您现在的位置是:首页 >技术杂谈 >【C++】位图应用 | 布隆过滤器网站首页技术杂谈
【C++】位图应用 | 布隆过滤器
文章目录
1. 位图应用
题目一
给40亿个不重复的无符号整数,没排过序,给一个无符号整数,如何快速判断一个数是否在这40亿个数中
正常思路:
1.排序 + 二分查找
2.放入 哈希表 或者 红黑树
10亿字节 约等于 1GB
40亿个整数约等于 16GB
如果使用上述的两种方法,内存不够
哈希 的 直接定址法 的 哈希映射 ,判断整形在不在
依次映射标记,将值存起来
最少用一个char来表示一个值在不在 ,这样即为40亿字节即4GB,但是这样还是太大
标识在不在,并不需要将值存起来,使用0/1去表示
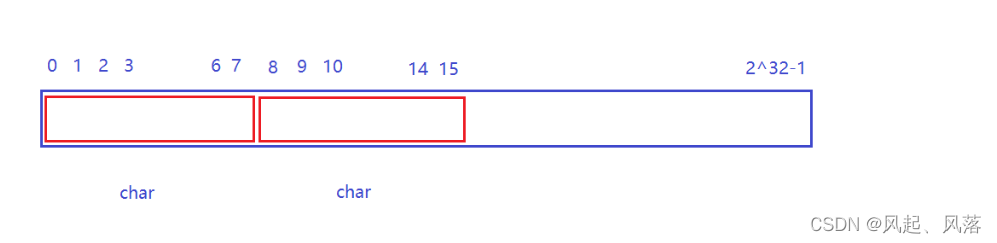
将每一个整数 所代表的值 用一个比特位去标识 即 位图
需要40亿个比特位,10亿字节 约等于 1GB ,40亿个比特位 约等于 500MB
代码实现
在bitset类中,
通过控制char,从而控制比特位
set
set 将x映射的比特位设置成1

由于下标从0开始计算
所以将0-7比特位算位第0个char ,8-15算为第1个char中,依次存储到对应的char
先计算在第几个char中,在计算在对应char的第几个比特位上面
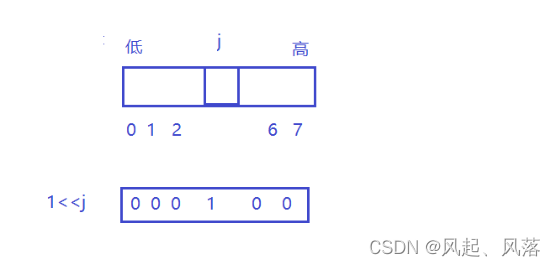
j 代表要寻找对应比特位的位置 ,想要将其置为1
<<是低到高的移位
1<<j 即 除了j位置 其他位置 都为0
所以 | 1 ,无论该位置的数为1/0 ,|后都为1
rset
rset将x映射的比特位设置成0

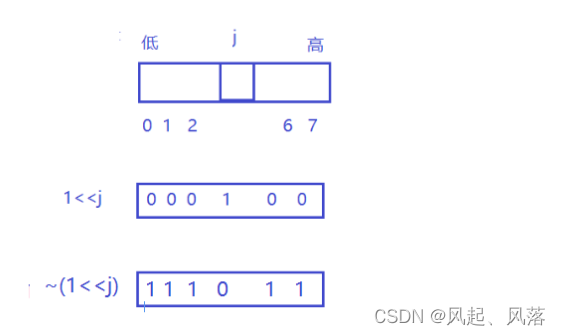
j 代表要寻找对应比特位的位置 ,想要将其置为 0
所以 &0 ,无论该位置的数为1/0 ,&后都为0
test
test 判断在不在

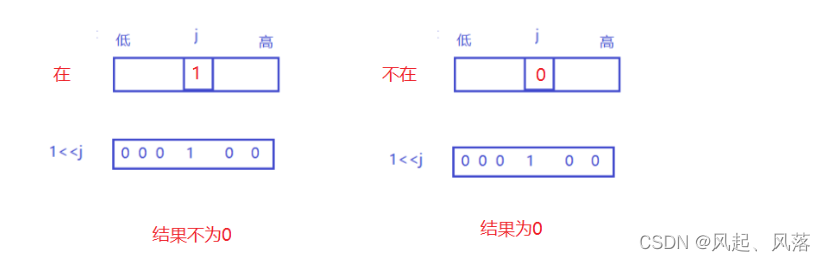
j 代表要寻找对应比特位的位置 将当前位置值 &1
由于在其他位置上也有可能存在11,所以结果不为0,则说明该位置存在
若结果为0, 则说明该位置不存在
具体代码
template<size_t N>
class bitset
{
public:
bitset()
{
_bits.resize((N / 8) + 1, 0);
}
void set(size_t x)
{
size_t i = x / 8;//第几个char上
size_t j = x % 8;//char上的第几个比特位
_bits[i] |= (1 << j);
}
void rset(size_t x)
{
size_t i = x / 8;//第几个char上
size_t j = x % 8;//char上的第几个比特位
_bits[i] &= ~(1 << j);
}
bool test(size_t x)//判断在不在
{
size_t i = x / 8;//第几个char上
size_t j = x % 8;//char上的第几个比特位
return _bits[i] & (1 << j);
}
private:
vector<char> _bits;
};
题目二
给定100亿个整数,设计算法找到只出现一次的整数?
用 2个比特位表示 当前数据
00 表示 0次 01 表示 1次 10 表示 1次以上
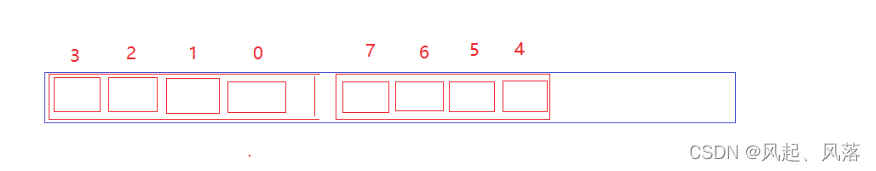
将题目一的代码进行封装即可
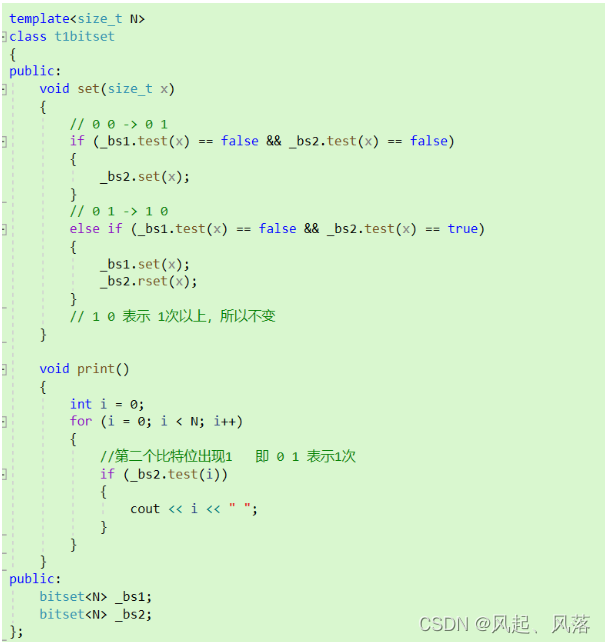
题目一的类为bitset,所以借此 来定义出 两个比特位 _bs1 _bs2
通过判断 两个比特位 是 1 /0
若出现次数为0,则 +1 变为 0 1
若出现次数为1 , 则+1 变为 1 0
若出现次数为1次以上,则不变
最终通过类中的print函数打印出出现一次的数
位图优缺点总结
优点:速度快 节省空间
缺点:
只能映射整形,string 浮点数 不能存储映射
所以提出布隆过滤器,用于一定程度解决 不能存储string类型的问题
2. 布隆过滤器
提出背景
用哈希表存储 缺点:浪费空间用位图存储 缺点: 位图一般只能处理整形,若为字符串,则无法处理
将哈希与位图结合 即布隆过滤器
概念
用多个哈希函数,将一个数据映射到位图结构中
既可以提升效率,又可以节省大量空间
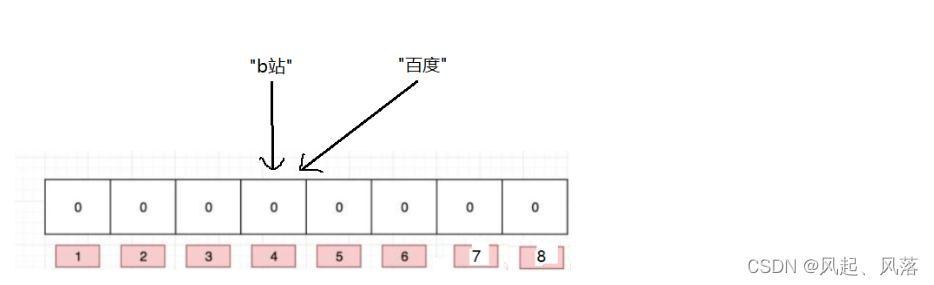
假设两个字符串映射到同一个位置,则会导致哈希冲突
布隆过滤器 想要 降低冲突概率
一个值映射到一个位置,容易误判,一个值映射到多个位置,就可以降低误判率

使用多种哈希映射算法,映射到不同的位置
如:每个值都映射到2个位置
具体实现
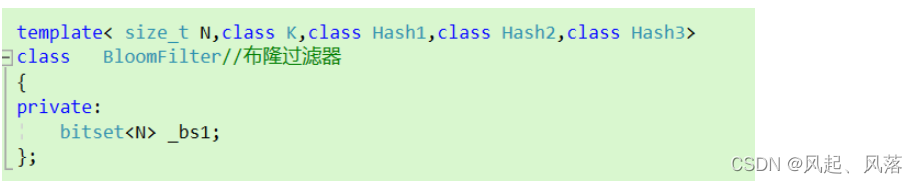
传递模板时,传入hash1 hash2 hash3 ,将K类型转换为整形
hash1 hash2 hash3 作为三种不同的映射方法
hash1 hash2 hash3

BKDRHash算法在哈希中的 针对string情况使用过 ,
当需使用字符串转化为整形时,将字符串中所有字符相加 ,用此确定对应的key
将BKDRHash作为缺省值 ,传给 hash1
点击查看详细解释:哈希

将APHash作为缺省值 ,传给hash2

将DJBHash作为缺省值 ,传给hash3
APHash 算法与 DJBHash 算法 是依据数学推导而来的
点击链接查看APHash 算法以及 DJBHash 算法的 具体解释: 哈希算法
N取值问题

N代表最多插入key数据的个数

k为哈希函数个数,m为布隆过滤器长度,n为插入元素个数
当k为3时, 3= ( m/n ) *0.69,m=4.3n
m越等于4n
布隆过滤器的长度 约等于 插入元素个数的4倍
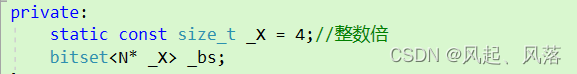
set
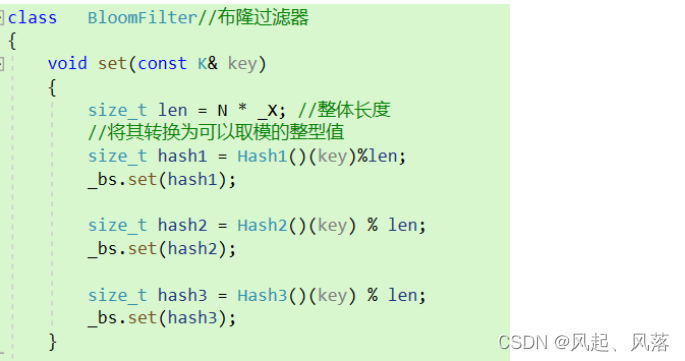
_bs作为题目一的实现的位图结构
通过调用对应hash1 hash2 hash3中的operator() 的不同实现
将传入对应的字符串转换为不同的整形,在使用位图插入在不同的映射位置
tset

只有当hash1 hash2 hash3 三个不同的位置都在,它才在,若有一个位置不在,则它就不在
就算是两个字符串的ASCII值相同,但是顺序不同,在对应hash1 hash2 hash3 的对应映射位置也是不同的
tset中在与不在那个准确?
不在是准确的,当不在时,当前映射位置为0,若数据存在不可能使映射位置为0
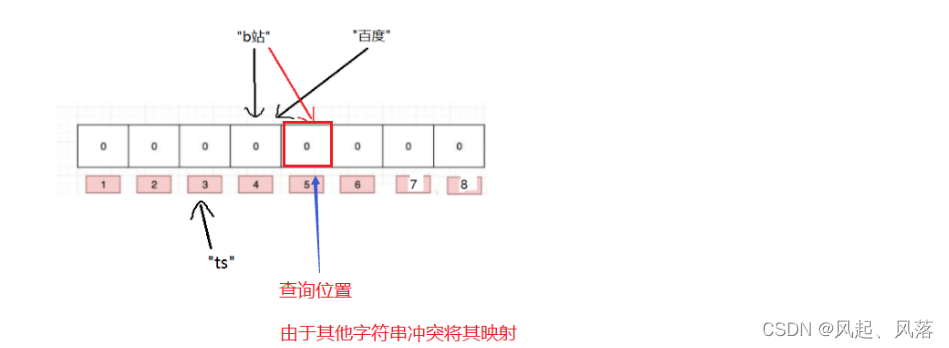
在是不准确的,
ts本来在检查位置是不存在的,但是由于其他字符串发生冲突,正好将其要对ts检查的位置映射了,就会误以为ts存在,导致误判
使用场景及特点
能容忍误判的场景
如:快速判断昵称是否使用过
昵称有可能是由于误判,导致可能创建重复的,但是并不会有什么影响存在
正常来说,手机号是不能放入布隆过滤器中的,若使用有可能误判, 没有注册过,显示用户存在

但是布隆过滤器也是可以做到的,
若当前数据不在,则直接返回false
若当前数据在,有可能存在误判问题,所以去数据库中查找,若在则直接返回数据存在,若不在,则返回false
布隆过滤器的特点
优点:快,节省内存
缺点:存在误判 (数据在)
具体代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
template<size_t N>
class bitset
{
public:
bitset()
{
_bits.resize((N / 8) + 1, 0);
}
void set(size_t x)
{
size_t i = x / 8;//第几个char上
size_t j = x % 8;//char上的第几个比特位
_bits[i] |= (1 << j);
}
void rset(size_t x)
{
size_t i = x / 8;//第几个char上
size_t j = x % 8;//char上的第几个比特位
_bits[i] &= ~(1 << j);
}
bool test(size_t x)//判断在不在
{
size_t i = x / 8;//第几个char上
size_t j = x % 8;//char上的第几个比特位
return _bits[i] & (1 << j);
}
private:
vector<char> _bits;
};
void test_bitset()
{
bitset<100> v;
v.set(10);
cout << v.test(10) << endl;
cout << v.test(15) << endl;
}
//仿函数
struct BKDRHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto e : s)
{
hash += e;
hash *= 31;
}
return hash;
}
};
struct APHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (long i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
size_t ch = s[i];
if ((i & 1) == 0)
{
hash ^= ((hash << 7) ^ ch ^ (hash >> 3));
}
else
{
hash ^= (~((hash) << 11) ^ ch ^ (hash >> 5));
}
}
return hash;
}
};
struct DJBHash
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 5381;
for (auto e : s)
{
hash += (hash << 5) + e;
}
return hash;
}
};
template< size_t N,
class K = string,
class Hash1 = BKDRHash,
class Hash2 = APHash,
class Hash3 = DJBHash>
class BloomFilter //布隆过滤器
{
public:
void set(const K& key)
{
size_t len = N * _X; //整体长度
//将其转换为可以取模的整型值
size_t hash1 = Hash1()(key) % len;
_bs.set(hash1);
size_t hash2 = Hash2()(key) % len;
_bs.set(hash2);
size_t hash3 = Hash3()(key) % len;
_bs.set(hash3);
}
//判断在不在
bool test(const K& key)
{
size_t len = N * _X; //整体长度
//三个位置都在才在,有一个位置不在 则不在
size_t hash1 = Hash1()(key) % len;
if (!_bs.set(hash1))
{
return false;
}
size_t hash2 = Hash2()(key) % len;
if (!_bs.set(hash2))
{
return false;
}
size_t hash3 = Hash3()(key) % len;
_bs.set(hash3);
if (!_bs.set(hash3))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
private:
static const size_t _X = 4;//整数倍
bitset<N* _X> _bs;
};
// 一般是字符串才使用 布隆过滤器
// 所以默认使用字符串类型
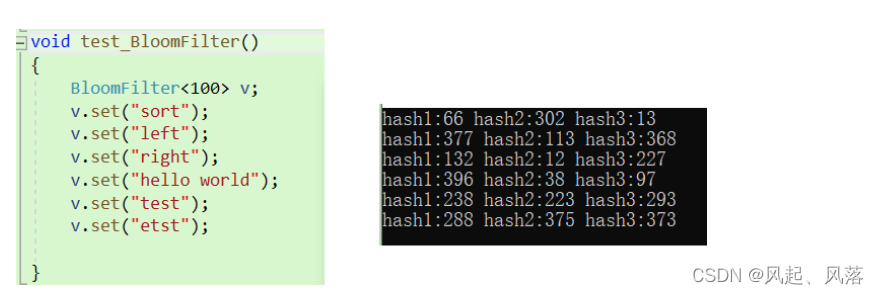
void test_BloomFilter()
{
BloomFilter<100> v;
v.set("sort");
v.set("left");
v.set("right");
v.set("hello world");
v.set("test");
v.set("etst");
}






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结