您现在的位置是:首页 >技术杂谈 >C/C++性能提升之cache分析网站首页技术杂谈
C/C++性能提升之cache分析
简介C/C++性能提升之cache分析
在开发过程中,我们有时会碰到程序性能瓶颈,这时候需要我们查找热点代码,借用一些命令、工具去分析自己的程序,下面我就介绍一下如何使用perf工具分析程序的cache命中率。
在编写代码前先介绍一下我们的硬件平台,我电脑的CPU 是酷睿i7-12700h (14个核20线程),系统ubuntu22.04, 内存16G,大概信息如下:



接下来上我们的代码:
//
// Created by rookie on 23-6-4.
//
#define _GNU_SOURCE /* See feature_test_macros(7) */
#include <sched.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h> /* For SYS_xxx definitions */
#if 0
struct multi_var
{
volatile int threadAVar;
volatile int threadBVar;
}g_multi_var __attribute__((aligned(64)));
#else
struct multi_var
{
volatile int threadAVar __attribute__((aligned(64)));
volatile int threadBVar __attribute__((aligned(64)));
}g_multi_var;
#endif
static const char *usage_str = "test cache
";
static void usage()
{
printf("%s", usage_str);
}
void test_cpu_performance(unsigned int cpu)
{
float f1 = 1.2;
double db1 = 2.3;
int i;
int count = 0;
int n = 0, n1 = 0;
double d = 1;
struct timeval a1, a2;
gettimeofday(&a1, NULL);
if(cpu == 0){
count = 0;
while (count++ <= 100){
for (n = 1; n < 1024*1024; ++n) {
g_multi_var.threadAVar += n;
}
}
} else if(cpu == 1){
count = 0;
while (count++ <= 100){
for (n = 1; n < 1024*1024; ++n) {
g_multi_var.threadBVar += n;
}
}
}
gettimeofday(&a2, NULL);
long time = 1000000*(a2.tv_sec-a1.tv_sec)+a2.tv_usec-a1.tv_usec;
printf("cpu = %d,time = %ld exit
", cpu, time);
}
static int set_cpu_affinity(unsigned int cpu)
{
cpu_set_t cpuset;
pid_t tid = syscall(SYS_gettid);
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset);
CPU_SET(cpu, &cpuset);
printf("before sched setaffinity cpu=%d
", cpu);
if(sched_setaffinity(tid, sizeof(cpuset), &cpuset) < 0){
perror("sched setaffinity");
printf("cpu %d
", cpu);
return -1;
}
printf("pid = %d, after sched setaffinity cpu=%d
", tid, cpu);
return 0;
}
static void* wast_cpu_body(void* arg)
{
int i = 2;
unsigned int cpu = *(unsigned int *)arg;
printf("wast_cpu_body in cpu=%d
", cpu);
set_cpu_affinity(cpu);
test_cpu_performance(cpu);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
pthread_t *thread;
int cpunum = 4;
int ret = 0;
int j = 0;
int *icpu = NULL;
pthread_attr_t *attr = NULL;
void *p_arg = NULL;
if(argc > 2){
usage();
}else if(argc == 2){
cpunum = atoi(argv[1]);
thread = malloc(sizeof(*thread) * cpunum);
attr = malloc(sizeof(*attr) * cpunum);
icpu = malloc(sizeof(*icpu) * cpunum);
for (j = 0; j < cpunum; ++j) {
ret = pthread_attr_init(&attr[j]);
// ret |= pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr[j], PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
icpu[j] = j;
ret |= pthread_create(&thread[j], &attr[j], (void*(*)(void*))wast_cpu_body, &icpu[j]);
printf("cpu index = %d
", j);
}
for (j = 0; j < cpunum; ++j) {
pthread_join(thread[j], NULL);
}
for (j = 0; j < cpunum; ++j) {
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr[j]);
}
free(icpu);
free(thread);
free(attr);
}
return ret;
}这里说明一下,关于代码中的__attribute__((aligned(64))) 对齐字节数为什么选择64?
这是由于我电脑的CPU的CACHE_LINE就是64,具体可以使用getconf命令查看

接下来我们编译出来两个可执行文件,test_cache0与test_cache1,与上述条件判断的对应关系如下:
//test_cache1 !!!!
struct multi_var
{
volatile int threadAVar;
volatile int threadBVar;
}g_multi_var __attribute__((aligned(64)));
//test_cache0 !!!!
struct multi_var
{
volatile int threadAVar __attribute__((aligned(64)));
volatile int threadBVar __attribute__((aligned(64)));
}g_multi_var;
然后我们使用perf检测它们执行的情况
sudo perf stat -e L1-dcache-load-misses,L1-icache-load-misses,L1-dcache-load,L1-dcache-stores,branch-load-miss,branch-loads ./test_cache0 10
sudo perf stat -e L1-dcache-load-misses,L1-icache-load-misses,L1-dcache-load,L1-dcache-stores,branch-load-miss,branch-loads ./test_cache1 10
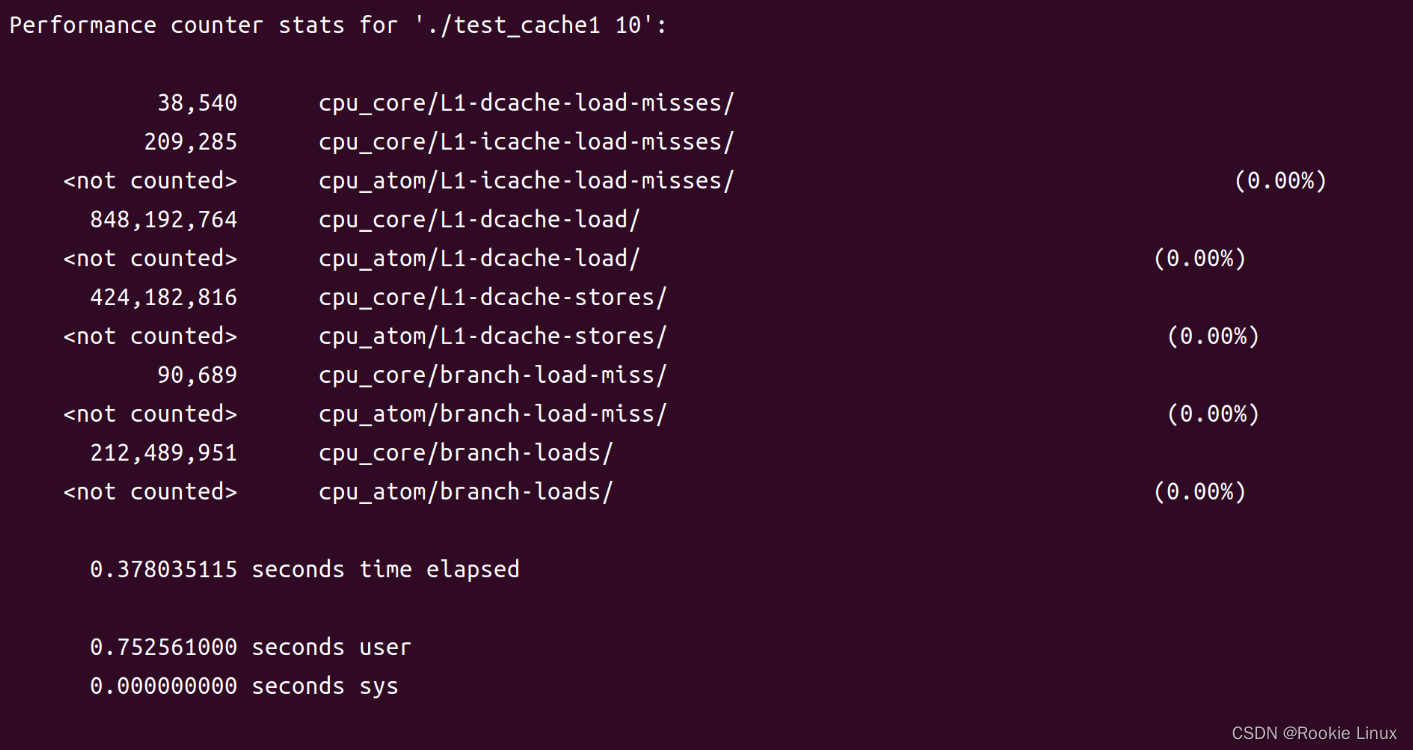
通过上述信息我们发现0方式比 1方式运行的时间少了几乎50%
0方式的 cpu_core/L1-dcache-load-misses/ 是36,246 , cpu_core/L1-dcache-load/ 是848,148,941,命中率为0.999957265
1方式的 cpu_core/L1-dcache-load-misses/ 是38,540 , cpu_core/L1-dcache-load/ 是848,192,764,命中率为0.999954562
所以我们写代码时应该多注意对齐、以及cache这些问题,感兴趣的同学还可以多试试不以64对齐的情况
风语者!平时喜欢研究各种技术,目前在从事后端开发工作,热爱生活、热爱工作。






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结