您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >systemctl 命令设置开机自启动失败网站首页学无止境
systemctl 命令设置开机自启动失败
1.案例现象
我在 3 月 31日的时候发表了一篇《shell 脚本之一键部署安装 Nginx 》,介绍了如何通过 shell 脚本一键安装 Nginx
我脚本中执行了 Nginx 开机自启动的命令,当我使用 systemctl status nginx 命令复核的时候,我发现 Nginx 服务设置开机自启动并没有生效

使用下面的命令设置一下
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable nginx.service
通常来说,设置开机自启动其实就是将 nginx.service 这个文件创建一个软连接然后挂在/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ 目录下面
举个例子,我要将 atd.service 设置开机自启动
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable atd.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/atd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/atd.service.
可以看到设置了开机自启动的服务都在这个目录下面有软连接,但是没有 Nginx 服务
我们使用下面的命令来看下 nginx 服务有没有设置开机自启动
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl is-enabled nginx.service
static
奇怪,怎么 systemctl enable nginx.service 没有生效?
手动创建一下软链接试试
[root@localhost ~]# ln -s /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service
发现设置开机自启动成功
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl is-enabled nginx.service
enabled
问题:使用 systemctl 命令不能设置 nginx 服务开机自启动,需要手动去挂载软连接
2.定位问题
在排查问题之前,我先给大家简单介绍一下 Linux 中的服务(service)
daemon 与 服务(service)
我们知道,在 Linux 中,服务(service)其实就是一个个程序,它们能够实现某一功能、提供某一服务
但通常我们在查阅类 Unix 系统相关的技术文档时,又经常会看到“请启动某某 daemon 来提供某某功能”
那么这个 daemon 到底是啥意思?它跟 service 有什么区别?
简单点来说,系统为了实现某些功能必须要提供一些服务(比如想要实现负载均衡的功能需要提供 Nginx 服务)
但是提供的 service 需要程序的运作(例如你需要启动 Nginx 进程),所以我们一般认为使系统能够提供某些 service 的程序称作 daemon(例如使系统能够提供负载均衡服务的程序 nginx 为 daemon)
看到这里小伙伴们可能都晕了,说实话我第一次看到的时候也是这样的
其实你不必去区分什么是 daemon 和 service,因为提供某一 service 是需要一个 daemon 在运作,没有这个运作的 daemon 就不会有这个 service
无论是命令行模式(runlevel 3),还是图像界面模式(runlevel 5),我们在开机进入 Linux 主机之后,系统已经开始提供很多 service 了(例如 sshd )
那么这些 service 是如何启动的,系统又是怎么管理它们的呢?
在早期 Linux 是使用 SystemV 来管理服务的,启动系统服务的管理方式被称为 SysV 的 init 脚本处理方式——系统内核第一个程序是 init,然后 init 去唤起所有系统需要的服务
启动:/etc/init.d/daemon start
关闭:/etc/init.d/daemon stop
重启:/etc/init.d/daemon restart
状态查看:/etc/init.d/daemon status
SystemV 管理服务的开机自启动有两种方式:
- 通过挂软连接的方式
将 /etc/rc.d/rc[0-6]/SXX 服务名字挂载到 /etc/init.d/ 下(其中 SXX 中的 S 表示启动该服务,XX 是数字,为启动的顺序)
[root@localhost ~]# ll /etc/rc.d/rc3.d
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 17 7月 11 2022 S10network -> ../init.d/network
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 18 10月 28 15:06 S98filebeat -> ../init.d/filebeat
- 通过 chkconfig 命令
创建软连接的方式比较麻烦,一般来说都是用命令来管理
#设置开机自启动
chkconfig daemon on
#关闭开机自启动
chkconfig daemon off
#查看自启动状态
chkconfig --list daemon
但是 CentOS 7 之后就放弃了使用多年的 SystemV ,改用 systemd 来管理服务
systemd 管理服务
systemd 将过去所谓的 daemon 程序称作一个个服务单位(unit),而每个 unit 根据功能来区分成不同的类型(type):
- 系统服务(service)
- 负责网络数据监听与交换的服务(socket)
- 快照服务(sanpshot)
而且 systemd 将许多的 unit 集合成一个所谓的 target 项目,你执行某个 target 其实就是执行 target 下的多个 unit
可能有小伙伴觉得,这么多 unit 分成不同的 type,然后又被合集到不同的 target ,管理起来不会很麻烦吗
其实也还好,因为相关的文件都存放在下面的目录当中了
#每个服务启动脚本所在目录,有点像 SysV 中的 /etc/init.d/
/usr/lib/systemd/system/
#设置了开机自启动的服务会将其启动脚本挂载到该目录下,有点像 SysV 中的 /etc/rc.d/
/etc/systemd/system/
总结,系统开机会不会执行某些服务是看 /etc/systemd/system/ 目录下有没有该服务的启动脚本,而服务的启动脚本是放在 /usr/lib/systemd/system/下的
systemctl 命令
systemd 来管理服务的方式是通过 systemctl 命令,相较于 SysV 通过 service / chkconfig / setup / init 一堆命令,systemd 管理服务的方式简单多了
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl [command] [unit]
command 主要有:
start: 启动该服务
stop: 停止该服务
restart: 重启该服务
reload: 重启该服务的启动脚本(即 /usr/lib/systemd/system/ 下的文件)
enable: 设置开机自启动
disable: 关闭开机自启动
status: 查看该服务的状态
is-active: 查看该服务目前有没有启动
is-enable:查看该服务有没有设置开机自启动
PS:关闭服务除了 systemctl 命令,也能用 kill 命令的方式,但是这两个命令不要混用!
systemctl start nginx
#关闭 nginx 时就只能用 systemctl 命令,不要使用 nginx -s stop
systemctl stop nginx
服务的状态
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl status nginx.service
● nginx.service - The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; static; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 四 2023-03-30 08:42:37 CST; 1 weeks 1 days ago
- 服务的当前状态:
- active (running):表示服务正在运行
- active (exited):表示该服务执行一次就正常结束,目前没有执行
- active (waiting):表示该服务正在运行,不要需要等待其他事件执行之后才能继续处理
- inactive:表示服务目前关闭,没有运行
- 服务预设状态:
- enable:开机的时候将自启动
- disable:开机的时候不会自启动
- static:这个服务不会开机自启动,但是有可能会被其他开机自启动的服务来唤醒(依赖性)
- mask:无论如何都不会被启动,因为已经被强制注销
服务的启动文件
前面我们说过,服务的启动脚本文件放在 /usr/lib/systemd/system/下的,如果需要对服务的启动脚本文件修改,需要进入到该目录下(官方不建议直接修改该目录下的文件,但是会比较麻烦且繁琐)

我们就拿 sshd.service 举例,来了解下服务的启动脚本里面的配置字段
[root@minion2 ~]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service
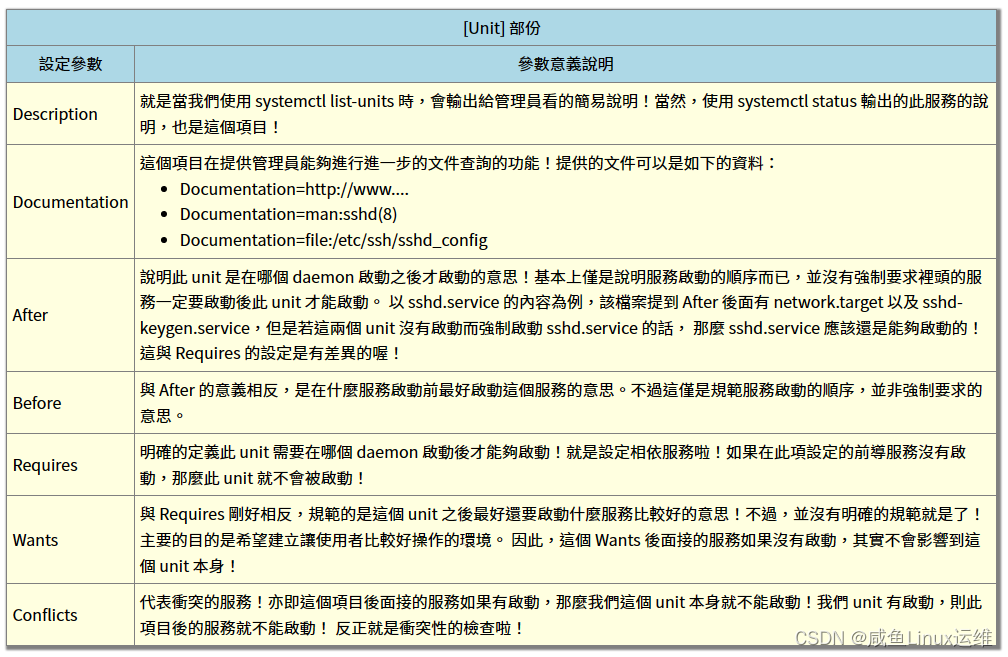
[Unit]
Description=OpenSSH server daemon
Documentation=man:sshd(8) man:sshd_config(5)
After=network.target sshd-keygen.service
Wants=sshd-keygen.service
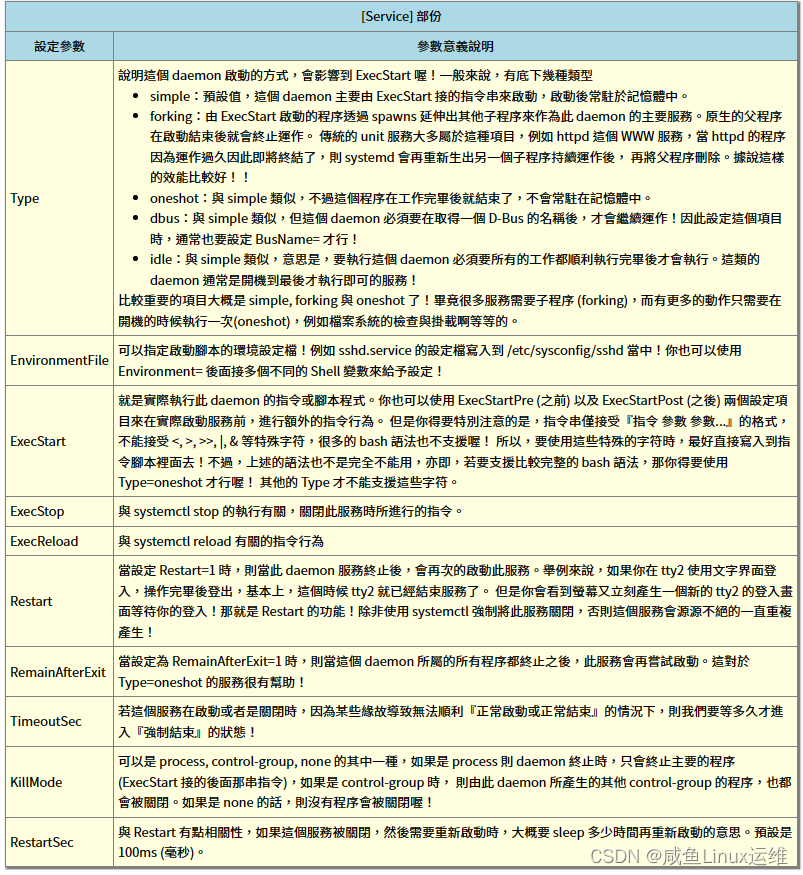
[Service]
Type=notify
EnvironmentFile=/etc/sysconfig/sshd
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/sshd -D $OPTIONS
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
KillMode=process
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=42s
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
分析上面文件中的内容,我们可以看到分成了三个部分(block):
- [Unit]
- unit(即服务)本身的说明,以及与其他服务的依赖性设定(After、Wants 字段)
- [Service]
- 还有 [Socket], [Timer], [Mount], [Path] 等等,不同的 type 就用不同的字段
- 我们拿的是 sshd.service,所以就是 [Service]
- 这个部分中主要规定了服务的启动脚本、环境文件名、重启方式等等
- [Install]
- 表示这个服务安装到哪个 target 下面去
- 这部分与
systemctl enable或systemctl disable命令相结合,用于 enable 或 disable 一个服务
下面我将分别列出三个部分的一些常见配置字段

3.解决问题
现在我们已经大致对 Linux 的服务有了一个初步了解
我们回到刚开始的问题:nginx 服务无法通过 systemctl 命令设置开机自启动,手动挂载软连接之后自启动状态不是 enable ,而是 static
既然是跟 systemctl 相关的,我们去看下 nginx 的服务启动脚本
cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
[Unit]
Description=The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server
After=network-online.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
Wants=network-online.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
ExecReload=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
KillSignal=SIGQUIT
TimeoutStopSec=5
KillMode=process
PrivateTmp=true
可以看到,这台机器上 nginx 的服务启动脚本只有两个部分([Unit]、[Service]),并没有 [Install]
而 [Install] 部分往往是跟服务的开机自启动相关


我们加上 [Install]
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
其中 multi-user.target 表示命令行模式(即等效于系统运行级别为 3 )
而 WantedBy 表示该服务放在哪个 target 下,一般来讲 WantedBy 对应的 target 为指定系统的运行级别
然后重启一下 nginx 启动脚本文件
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl daemon-reload
设置开机自启动,发现创建软连接成功了
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable nginx.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.
看下状态
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl is-enabled nginx.service
enabled
总结:
- 一般来讲,服务无法设置开机自启动首先考虑是不是服务启动脚本配置有问题(
/usr/lib/systemd/system/目录下),这种情况常见于编译安装的时候需要自己编写服务启动文件 - 服务能够开机自启动其实就是将
/usr/lib/systemd/system/目录下的服务启动脚本挂载到了/etc/systemd/system/下,一般是挂载到/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/- multi-user.target.wants:表示启动了 multi-user.target 之后(即系统启动且运行级别为 3,为系统的默认启动 target)这个目录下的文件都会跟着启动
systemctl status命令显示的内容里面有一个vendor preset: disabled字段,这个表示该服务首次安装之后不会自启动,需要手动启动(systemctl enable)






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结