您现在的位置是:首页 >技术交流 >单链表————经典面试题LeetCode网站首页技术交流
单链表————经典面试题LeetCode
- 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有结点
- 反转一个单链表。
- 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
- 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
- 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有结点组成的。
- . 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
- 链表的回文结构。
- 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有结点
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
思路1: 把不等于定值 val 的所有结点 拿下了尾插
思路2: 在原链表上等于定值 val 的所有结点 全部释放
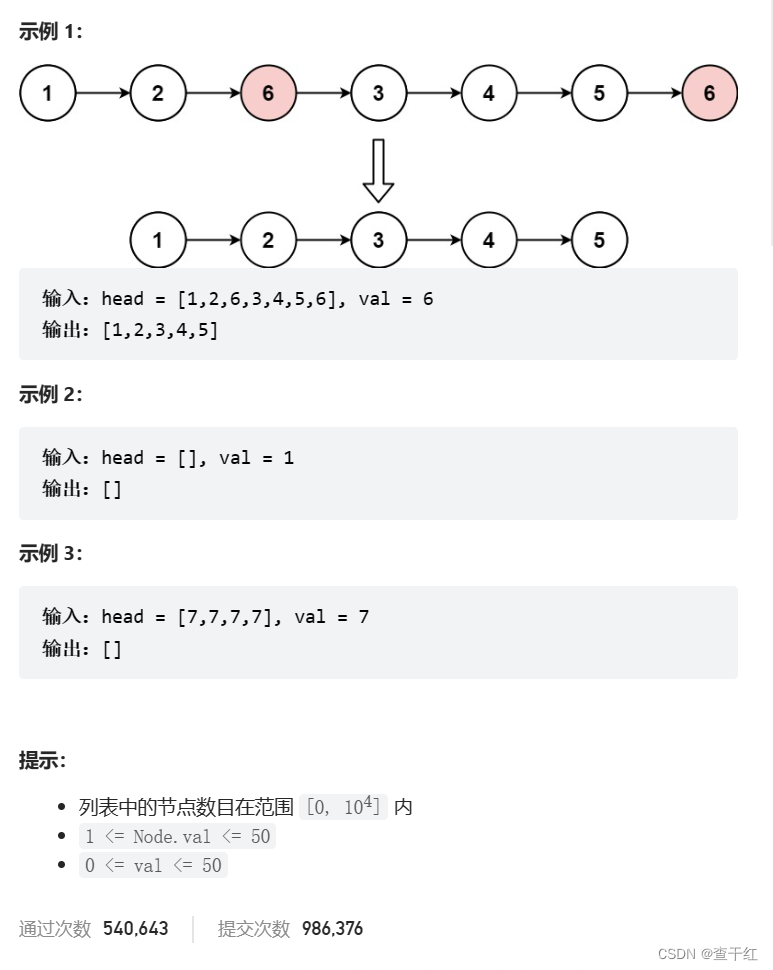
思路1: 把不等于定值 val 的所有结点 拿下了尾插 ,等于定值 val 的所有结点 释放
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
struct ListNode* cur =head;
//定义两个结构体指针 Phead 保存
struct ListNode* Phead = NULL,*ptail=NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == val)
{
head = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = head;
}
else
{
if(Phead == NULL)
{
Phead = ptail = cur;
}
else
{
ptail->next = cur;
ptail = ptail->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
if(ptail) //最后一个元素就是要删除的数字,时候必须改变 ptail->next 不然
/ptail->next 还是指向 最后一个元素 所以 ptail->next 置空 NULL
ptail->next =NULL;
}
return Phead;//返回新链表的头节点
}
思路2: 在原链表上等于定值 val 的所有结点 全部释放
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* prevt = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{ //等于定值 val 值
if(cur->val != val)
{
prevt = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{ //如果第一个节点 前面的循环都没有进去prevt 等于NULL 所以就是要删除的节点需要单独判断
if(prevt == NULL)
{
head = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = head;
}
else
{ //prevt->next保存 cur的节点的下一个节点
prevt->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = prevt->next;
}
}
}
return head;
}
反转一个单链表。
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表
思路1:从头节点开始分别把每一个节点都拿下了头插 到新链表中
思路2:改变节点的指向
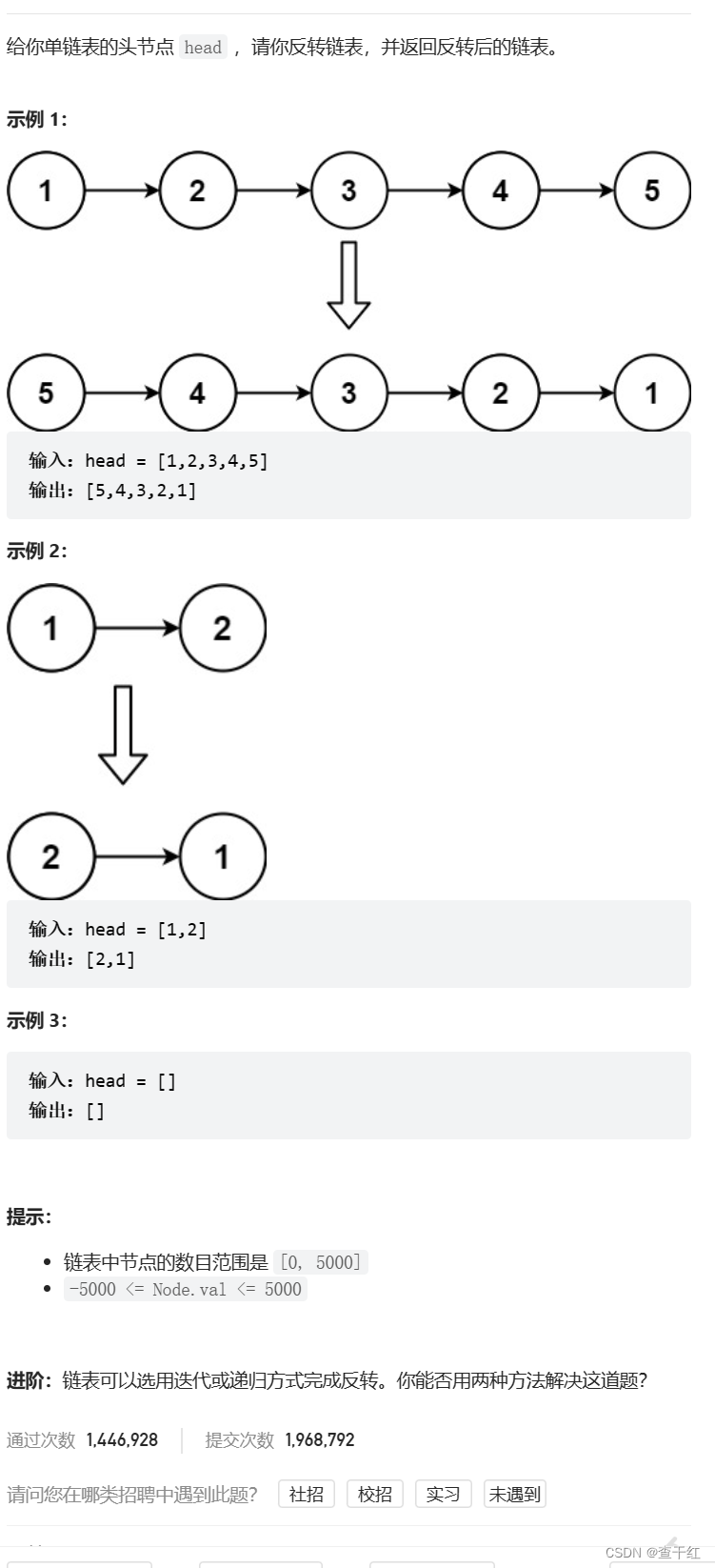
思路1:从头节点开始分别把每一个节点都拿下了头插 到新链表中
//思路:从头节点开始分别把每一个节点都拿下了头插 到新链表中
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* Phead =NULL;
while(cur)
{
//next 保存 cur->next cur的下一个节点
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = Phead;
Phead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return Phead;
}
思路2:改变节点的指向
//思路: 2,改变节点的指向
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;
n1 =NULL;
//n2指向头节点
n2 = head;
//n3 保存 n2->next n2的下一个节点
n3 = n2->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)//n3为空 n3就没有必要找n3->next
n3 = n3->next;
}
return n1;
}
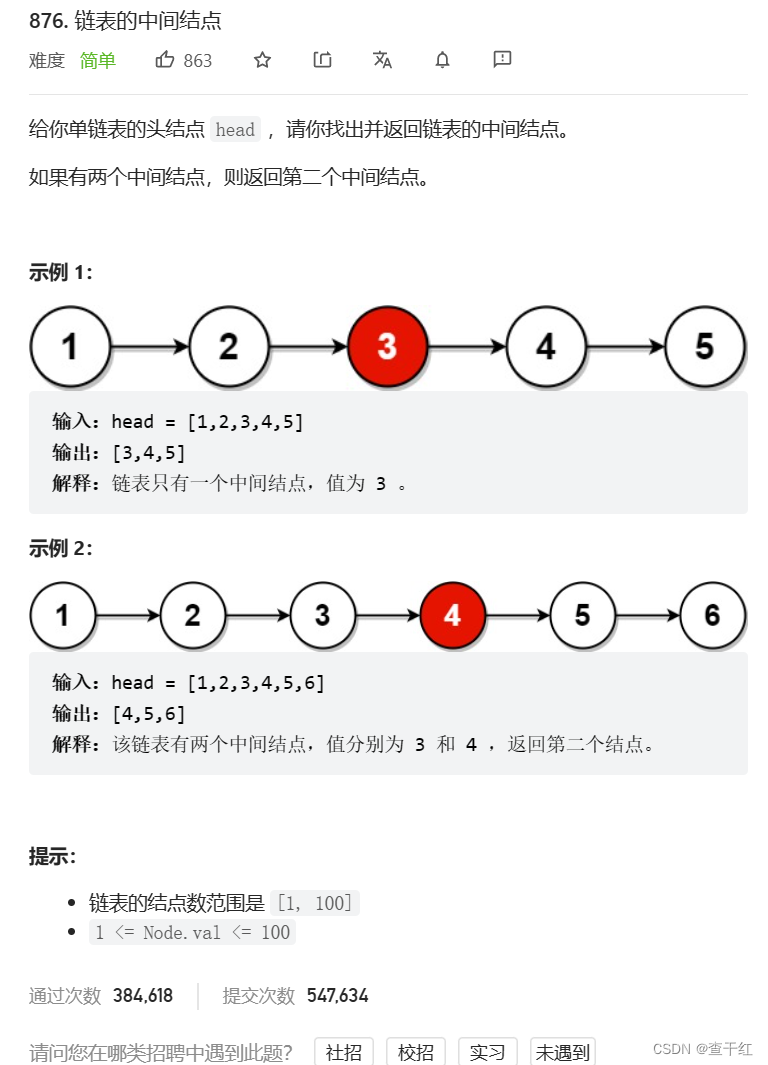
给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
给你单链表的头结点 head ,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
思路: slow 为 慢 fast为快 快慢指针 快指针一次走两步 慢指针一次走 一步,两种情况:1.如果有1个中间结点 fast->next 等于NULL 的时候 slow 走到到中间 2.如果有两个中间结点,fast等于NULL 的时候 slow走到中间
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* slow, *fast;
slow = fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
思路:快慢指针 注意和上面不一样 快指针先走k步 再和慢指针一起走 快指针fast 走到NULL 慢指针slow 达到倒数第k个结点
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
// write code here
if(pListHead == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* slow,*fast;
slow = fast = pListHead;
while(k--)
{
if(fast == NULL)
return NULL;//
fast =fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有结点组成的
思路:取较小的依次尾插到新链表
1.不带头单链表 需要判断新链表为空的情况
2.带头单链表 不需要判断新链表为空的情况
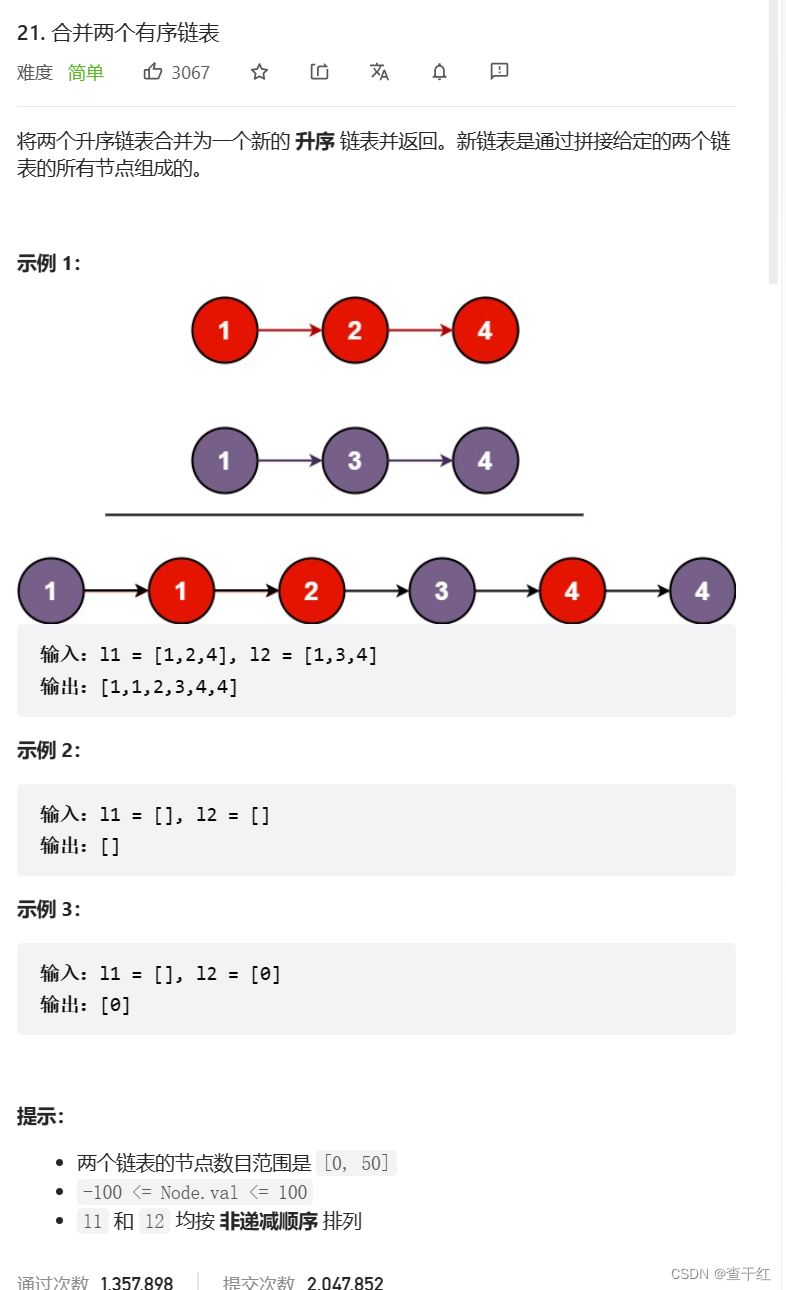
1.不带头单链表 需要判断新链表为空的情况
//思路:取较小的依次尾插到新链表
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
if(list1== NULL && list2 == NULL)
return NULL;
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1;
struct ListNode* cur2 = list2;
struct ListNode* Phead =NULL,*ptail=NULL;
while(cur1 && cur2)
{
if(cur1->val < cur2->val)
{
if(Phead == NULL)
{
Phead = ptail = cur1;
}
else
{
ptail->next = cur1;
ptail = ptail->next;
}
cur1= cur1->next;
}
else
{
if(Phead == NULL)
{
Phead = ptail = cur2;
}
else
{
ptail->next = cur2;
ptail = ptail->next;
}
cur2= cur2->next;
}
}
while(cur1)
{
ptail->next = cur1;
ptail = ptail->next;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
while(cur2)
{
ptail->next = cur2;
ptail = ptail->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
return Phead;
}
2.带头单链表 不需要判断新链表为空的情况
//思路:取较小的依次尾插到新链表
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
if(list1== NULL && list2 == NULL)
return NULL;
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1;
struct ListNode* cur2 = list2;
struct ListNode* Phead =NULL,*ptail=NULL;
//带头 单链表
//malloc()出一个头 就不用考虑 NULL的情况
Phead = ptail =(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
ptail->next =NULL;
while(cur1 && cur2)
{
if(cur1->val < cur2->val)
{
ptail->next = cur1;
ptail = ptail->next;
cur1= cur1->next;
}
else
{
ptail->next = cur2;
ptail = ptail->next;
cur2= cur2->next;
}
}
while(cur1)
{
ptail->next = cur1;
ptail = ptail->next;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
while(cur2)
{
ptail->next = cur2;
ptail = ptail->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
struct ListNode* head = Phead->next;
free(Phead); //一定记得释放头节点
return head;
}
编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
题目描述:
现有一链表的头指针 ListNode* pHead,给一定值x,编写一段代码将所有小于x的结点排在其余结点之前,且不能改变原来的数据顺序,返回重新排列后的链表的头指针。
思路:把小于x 的节点 尾插 到一个新链表 guhead ,大于等于x的 尾插 到一个新链表Tuhead 最后把它们连接起来,一定要使用带头的链表,malloc()出一个带头的链表,不然空指针的问题会烦死你的
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
// write code here
ListNode*guhead, *gutail;
ListNode*Tuhead, *Tutail;
guhead = gutail =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
Tuhead = Tutail =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
ListNode* cur = pHead;
while(cur)
{
//小于 x的节点 尾插 到一个新链表 guhead
if(cur->val < x)
{
gutail->next = cur;
gutail = gutail->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
Tutail->next = cur;
Tutail = Tutail->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
if(gutail)
gutail->next =NULL;//gutail->next一定置空
if(Tutail)
Tutail->next =NULL; //Tutail->next一定置空
}
gutail->next = Tuhead->next;
ListNode* NewHead = guhead->next;
free(guhead);
free(Tuhead);
return NewHead;
}
};
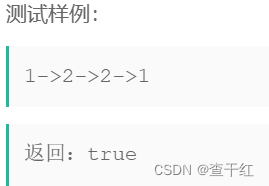
链表的回文结构。
题目描述:
对于一个链表,请设计一个时间复杂度为O(n),额外空间复杂度为O(1)的算法,判断其是否为回文结构。
给定一个链表的头指针A,请返回一个bool值,代表其是否为回文结构。保证链表长度小于等于900。
思路:, 找到中节点 2,从中间节点开始 逆序 3,依次进行判断 是否相等
ListNode* mindNode(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* slow,*fast;
slow = fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
//头插
ListNode* reverseNode(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* Phead = NULL;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = Phead;
Phead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return Phead;
}
//思路:1, 找到中节点 2,从中间节点开始 逆序 3,依次进行判断 是否相等
//逆序完的节点
//
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
// write code here
// 1.找到中节点
ListNode* MindHead = mindNode(head);
//2.从中间节点开始 逆序
ListNode* newhead = reverseNode(MindHead);
///while(head)//err
//while(newhead)//ok
//3,依次进行判断 是否相等
while(head && newhead)
{
if(head->val != newhead->val)
return false;
head = head->next;
newhead = newhead->next;
}
return true;
}
};
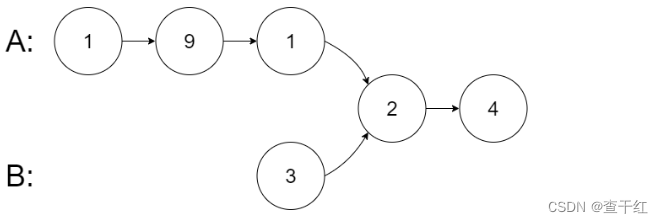
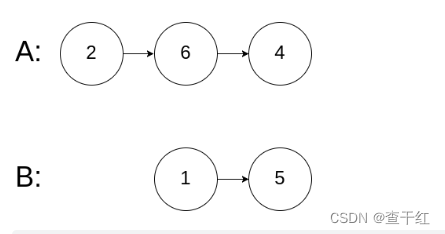
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
思路:
1.分别计算两个链表的长度
2.让长的那个链表 先走 差距步
3.再依次判断 链表的节点是否相同 就相交 不能判断两个链表的值 链表的值 可能重复
例1:
例2:
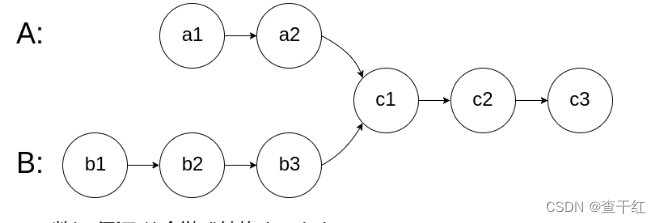
例3:

int CountNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head;
int count=0;
while(cur)
{
count++;
cur =cur->next;
}
return count;
}
//思路:
//1.分别计算两个链表的长度
//2.让长的那个链表 先走 差距步
//3.再依次判断 链表的节点是否相同 就相交 不能判断两个链表的值 链表的值 可能重复
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
//1.分别计算两个链表的长度
int len1 = CountNode(headA);
int len2 = CountNode(headB);
int gaut =abs(len1-len2);
//假设headA是长的那个链表
struct ListNode *longhead= headA;
//假设headB是的那个链表
struct ListNode *shorthead= headB;
//如果len2 比len1大
//那就改一下
if(len1 <len2)
{
longhead = headB;
shorthead = headA;
}
2.让长的那个链表 先走 差距步
while(gaut--)
{
longhead = longhead->next;
}
while(longhead && shorthead)
{
再依次判断 链表的节点是否相同
if(longhead == shorthead)
{
return longhead;
}
else
{
longhead = longhead->next;
shorthead = shorthead->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}
总结:
学习数据结构 除了代码反复敲 感觉没有其他办法 视频看了3,4遍不如手敲代码一遍来的的踏实
以上就是本文所要描述的所有内容,感谢您对本文的观看






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结