您现在的位置是:首页 >技术交流 >LeetCode 1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix【BFS,A星】中等网站首页技术交流
LeetCode 1091. Shortest Path in Binary Matrix【BFS,A星】中等
本文属于「征服LeetCode」系列文章之一,这一系列正式开始于2021/08/12。由于LeetCode上部分题目有锁,本系列将至少持续到刷完所有无锁题之日为止;由于LeetCode还在不断地创建新题,本系列的终止日期可能是永远。在这一系列刷题文章中,我不仅会讲解多种解题思路及其优化,还会用多种编程语言实现题解,涉及到通用解法时更将归纳总结出相应的算法模板。
为了方便在PC上运行调试、分享代码文件,我还建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/memcpy0/LeetCode-Conquest。在这一仓库中,你不仅可以看到LeetCode原题链接、题解代码、题解文章链接、同类题目归纳、通用解法总结等,还可以看到原题出现频率和相关企业等重要信息。如果有其他优选题解,还可以一同分享给他人。
由于本系列文章的内容随时可能发生更新变动,欢迎关注和收藏征服LeetCode系列文章目录一文以作备忘。
给你一个 n x n 的二进制矩阵 grid 中,返回矩阵中最短 畅通路径 的长度。如果不存在这样的路径,返回 -1 。
二进制矩阵中的 畅通路径 是一条从 左上角 单元格(即,(0, 0))到 右下角 单元格(即,(n - 1, n - 1))的路径,该路径同时满足下述要求:
- 路径途经的所有单元格的值都是
0。 - 路径中所有相邻的单元格应当在 8 个方向之一 上连通(即,相邻两单元之间彼此不同且共享一条边或者一个角)。
畅通路径的长度 是该路径途经的单元格总数。
示例 1:
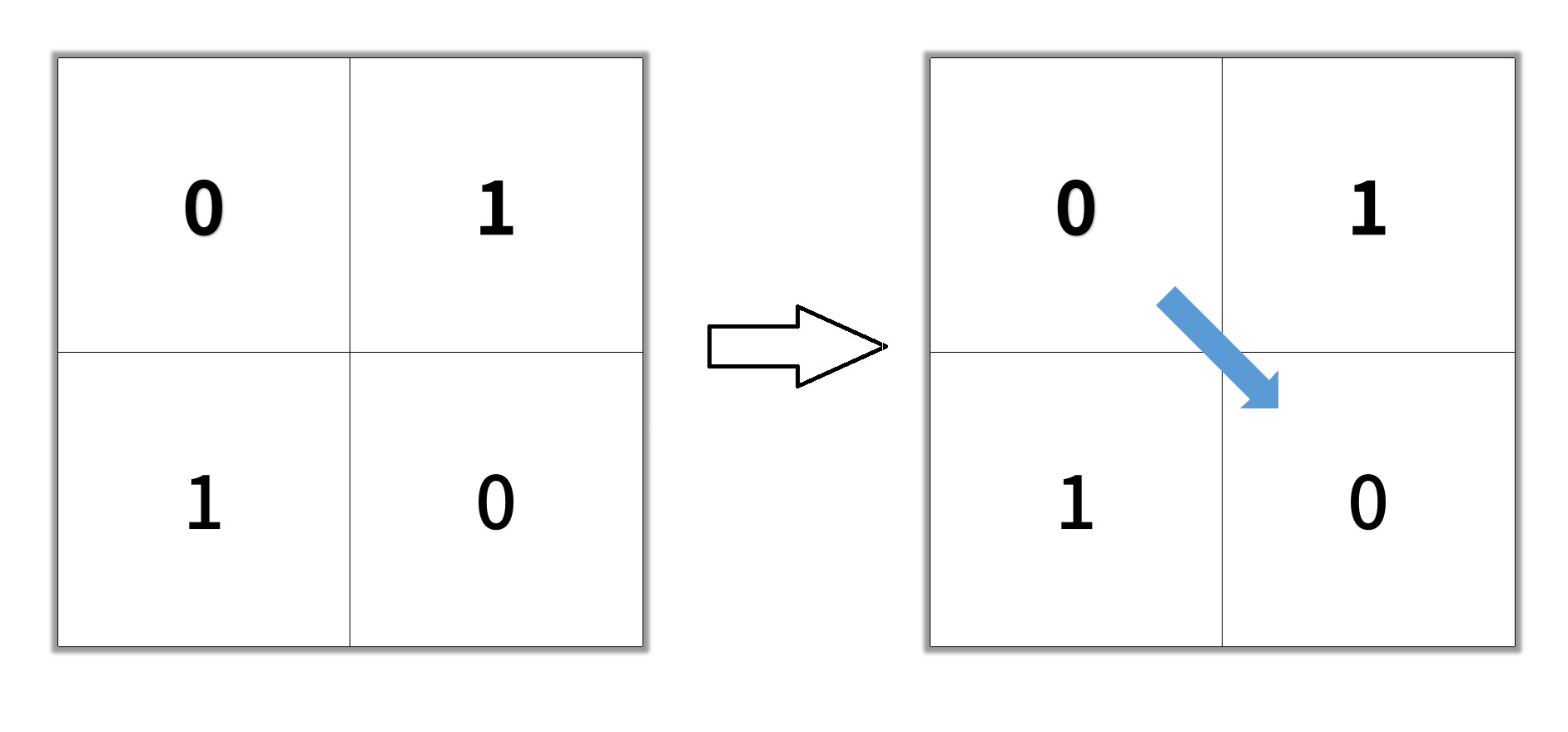
输入:grid = [[0,1],[1,0]]
输出:2
示例 2:
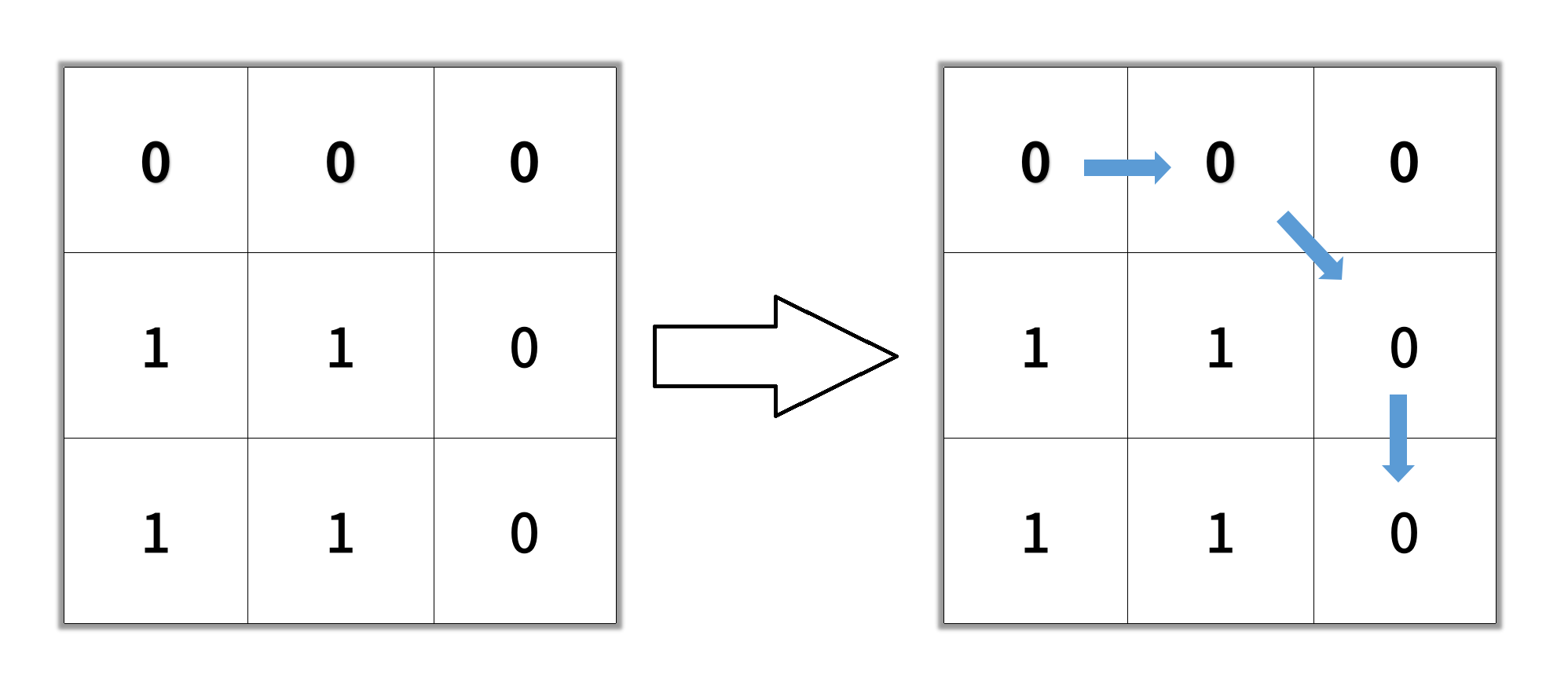
输入:grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
输出:4
示例 3:
输入:grid = [[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
输出:-1
提示:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 100grid[i][j]为0或1
解法1 BFS
使用宽度优先算法,对八个方向一层层的搜索,从出发点开始,第一次遍历到终点时经过的那条路径就是最短的路径。因为这条路径没有多绕一个不相关节点,所以它是最短的,也符合题目最短畅通路径。
要注意的是,出发点和目的地都可能是 1 1 1 ,这时直接返回 − 1 -1 −1 表示不可通过即可。
class Solution {
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
if (grid[0][0] == 1 || grid[n - 1][n - 1] == 1) return -1; // 不可能出发或到达
if (n <= 2) return n; // 1x1 2x2
var q = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
int[][] d = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 1}};
q.offer(0);
grid[0][0] = 1;
int step = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
int u = q.poll();
int x = u / n, y = u % n;
if (x == n - 1 && y == n - 1) return step;
for (int j = 0; j < 8; ++j) {
int tx = x + d[j][0], ty = y + d[j][1];
if (tx >= 0 && tx < n && ty >= 0 && ty < n && grid[tx][ty] == 0) {
q.offer(tx * n + ty);
grid[tx][ty] = 1;
}
}
}
++step;
}
return -1;
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) ,为二进制矩阵的大小。
- 空间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
解法2 A* Search启发式搜索
在说明 A* 算法前,先将上述代码改造成「可以延伸出 A* 算法」的形式:
class Solution {
static class Node {
public int x, y;
public int step;
public Node(int start, int end, int step) {
this.x = start;
this.y = end;
this.step = step;
}
};
private int[][] d = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 1}};
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
if (grid[0][0] == 1 || grid[n - 1][n - 1] == 1) return -1; // 不可能出发或到达
if (n <= 2) return n; // 1x1 2x2
Node node = new Node(0, 0, 2);
Deque<Node> q = new ArrayDeque();
q.addLast(node);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = q.removeFirst();
int x = cur.x;
int y = cur.y;
int step = cur.step;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int tx = x + d[i][0];
int ty = y + d[i][1];
if (tx >= 0 && tx < n && ty >= 0 && ty < n && grid[tx][ty] == 0) {
// 找到终点
if (tx == n - 1 && ty == n - 1) return step;
q.addLast(new Node(tx, ty, step + 1));
grid[tx][ty] = 1; // 标记遍历过,避免重复
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
在这一代码的基础上,稍作修改。A* Search中不再使用简单的队列,而是改用优先队列,将最有前途的点优先弹出查找。相比普通队列按顺序依次弹出,要智能很多,而这个算法的启发式函数很重要,如果没有选好、速度反而会变慢。
这里顺便加了个路径记录,有些题目输出路径可能需要:顺着终点方向,找到它的父亲,再找到父亲的父亲……,如此依次回溯,就能找到从起点到终点的一条最佳路径了。本题可以去掉。
下面使用的启发式函数是欧几里得距离:
class Solution {
static class Node {
public int x, y;
public int step;
public double cost; // 用于启发式函数评估
public Node(int start, int end, int step) {
this.x = start;
this.y = end;
this.step = step;
}
public Node(int start, int end, int step, double cost) {
this.x = start;
this.y = end;
this.step = step;
this.cost = cost;
}
// 用于输出路径
public Node parent = null;
public Node getParent() { return parent; }
public void setParent(Node parent) { this.parent = parent; }
// 用于优先队列
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Node node = (Node) o;
return x == node.x && y == node.y;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(x, y); }
};
private int pathLength(Node node) { // 输出路径的方法
if (node == null) return 0;
int pathLength = 1;
while (node.getParent() != null) {
node = node.getParent();
pathLength++;
}
return pathLength;
}
private int[][] d = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 1}};
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
if (grid[0][0] == 1 || grid[n - 1][n - 1] == 1) return -1; // 不可能出发或到达
if (n <= 2) return n; // 1x1 2x2
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>(10, (i, j) -> Double.compare(i.cost, j.cost));
q.add(new Node(0, 0, 1, 0));
grid[0][0] = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = q.poll();
int x = cur.x;
int y = cur.y;
int step = cur.step;
if (x == n - 1 && y == n - 1) return step;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int tx = x + d[i][0];
int ty = y + d[i][1];
if (tx >= 0 && tx < n && ty >= 0 && ty < n && grid[tx][ty] == 0) {
double cost = cur.cost + 1 + distance(tx, ty, x, y); // 之前的距离+1+现在新增的距离
Node next = new Node(tx, ty, step + 1, cost);
if (q.contains(next)) continue; // 不能重复入队
next.setParent(cur); // 保存路径方便后续打印
q.add(next);
grid[tx][ty] = 1; // 标记遍历过,避免重复
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public double distance(int x, int y, int tx, int ty) { // 启发式函数,使用两点距离坐标公式
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(tx - x, 2) + Math.pow(ty - y, 2));
}
}
下面将启发式函数改为切比雪夫距离。 距离计算方法有很多,选择合适的启发式函数有利于速度的提升。这题可以用好几种启发式函数:
-
曼哈顿距离 Manhattan Distance : 一般只能在四个方向上移动时用(右、左、上、下)
-
对角线距离 Diagonal Distance : 当我们只允许向八个方向移动时用(国际象棋中的王移动方式那种)
-
欧几里得距离 Euclidean Distance : 不受限制,允许向任何方向移动时。
-
切比雪夫距离:对于平面上的两个点 x = ( x 0 , x 1 ) x = (x_0, x_1) x=(x0,x1) 和 y = ( y 0 , y 1 ) y = (y_0, y_1) y=(y0,y1) ,设它们横坐标距离之差为 d x = ∣ x 0 − y 0 ∣ dx = |x_0 - y_0| dx=∣x0−y0∣ ,纵坐标距离之差为 d y = ∣ x 1 − y 1 ∣ dy = |x_1 - y_1| dy=∣x1−y1∣ ,对于以下三种情况,我们可以分别计算出从 x x x 移动到 y y y 的最少次数:
- d x < d y d_x < d_y dx<dy :沿对角线移动 d x d_x dx 次,再竖直移动 d y − d x d_y - d_x dy−dx 次,总计 d x + ( d y − d x ) = d y d_x + (d_y - d_x) = d_y dx+(dy−dx)=dy 次;
- d x = = d y d_x == d_y dx==dy :沿对角线移动 d x d_x dx 次;
- d x > d y d_x > d_y dx>dy :沿对角线移动 d y d_y dy 次,再水平移动 d x − d y d_x - d_y dx−dy 次,总计 d y + ( d x − d y ) = d x d_y + (d_x - d_y) = d_x dy+(dx−dy)=dx 次。
可以发现,对于任意一种情况,从 x x x 移动到 y y y 的最少次数为 d x d_x dx 和 d y d_y dy 中的较大值 max ( d x , d y ) max(d_x, d_y) max(dx,dy) ,这也被称作 x x x 和 y y y 之间的 切比雪夫距离。
class Solution {
int n = 0;
public class Node {
public int x, y;
public int cost; // 用于启发式函数评估
public Node(int start, int end, int step) {
this.x = start;
this.y = end;
this.cost = distance(x, y, step);
}
public int distance(int x, int y, int step) {
return step + Math.max(n - 1 - x, n - 1 - y); // 已走距离+到目标的切比雪夫距离
}
};
private int[][] d = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 1}};
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {
n = grid.length;
if (grid[0][0] == 1 || grid[n - 1][n - 1] == 1) return -1; // 不可能出发或到达
if (n <= 2) return n; // 1x1 2x2
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(v -> v.cost)); // 小顶堆 // (a, b) -> a.cost - b.cost
q.add(new Node(0, 0, 1));
grid[0][0] = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = q.poll();
int x = cur.x;
int y = cur.y;
if (x == n - 1 && y == n - 1) return grid[x][y];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int tx = x + d[i][0];
int ty = y + d[i][1]; // 注意判断 grid[tx][ty] > grid[x][y] + 1
if (tx >= 0 && tx < n && ty >= 0 && ty < n && (
grid[tx][ty] == 0 || grid[tx][ty] > grid[x][y] + 1)) {
grid[tx][ty] = grid[x][y] + 1; // 标记遍历过,避免重复
q.add(new Node(tx, ty, grid[tx][ty]));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结