase(w);
}
q1 = q;
}
if(found){
vector<string> path;
path.push_back(endWord);
dfs(endWord, beginWord,next,path,ans);
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(string beginWord, string endWord, unordered_map<string,vector<string>>& next, vector<string>& path, vector<vector<string>>& ans ){
if(beginWord==endWord){
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
ans.push_back(path);
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
}
for(const auto& w:next[beginWord]){
path.push_back(w);
cout<<"*push**** "<<w<<endl;
dfs(w,endWord,next,path,ans);
cout<<"-pop----- "<<w<<endl;
path.pop_back();
}
}
};






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结