您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >【数据结构】栈的实现网站首页学无止境
【数据结构】栈的实现
简介【数据结构】栈的实现
😛作者:日出等日落
📘 专栏:数据结构
🌹 如果说,读书是在奠定人生的基石,在梳理人生的羽毛,那么,实践,就是在构建人生的厅堂,历练人生的翅膀。是不是,人生经过了实践,才能真正矗立、飞翔在天地之间。
目录
1. 栈
1.1 栈的概念及结构
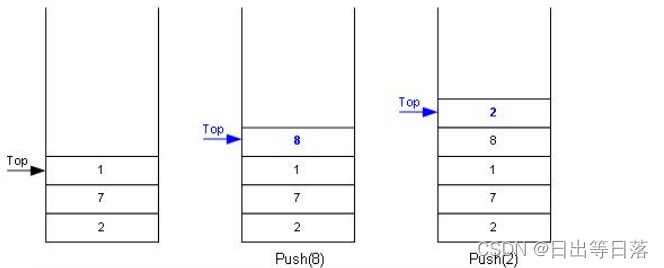
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。 压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。 出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
1.2栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的 代价比较小。
1.2.1 入栈
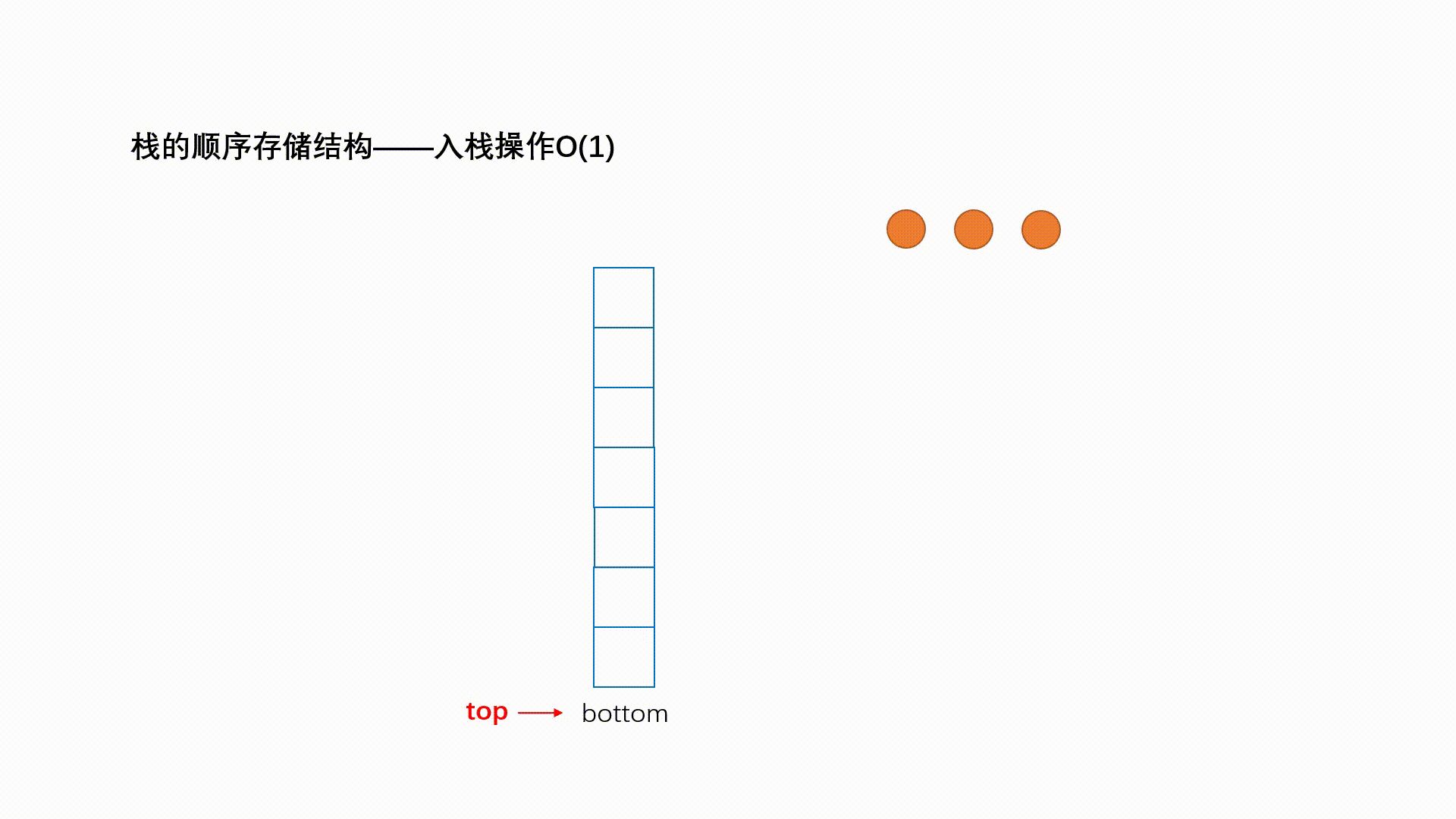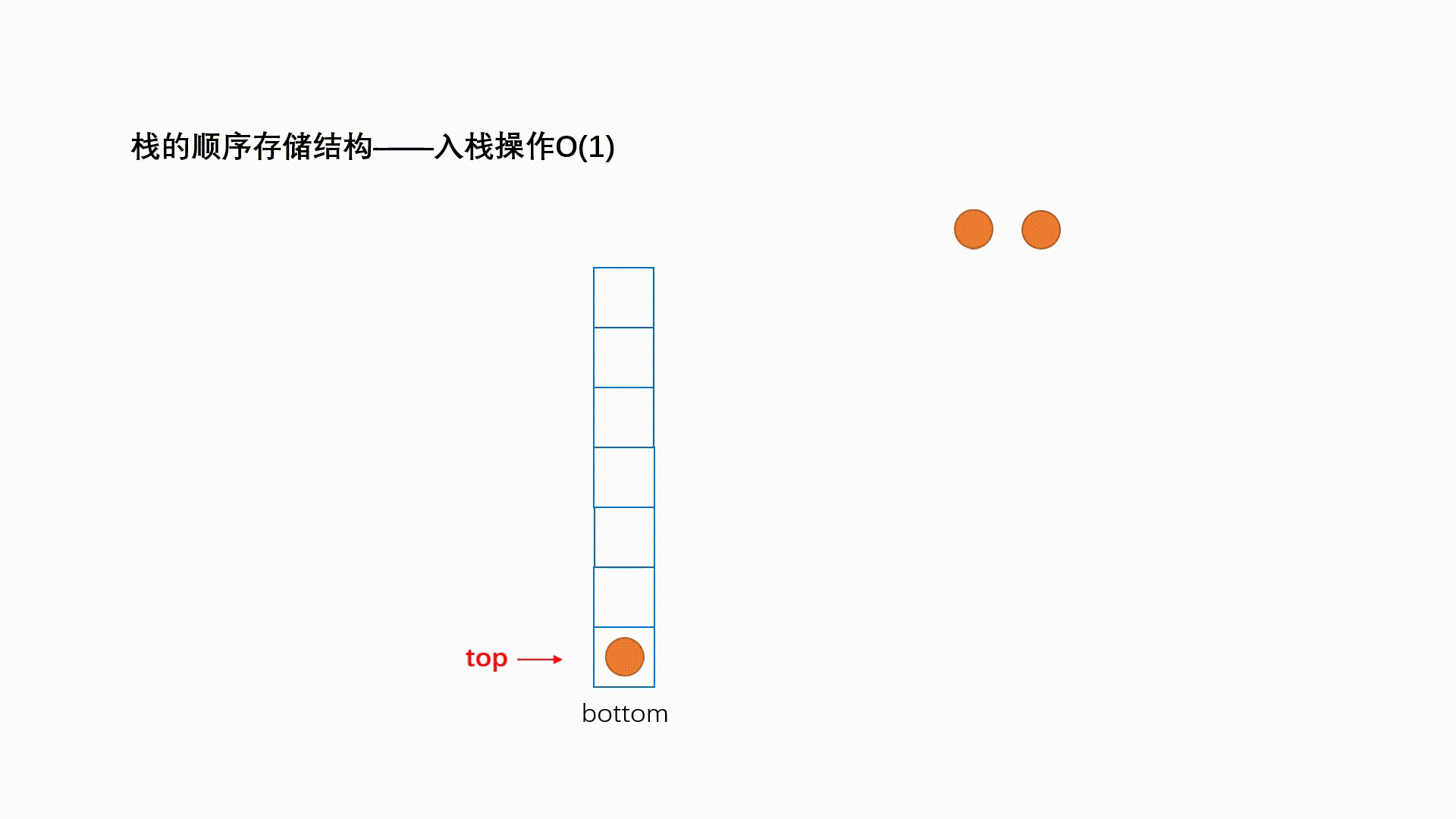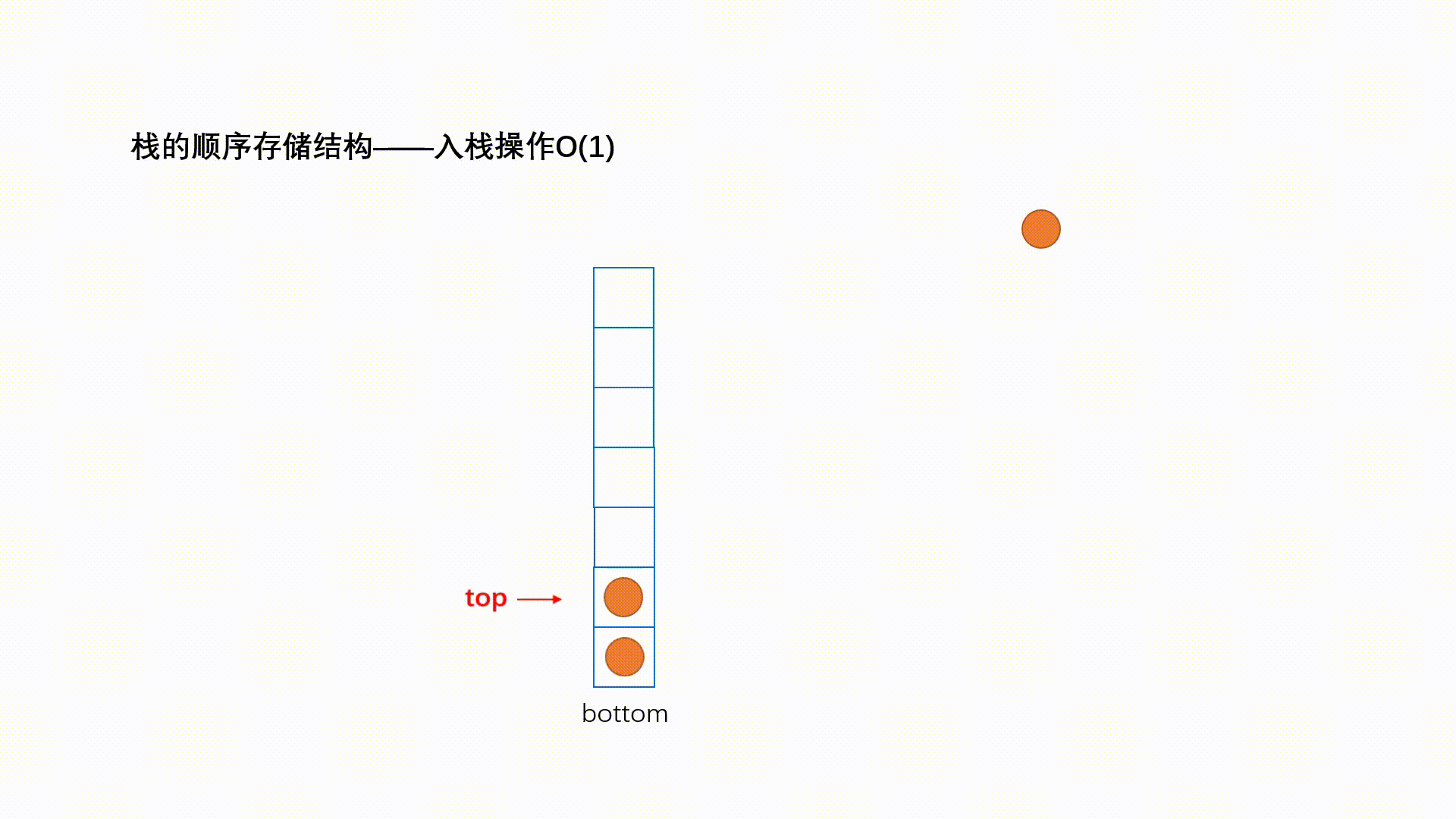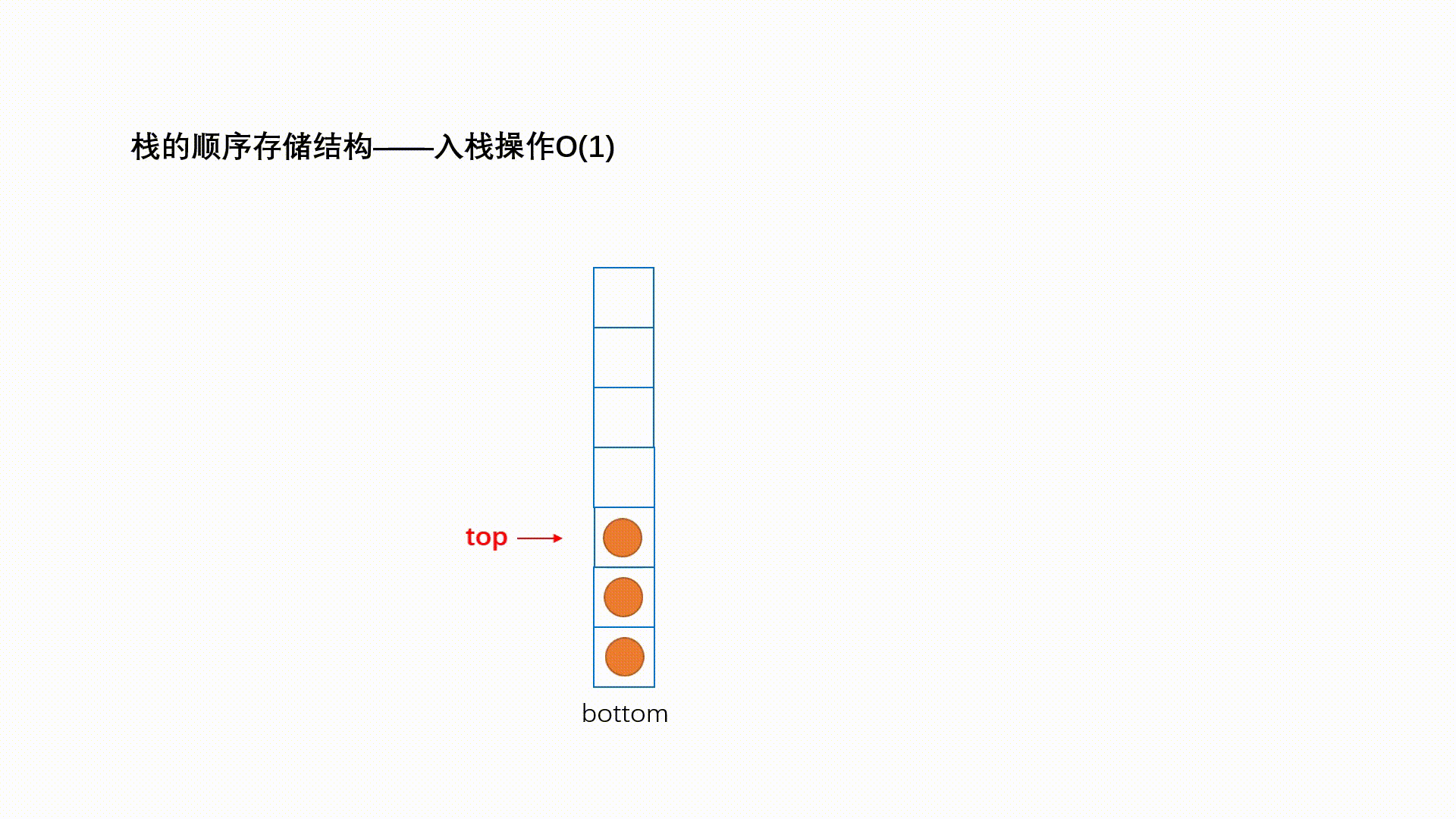
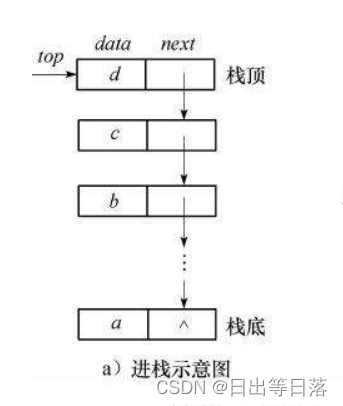
1.2.2 出栈
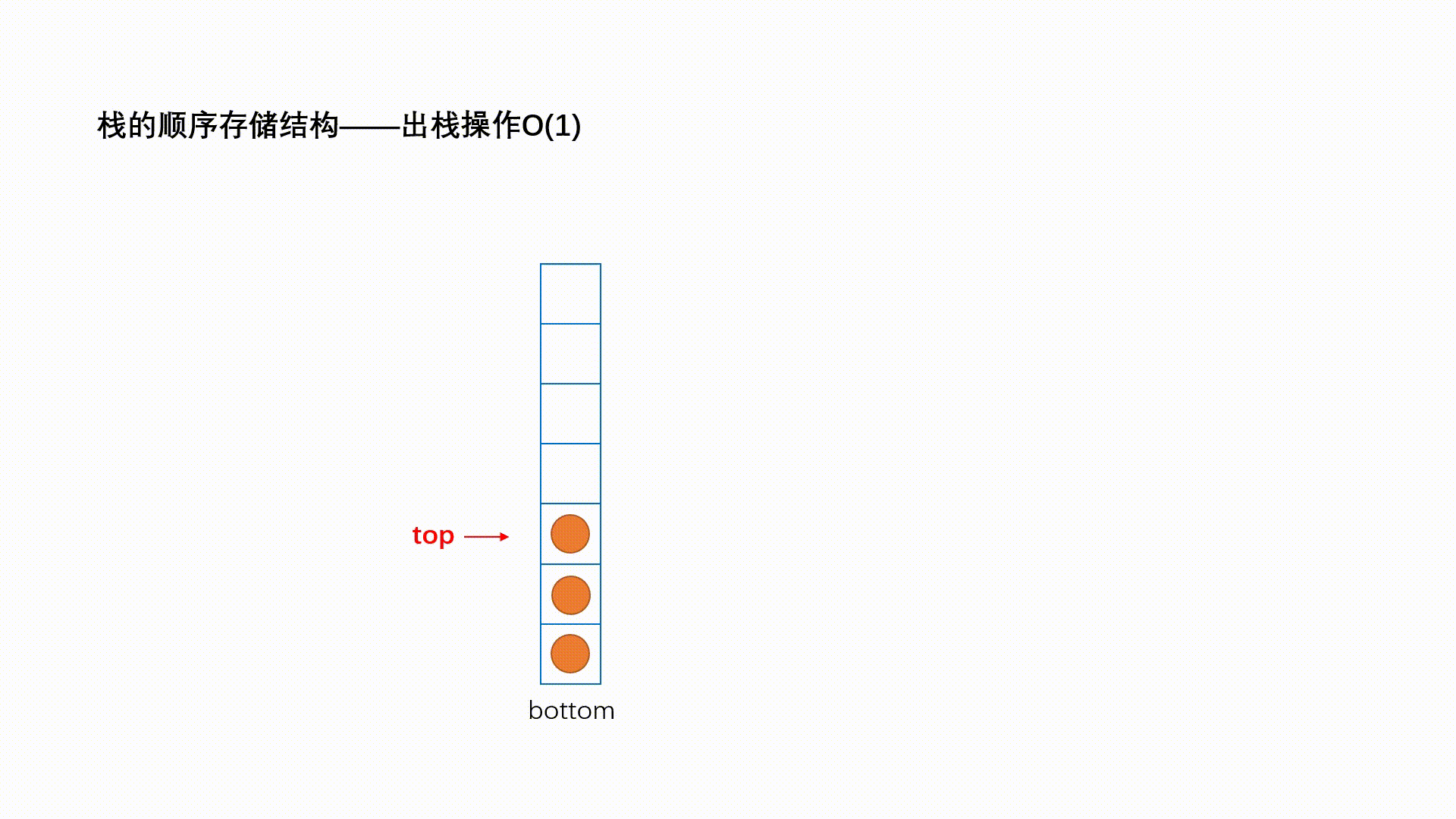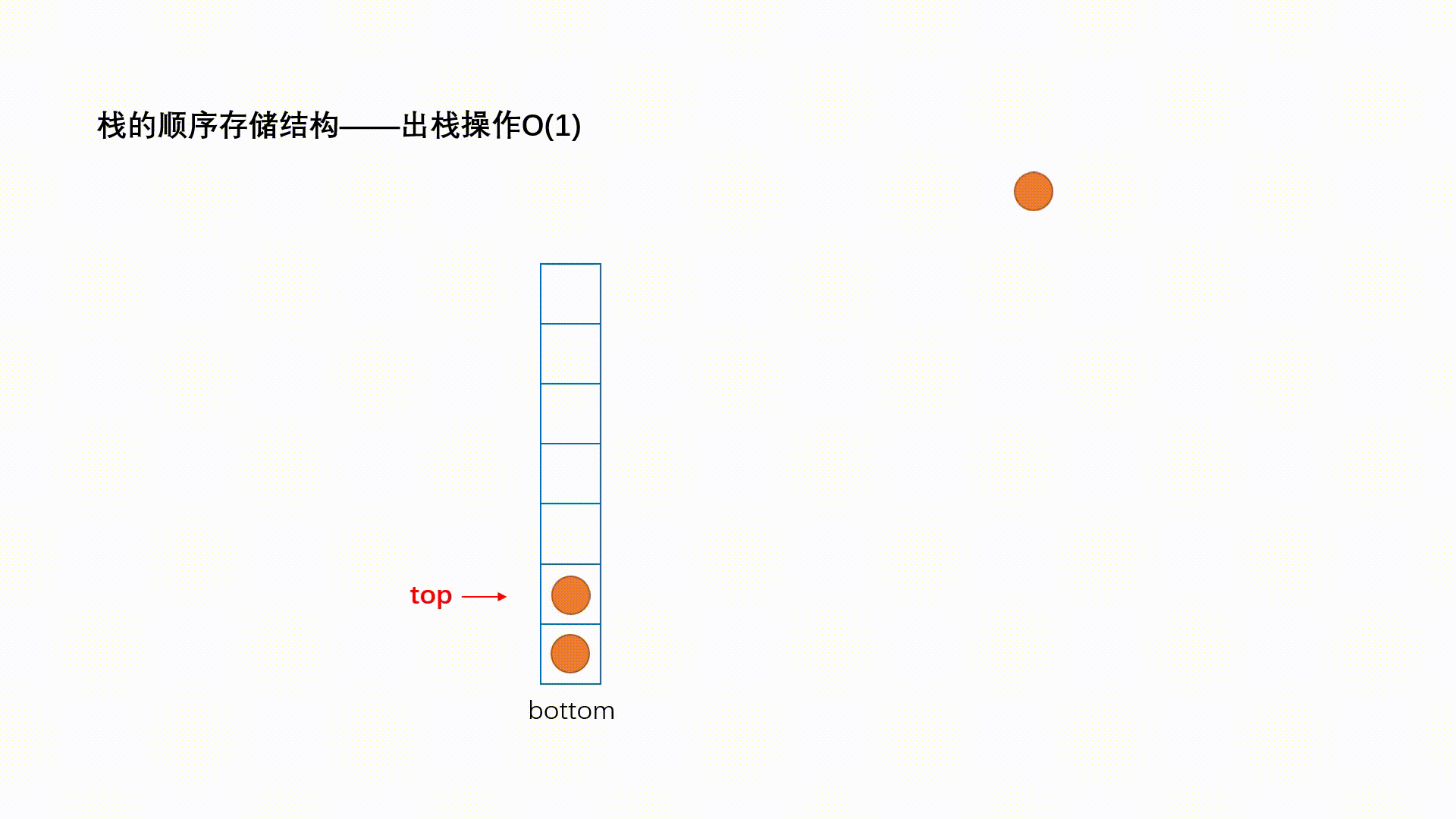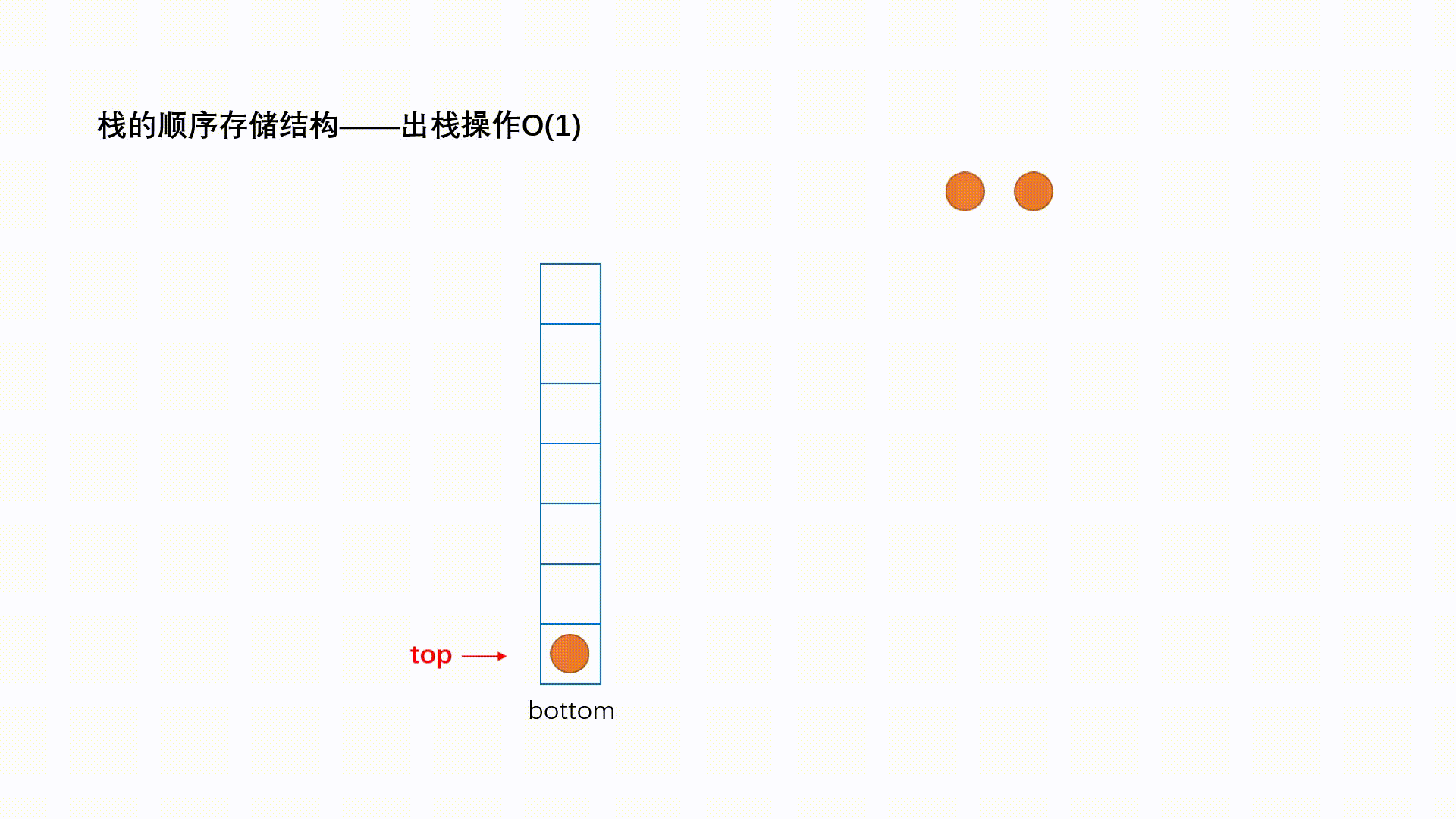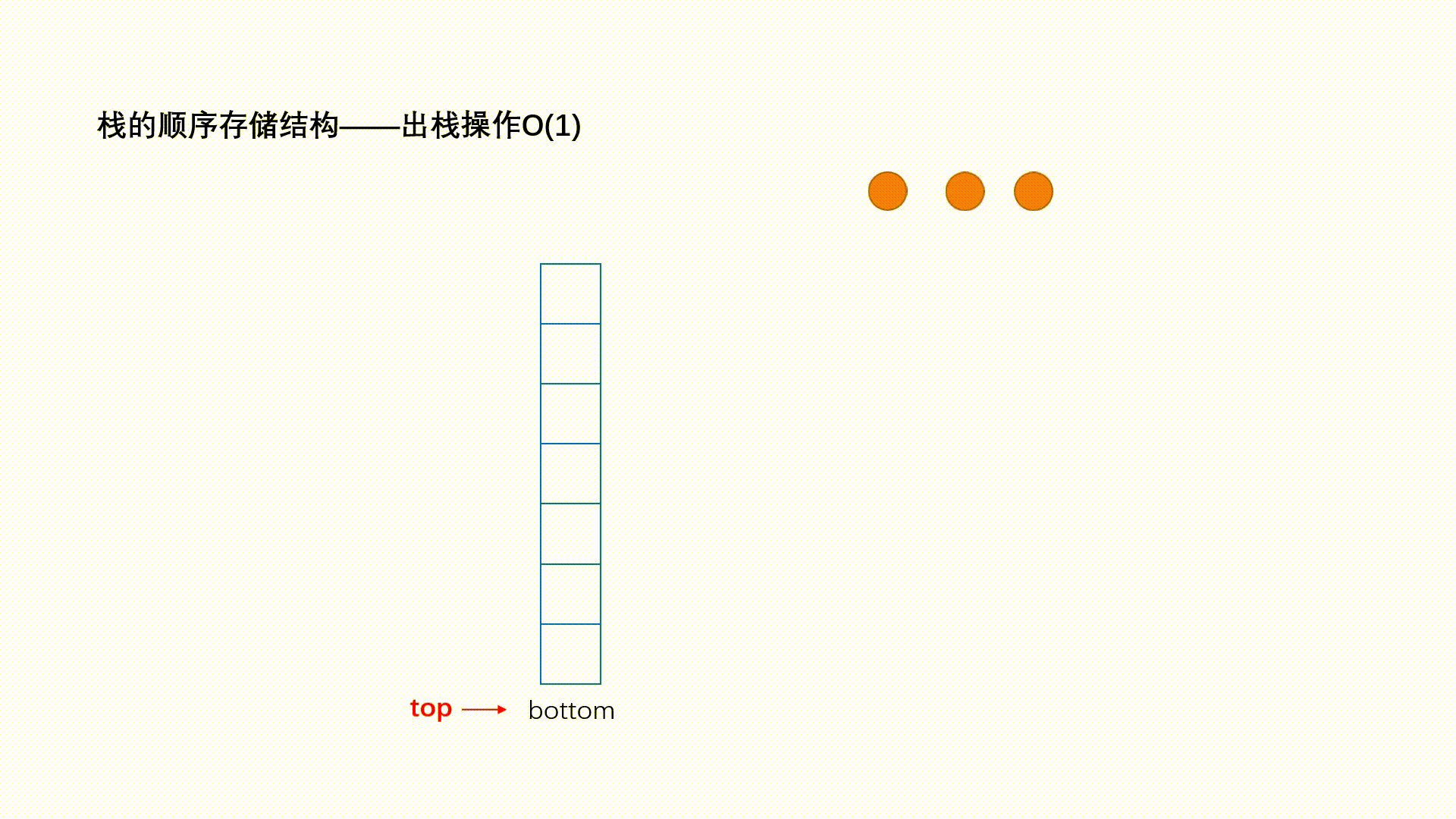
2. 栈的代码实现(采用数组栈):
2.1 结构体:

2.2 StackInit函数:
//初始化栈
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;
}2.3 StackDestory函数:
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}2.4 StackPush 函数:
// 入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = data;
ps->top++;
}2.5 StackTop函数:
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top-1];
}
2.6 StackPop函数:
// 删除栈顶元素
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}2.7 StackEmpty函数:
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}2.8 StackSize函数:
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
3. 完整代码:
3.1 Stack.h(函数的定义):
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
//动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // 栈顶
int capacity; // 容量
}ST;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(ST* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType data);
// 删除栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(ST* ps);
3.2 Stack.c(功能函数):
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Stack.h"
//初始化栈
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;
}
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = 0;
}
// 入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType data)
{
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = data;
ps->top++;
}
// 删除栈顶元素
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
3.3 Text.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Stack.h"
void TextStack1()
{
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
StackPush(&st, 4);
StackPush(&st, 5);
printf("%d
", StackTop(&st));
//printf("size:%d
", StackSize(&st)); // 不关心底层实现
//printf("size:%d
", st.top); // 关心
//printf("size:%d
", st.top + 1); // 关心
StackPop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
printf("%d
", StackTop(&st));
//StackPop(&st);
StackDestroy(&st);
}
int main()
{
TextStack1();
return 0;
}风语者!平时喜欢研究各种技术,目前在从事后端开发工作,热爱生活、热爱工作。







 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结