您现在的位置是:首页 >其他 >【SpringMVC】| 域对象共享数据网站首页其他
【SpringMVC】| 域对象共享数据
目录
1. 使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据(了解)
2. 使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
前期准备
pomx.ml:引入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc-thymeleaf003</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>springmvc-thymeleaf003 Maven Webapp</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<!--指定资源文件的位置-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>
web.xml:配置请求乱码的CharacterEncodingFilter和注册前端控制器DispatcherServlet
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--注册过滤器:解决post请求乱码问题-->
<filter>
<filter-name>encode</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<!--指定字符集-->
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--强制request使用字符集encoding-->
<init-param>
<param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--强制response使用字符集encoding-->
<init-param>
<param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<!--所有请求-->
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encode</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--注册SpringMVC框架-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!--配置springMVC位置文件的位置和名称-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--将前端控制器DispatcherServlet的初始化时间提前到服务器启动时-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<!--指定拦截什么样的请求
例如:http://localhost:8080/demo.action
-->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>springmvc核心配置文件:引入包扫描组件、配置Thymeleaf视图解析器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!--配置包扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zl.controller"/>
<!-- 配置Thymeleaf视图解析器 -->
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="1"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<property name="templateEngine">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver">
<!-- 视图前缀 -->
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/>
<!-- 视图后缀 -->
<property name="suffix" value=".html"/>
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>域对象共享数据
一:向request域共享数据(五种方法)
1. 使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据(了解)
index.html发出请求
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试</h1>
<a th:href="@{/testRequestServletAPI}">使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据</a>
</body>
</html>ActionTest接收请求并存取数据
package com.zl.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@Controller
public class ActionTest {
// 是为了开启就跳转到index.html目录下
@RequestMapping("/")
public String test(){
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/testRequestServletAPI")
public String testRequestServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request){
// 使用原生的ServletAPI存取数据
request.setAttribute("requestScope","hello");
return "success";
}
}
success.html取出数据
注:这是使用的不是jsp,不能直接用${变量名}取出数据;需要借助于thymeleaf!
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<font color="#dc143c" th:text="${requestScope}"></font>
</body>
</html>2. 使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
ModelAndView主要有两个功能:一个模型,一个视图。
模型:指的是向域中共享数据的功能;
视图:指的是根据我们设置的视图名称,经过视图解析器解析,跳转到指定页面的过程。
index.html发出请求
<a th:href="@{/testRequestModelAndView}">使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据</a><br>
ActionTest接收请求并存取数据
①方法的返回值必须是ModelAndView,这样才能被前端控制器DispatcherServlet解析。
②创建ModelAndView对象,调用addObject()方法设置共享的数据。
③调用setViewName()方法,设置要跳转的视图名称,最终返回这个ModelAndView对象。
@RequestMapping("/testRequestModelAndView")
public ModelAndView testRequestModelAndView(){
// 创建ModelAndView对象
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView();
// 处理模型数据,即向请求域request中共享数据
mav.addObject("requestScope","hello,ModelAndView");
//设置视图名称
mav.setViewName("success");
// 返回ModelAndView对象
return mav;
}3. 使用Model向request域对象共享数据
Model就是ModelAndView中的Model,用法和原生的Servlet用法很类似!
index.html发出请求
<a th:href="@{/testRequestModel}">使用Model向request域对象共享数据</a><br>ActionTest接收请求并存取数据
Model向reuqest一样以方法的属性方式存在,然后调用Model对象的addAttreibute()方法存取共享的数据!
@RequestMapping("/testRequestModelw")
public String testRequestModel(Model model){
// 使用model存取共享的数据
model.addAttribute("requestScope","hello,Model");
return "success";
}4. 使用map向request域对象共享数据
这里的Map集合就是前面我们学过的普通Map,用法和Model、原生的Servlet用法很类似!
index.html发出请求
<a th:href="@{/testRequestMap}">使用Map向request域对象共享数据</a><br>ActionTest接收请求并存取数据
调用map集合的put()方法存取共享的数据!
@RequestMapping("/testRequestMap")
public String testRequestMap(Map<String,Object> map){
// 使用map存取共享的数据
map.put("requestScope","hello,Map");
return "success";
}5. 使用ModelMap向request域对象共享数据
ModelMap和Model的用法是一模一样的!
index.html发出请求
<a th:href="@{/testRequestModelMap}">使用ModelMap向request域对象共享数据</a><br>ActionTest接收请求并存取数据
和Model一样也是调用addAttribute()方法存取共享数据;但是因为ModelMap本身是继承LinkedHashMap集合,所以使用put()方法也可以存取共享数据。
@RequestMapping("/testRequestModelMap")
public String testRequestModelMap(ModelMap modelMap){
// 使用modelMap存取共享的数据
modelMap.addAttribute("requestScope","hello,ModelMap");
// 调用put方法也可以
modelMap.put("requestScope","hello,ModelMap");
return "success";
}6. Model、ModelMap、Map的关系
现象:Model、ModelMap、Map输出的引用格式是相同的!
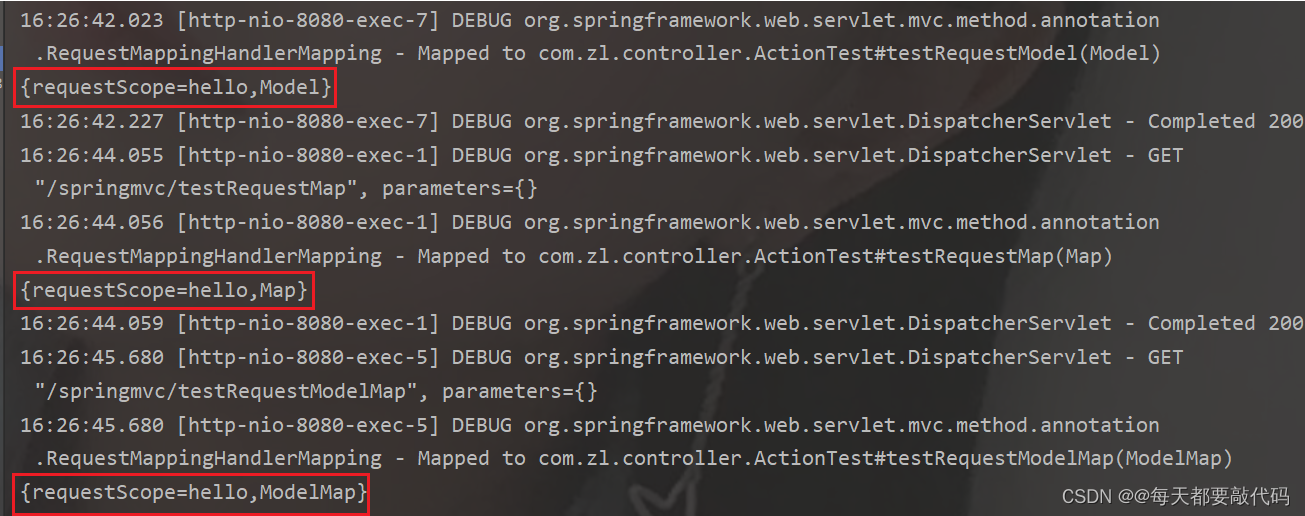
解释:说明调用的是同一个类的toString方法;实际上Model、ModelMap、Map类型的参数其实本质上都是 BindingAwareModelMap 类型的!
怎么验证?通过反射机制!调用getClass()方法获取当前类,在调用getName()方法就可以获取到参数的类型。例如:modelMap.getClass().getName()

通过源码解析
对于Model:说明是一个顶级接口
public interface Model {}对于Map:就是前面我们学习的Map集合
public interface Map<K,V> {对于ModelMap继承了 LinkedHashMap,本质上就是一个Map
public class ModelMap extends LinkedHashMap<String, Object> {}此时Map和ModelMap已经建立了关系,目前就看Model和ModelMap(Map)有什么关系?
选定Model,ctrl+h查看它的继承结构,发现有一个子类BindingAwareModelMap类
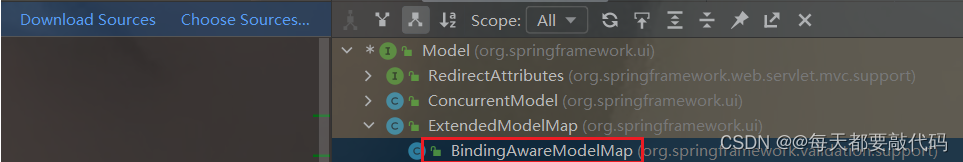
通过点开原码发现BindingAwareModelMap又是继承ExtendedModelMap的
public class BindingAwareModelMap extends ExtendedModelMap {}而ExtendedModelMap又是继承ModelMap实现Model的,此时就使Model和ModelMap建立了联系
public class ExtendedModelMap extends ModelMap implements Model {}结果:BindingAwareModelMap间接或直接继承或实现了Model、ModelMap、Map,是它们的子类,可以通过它去实例化对象!
小总结:以上的五种方式:无论是原生的Servlet、ModelAndView、Model、Map、ModelMap最终都是把数据封装到ModelAndView当中去!
二:向session域共享数据
向session域中共享数据,建议使用原生的ServletAPI,比较简单!
index.html发出请求
<a th:href="@{/testSessionServletAPI}">使用ServletAPI向session域对象共享数据</a><br>
ActionTest接收请求并存取数据
注意:此时的方法参数是HttpSession对象!
@RequestMapping("/testSessionServletAPI")
public String testSessionServletAPI(HttpSession session){
session.setAttribute("sessionScope","hello session");
return "success";
}success.html取出数据
注意:对于session域中的数据,访问时不像request域中的数据那样,直接使用${变量名}就可以访问到;必须使用${session.变量名}的方式进行访问!
<font color="#dc143c" th:text="${session.sessionScope}"></font>三:向application域共享数据
application域本质上就是ServletContext(上下文对象)!所以我们只需要获取到ServletContext对象即可!
获取ServletContext对象的方式有多种,例如:
(1)通过request对象获取
ServletContext application=request.getServletContext();(2)通过session对象获取
ServletContext application=request.getServletConfig().getServletContext();index.html发出请求
<a th:href="@{/testApplicationServletAPI}">使用ServletAPI向application域对象共享数据</a><br>ActionTest接收请求并存取数据
获取ServletContext对象的方式很多,例如:request、session、ServletConfig对象!
@RequestMapping("/testApplicationServletAPI")
public String testApplicationServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request){
// 通过request
ServletContext application = request.getServletContext();
// 通过session
// ServletContext application = request.getSession().getServletContext();
application.setAttribute("applicationScope","hello application");
return "success";
}success.html取出数据
必须使用${application.变量名}的方式进行访问!
<font color="#dc143c" th:text="${application.applicationScope}"></font>





 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结