您现在的位置是:首页 >技术杂谈 >leetcode刷题(6)网站首页技术杂谈
leetcode刷题(6)
各位朋友们大家好,今天是我的leetcode刷题系列的第六篇。这篇文章将与队列方面的知识相关,因为这些知识用C语言实现较为复杂,所以我们就只使用Java来实现。
设计循环队列
题目要求
设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
你的实现应该支持如下操作:
MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。
Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。
deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。
isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。
isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。
这是题目提供的接口
class MyCircularQueue {
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
}
public boolean deQueue() {
}
public int Front() {
}
public int Rear() {
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
}
public boolean isFull() {
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/
用例输入
示例:
MyCircularQueue circularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3); // 设置长度为 3
circularQueue.enQueue(1); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(2); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(3); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 false,队列已满
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 3
circularQueue.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.deQueue(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 true
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 4
提示
所有的值都在 0 至 1000 的范围内;
操作数将在 1 至 1000 的范围内;
请不要使用内置的队列库。
做题思路
在做这个题之前我们需要知道什么是循环队列。普通的队列我们应该知道吧,队列是一种数据结构,他的特点是一端进,一端出,先进先出(FIFO)。但是当它出队列了之后它队头的空间就被空出来了,我们插入数据的时候又只能从队尾插入,所以我们队头的空间就得不到利用了,这就造成了空间的浪费。而我么循环链表的原理是,当我们的队尾到达了数组的末尾时,我们再回来利用队头已经出去了的空间。
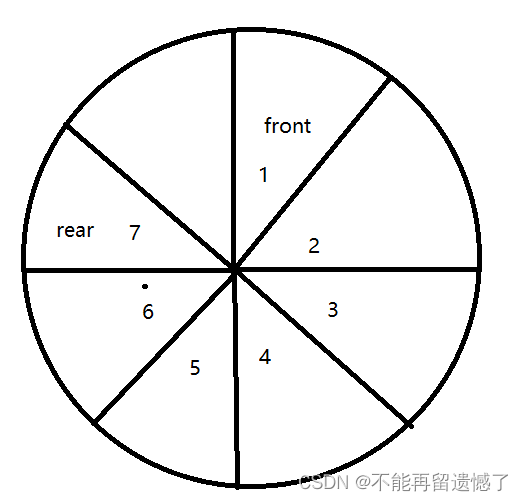
当队列里面为空时,front和rear都指向数组下表为0的位置,当向队列中插入数据的时候我们的rear就向后移动,rear = (rear+1)%length,当(rear+1)%length == front的时候说明队列满了。
代码实现
class MyCircularQueue {
//用数组实现队列
private int[] elem;
//队列的头
private int front;
//队列的尾
private int rear;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
//这里我们浪费一个空间来判断队列是否满了
this.elem = new int[k+1];
}
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()) {
return false;
}
this.elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
front = (front+1)%elem.length;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return elem[front];
}
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
//因为rear总是指向队列尾的下一个位置,
//所以我们返回队尾的值的时候就返回rear的前一个位置的值,
//但是当rear为0时,我们不能返回-1,我们返回数组下标最大的值
int index = (rear == 0) ? elem.length-1:rear-1;
return elem[index];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if(front == rear) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear+1)%elem.length == front;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/
用栈实现队列
题目要求
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
这是题目提供的接口
class MyQueue {
public MyQueue() {
}
public void push(int x) {
}
public int pop() {
}
public int peek() {
}
public boolean empty() {
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
用例输入
示例 1:
输入:
[“MyQueue”, “push”, “push”, “peek”, “pop”, “empty”]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
提示
1 <= x <= 9
最多调用 100 次 push、pop、peek 和 empty
假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用 pop 或者 peek 操作)
做题思路
我们都知道栈和队列的特点是不同的,栈是一端进出,先进后出(FILO),这与队列的一端进一端出,先进先出(FIFO)是不一样的。也就是我们用一个栈来实现队列是很难的,所以我们需要用两个栈stack1和stack2来实现队列。当我们插入数据的时候,如果satck2不为空,需要先将stack2中的数据弹出并插入到satck1中,然后再将需要插入的数据插入到stack1中,当我们取出数据的时候我们就将satack1中的数据弹出并插入到satck2中,然后我们对stack2进行弹出。
我们先来看个例子:先push1,2,3,4,然后pop,再push5
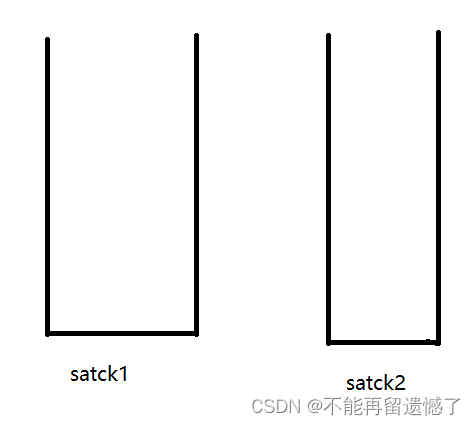
插入1,2,3,4
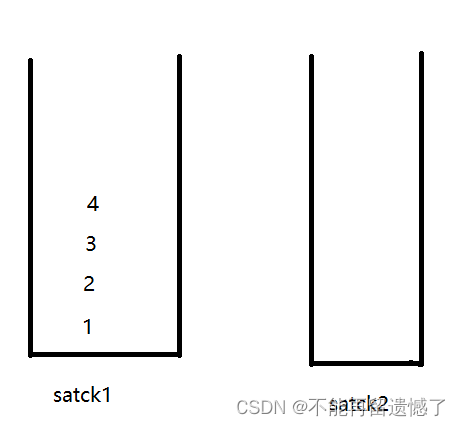
取出数据
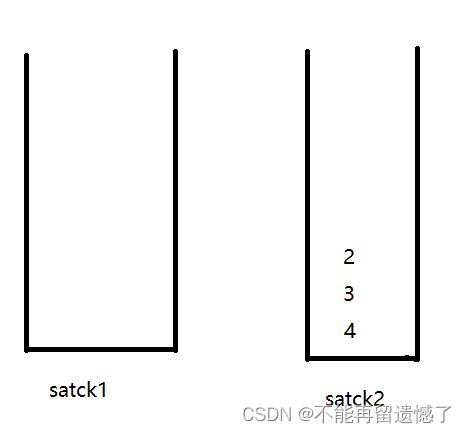
插入5
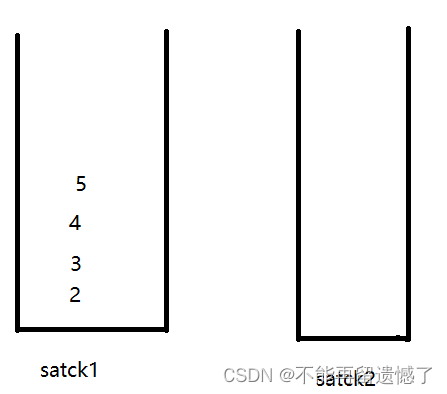
取出数据
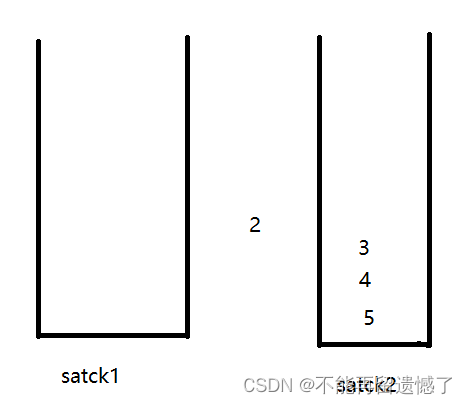
代码实现
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
while(!stack2.isEmpty()) {
stack1.push(stack2.pop());
}
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(stack2.isEmpty()) {
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
用队列实现栈
题目要求
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
用例输入
示例:
输入:
[“MyStack”, “push”, “push”, “top”, “pop”, “empty”]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]
解释:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
这是题目提供的接口
class MyStack {
public MyStack() {
}
public void push(int x) {
}
public int pop() {
}
public int top() {
}
public boolean empty() {
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
做题思路
这个题目我们同样只使用一个队列是无法实现栈的,所以我们还是需要两个队列qu1和qu2。我们插入数据就插入到非空队列中,如果两个队列都为空,我们就插入到qu1中;当我们需要取出数据的时候,我们需要将非空队列中size-1个数据弹出并插入到那个空队列中,然后再弹出非空队列中剩下的那个数据就是我们需要的数据。
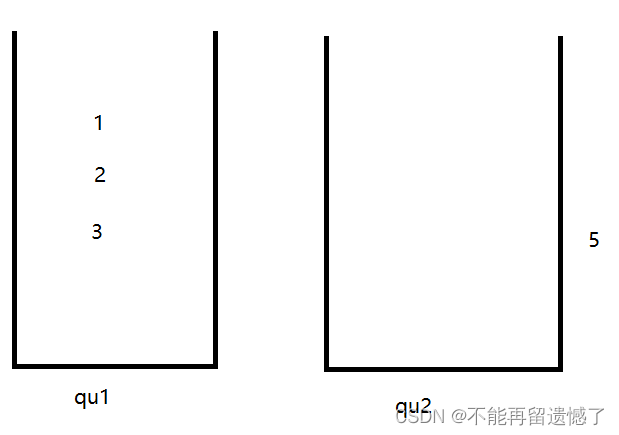
举个例子:我们需要先插入1,2,3,4,然后弹出一次,再插入5,再弹出。
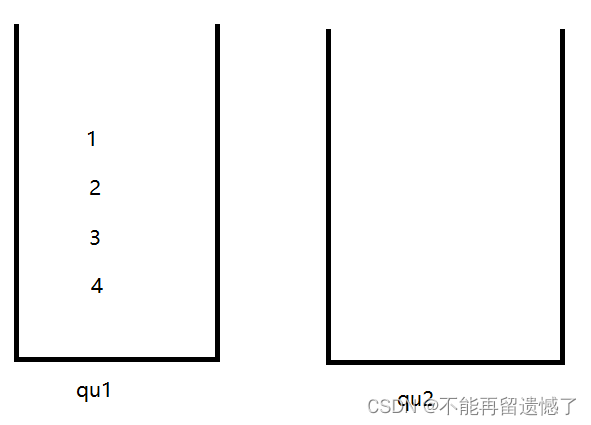
弹出4
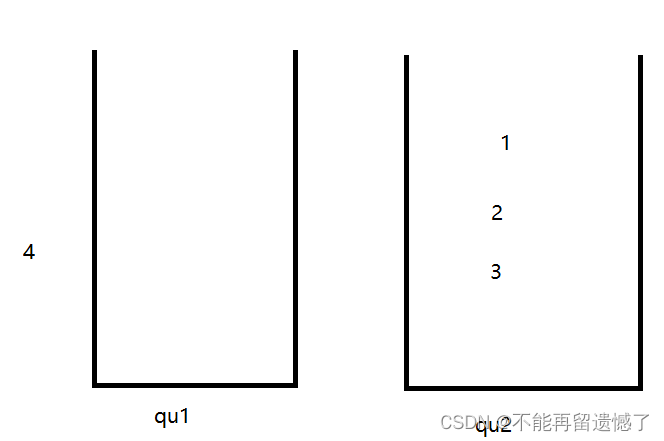
插入5
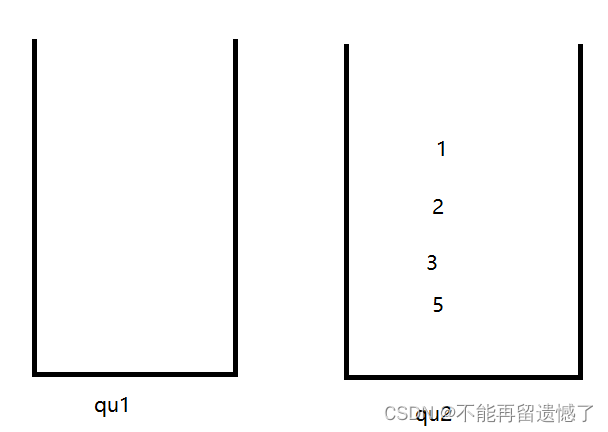
弹出5
代码实现
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> qu1;
private Queue<Integer> qu2;
public MyStack() {
qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
qu1.offer(x);
} else if(!qu2.isEmpty()) {
qu2.offer(x);
} else {
qu1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int size = qu1.size();
for(int i = 0; i<size-1; i++) {
int val = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(val);
}
return qu1.poll();
} else {
int size = qu2.size();
for(int i = 0; i<size-1; i++) {
int val = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(val);
}
return qu2.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
int val1 = -1;
if(!qu1.isEmpty()) {
int size = qu1.size();
for(int i = 0; i<size; i++) {
int val = qu1.poll();
val1 = val;
qu2.offer(val);
}
} else {
int size = qu2.size();
for(int i = 0; i<size; i++) {
int val = qu2.poll();
val1 = val;
qu1.offer(val);
}
}
return val1;
}
public boolean empty() {
return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结