您现在的位置是:首页 >学无止境 >SpringBoot网站首页学无止境
SpringBoot
SpringBoot(2023.3.6)
1、什么是Spring Boot
SpringBoot约定大于配置,默认配置了很多框架的使用方式,就像maven整合了所有的jar包,spring boot整合了所有的框架 。
spring boot的主要优点
- 为所有Spring开发者更快的入门
- 开箱即用,提供各种默认配置来简化项目配置
- 内嵌式容器简化Web项目
- 没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
2、第一个SpringBoot程序
使用 IDEA 直接创建项目
1、创建一个新项目
2、选择spring initalizer , 可以看到默认就是去官网的快速构建工具那里实现
3、填写项目信息(springboot版本不宜过高,否则运行报错)
4、选择初始化的组件(初学勾选 Web 即可)
5、填写项目路径
6、等待项目构建成功
项目结构分析:
通过上面步骤完成了基础项目的创建。就会自动生成以下文件。
1、程序的主启动类
2、一个 application.properties 配置文件
3、一个 测试类
4、一个 pom.xml
编写一个接口
1、在主程序的同级目录下,新建一个controller包,一定要在同级目录下,否则识别不到
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-M8oTF6uK-1684392412403)(D:XPicturesJavaspringboothelloworld.png)]
2、在包中新建一个HelloController类
//自动装配,是@ResponsBody与@Controller的结合体
@RestController
public class HelloController {
//接口:http://localhost:8080/hello
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello world";
}
}
3、编写完毕后,从主程序启动项目,浏览器发起请求,看页面返回;控制台输出了 Tomcat 访问的端口号!
简单几步,就完成了一个web接口的开发,SpringBoot就是这么简单。所以我们常用它来建立我们的微服务项目!
pom.xml分析
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<!-- 父依赖 -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.7</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.jiang</groupId>
<artifactId>helloworld</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>helloworld</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- web场景启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>11</source>
<target>11</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
改变端口号
# springboot核心配置文件:application.properties
server.port=8081
3、SpringBoot原理初探
启动器(本机需手动添加)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 启动器即Springboot的启动场景
- springboot会将所有的功能场景都变成一个个的启动器
- 我们要使用什么功能,只需要找到对应的启动器
主程序
@SpringBootApplication//标注这个类是一个springboot的应用
public class HelloworldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
}
注解
@SpringBootConfiguration //SpringBoot的配置类 ,标注在某个类上 , 表示这是一个SpringBoot的配置类;
@Configuration//说明这是一个配置类 ,配置类就是对应Spring的xml 配置文件;
@Component //说明,启动类本身也是Spring中的一个组件而已,负责启动应用!
@EnableAutoConfiguration //开启自动配置功能
@AutoConfigurationPackage//自动配置包
@import //Spring底层注解@import , 给容器中导入一个组件
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) //给容器导入组件 ;
@RequestParam //用于将指定的请求参数赋值给方法中的形参。
Controller,ResponseBody, RestController
-
@Controller:标识一个Spring类是Spring MVC controller处理器,@RestController
-
@RestController是@Controller和@ResponseBody的结合体,两个标注合并起来的作用。
-
@Controller类中的方法可以直接通过返回String跳转到jsp、ftl、html等模版页面。
-
在方法上加@ResponseBody注解,也可以返回实体对象。@RestController类中的所有方法只能返回String、Object、Json等实体对象,不能跳转到模版页面。
-
spring.factories
- SpringBoot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值
- 将这些值作为自动配置类导入容器 , 自动配置类就生效 , 帮我们进行自动配置工作;
- 整个J2EE的整体解决方案和自动配置都在springboot-autoconfigure的jar包中;
- 它会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类 (xxxAutoConfiguration), 就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件 , 并配置好这些组件 ;
- 有了自动配置类 , 免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作;
4、SpringBoot配置
yml语法
yml基础语法
1、空格不能省略
2、以缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一列数据都是同一个层级的。
3、属性和值的大小写都是十分敏感的。
yml可以直接给实体类赋值
product:
id: 1001
name: cake
sell: false
date: 2023/1/23
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- soft
- white
- sweet
person:
name: jyh
age: 20
@Component//注册bean
@Data
/*
@ConfigurationProperties作用:
将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中;
告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定
参数 prefix = “product” : 将配置文件中的product下面的所有属性一一对应
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "product")
public class Product {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Boolean sell;
private Date date;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Person person;
}
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot02ConfigApplicationTests {
@Autowired //将product自动注入进来
private Product product;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(product);
}
}
//加载指定的配置文件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:application.properties")
JSR303数据校验
@Component //注册bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated //数据校验
public class Person {
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误") //name必须是邮箱格式
private String name;
}
常见参数
@NotNull(message="名字不能为空")
private String userName;
@Max(value=120,message="年龄最大不能查过120")
private int age;
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误")
private String email;
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) string is between min and max included.
日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
.......等等
除此以外,我们还可以自定义一些数据校验规则
多环境切换
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml , 用来指定多个环境版本;
例如:
application-test.properties 代表测试环境配置
application-dev.properties 代表开发环境配置
但是Springboot并不会直接启动这些配置文件,它默认使用application.properties主配置文件;
我们需要通过一个配置来选择需要激活的环境:
#比如在配置文件中指定使用dev环境,我们可以通过设置不同的端口号进行测试;
#我们启动SpringBoot,就可以看到已经切换到dev下的配置了;
spring.profiles.active=dev
yml的多文档块
server:
port: 8081
#选择要激活那个环境块
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev #配置环境的名称
---
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod #配置环境的名称
注意:如果yml和properties同时都配置了端口,并且没有激活其他环境 , 默认会使用properties配置文件的!
配置文件加载位置
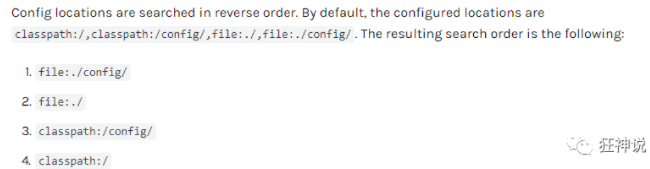
在配置文件中能配置的东西,都存在一个固有的规律: xxxAutoConfiguration默认值 xxxProperties和配置文件绑定,我们就可以使用自定义的配置了。
shift+shift键搜索所有
自动装配原理
1、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2、我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
3、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
4、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
**xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;**给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
通过yml文件修改相关属性的值
5、SpringBoot Web开发
自动装配
要解决的问题:
- 导入静态资源
- 首页
- jsp,模板引擎Thymeleaf
- 装配扩展SpringMVC
- 增删改查
- 拦截器
- 国际化
导入静态资源
拿到静态资源的方式:
(1)webjars
http://localhost:8080/webjars/github-com-jquery-jquery/3.4.1/jquery.js
(2)resources目录下
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8LaJGUUl-1684392412405)(D:XPicturesJavaspringboot esource.jpg)]
resource目录下的public、resources、static、templates文件夹中的资源可被识别,其中优先级从高到低为:resources > static (默认)>public
http://localhost:8080/**/
<!-- http://localhost:8080/1.js >
很少使用webjars
定制首页
放在public或者static目录下
模板引擎
作用:写一个页面
需要使用thymeleaf,只需要导入对应的依赖.我们将html页面放在templates目录下
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
html文件中添加
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
//在templates目录下的所有页面,只能通过controller来跳转
//需要thyeleaf模板引擎的支持
@Controller
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","<h1>hello,springboot</h1>");
return "test";
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--所有的html元素都可以被thymeleaf替换接管: th:元素名-->
<!--不转义-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
<!--转义-->
<div th:utext="${msg}"></div>
</body>
</html>
扩展MVC
不要加注解@EnableWebMvc(此注解就是导入了一个类DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration:从容器中获取所有的WebMvcConfig),否则其他注解会失效
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//视图跳转
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/jiang").setViewName("/test");
}
}
在springboot中,有非常多的xxx Configuration,这是用来扩展的
员工管理系统
国际化
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-yznmu2dr-1684392412406)(D:XPicturesJavaspringbooti18n.jpg)]
login.password=password
login.remember=Remember me
login.tip=Please sign in
login.username=username
login.btn=Sign in
shift+shift快速查找
如果需要在项目中进行按钮自动切换,我们需要自定义一个组件LocaleResolver
public class MyLocalResolver implements LocaleResolver {
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
String language = request.getParameter("lang");
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(language)){
String[] strings=language.split("_");
return new Locale(strings[0],strings[1]);
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
}
注册到容器
//MyMVCConfig类中
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocalResolver();
}
<body class="text-center">
<form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html">
<img class="mb-4" src="/img/bootstrap-solid.svg" alt="" width="72" height="72">
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1>
<label class="sr-only" >Username</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus="">
<label class="sr-only" >Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required="">
<div class="checkbox mb-3">
<label th:text="#{login.remember}">
<input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"> Remember me
</label>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit" th:text="#{login.btn}">Sign in</button>
<p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2022-2023</p>
<!添加超链接路径-->
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(lang='zh_CN')}">中文</a>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(lang='en_US')}">English</a>
</form>
</body>
员工信息
- 抽取公共部分(thymleaf)
<nav class="navbar navbar-dark sticky-top bg-dark flex-md-nowrap p-0" th:fragment="topbar"></nav>
<div th:insert="~{commons::topbar}"></div>
- 若要传递参数,可以直接用( )传参,接收判断即可
- 列表循环展示
添加员工
- 按钮提交
- 跳转到添加页面
- 添加员工成功
- 返回首页
修改员工
Druid
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
在配置文件中选择数据源为druid
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&userUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
initial-size: 5
min-idle: 5
max-active: 20
max-wait: 60000
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 6000
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 30000
validation-query: select 1 from dual
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
pool-prepared-statements: true
filters: stat,wall,log4j
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20
use-global-data-source-stat: true
connection-properties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid")
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//后台监控:web.xml
//因为SpringBoot内置了servlet容器,所以没有web.xml
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean StatViewServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean<StatViewServlet> bean = new ServletRegistrationBean<StatViewServlet>(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
//后台需要有人登录,账号密码配置
HashMap initParameters = new HashMap<String, String>();
//登录的key是固定的:loginUsername,loginPassword
initParameters.put("loginUsername","admin");
initParameters.put("loginPassword","123456");
//允许谁可以访问
initParameters.put("allow","");
//禁止谁访问
bean.setInitParameters(initParameters);
return bean;
}
//filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean<Filter>();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
//可以过滤哪些请求
Map<String,String> initParameters = new HashMap();
//这些东西不进行统计(让druid不监控这些)
initParameters.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*");
return bean;
}
}
整合Mybatis
- 导入对应依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
- 在配置文件中整合mybatis
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.jiang.entity
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
- mapper
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> queryUserList();
User queryUserById(int id);
int addUser(User user);
int updateUser(User user);
int deleteUser(User user);
}
- mapper.xml中编写sql
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.jiang.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="queryUserList" resultType="User">
select * from user
</select>
<select id="queryUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="User">
select* from user where id=#{id}
</select>
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="User">
insert into user(id,name,pwd) values (#{id},#{name},#{pwd})
</insert>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="User">
update user set name=#{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="User">
delete from user where id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
- controller调用service
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
//url请求都是GetMapping
@GetMapping("/UserList")
public List<User> queryUserList(){
List<User> userList = userMapper.queryUserList();
return userList;
}
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public User queryUserById(@PathVariable("id") int id){
return userMapper.queryUserById(id);
}
@GetMapping("/add")
public String addUser(){
int result=userMapper.addUser(new User(5,"李四","1111"));
return result==0?"failed":"success";
}
@GetMapping("/update")
public String updateUser(){
int result= userMapper.updateUser(new User(1,"Amy","111111"));
return result==0?"failed":"success";
}
@GetMapping("/delete")
public String deleteUser(){
int result=userMapper.deleteUser(new User(5,"李四","1111"));
return result==0?"failed":"success";
}
}
SpringSecurity(安全)
安全要在设计之初考虑
两个框架—shiro、SpringSecurity:非常相似,除了类不一样,名字不一样
认证、授权(VIP1,VIP2,VIP3)
- 功能权限
- 访问权限
- 菜单权限
- 拦截器、过滤器
springsecurity简介
customizable authentication and access-control framework(身份验证和访问控制的框架)
记住几个类:
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter:自定义Security策略
- AuthenticationManagerBuilder:自定义认证策略
- @EnableWebSecurity:开启WebSecurity模式
两个主要目标:
- 认证(Authentication)
- 授权(Authorization)
//授权
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//首页所有人都可以访问,功能页只有对应有权限的人才能访问
//请求授权的规则:
http.authorizeHttpRequests().antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
//无权限默认到登录页,我们需要 开启登录页面
//loginPage the login page to redirect to if authentication is required 身份验证跳转的页面
//loginProcessingUrl :the URL to validate username and password验证表单中的用户名和密码,即form表单提交的地址
http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin").loginProcessingUrl("/login");
//注销,然后跳回首页
http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf(跨域攻击),否则post请求不生效
//开启记住我功能(cookie):默认保存14天
http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");
}
//认证
//密码编码(PasswordEncoder)
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//这些数据正常应该从数据库中获得
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("jiang").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip2","vip3").and()
.withUser("kuangshen").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123123")).roles("vip1").and()
.withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3");
}
}
shiro
Apache Shiro 是一个强大灵活的开源安全框架,可以完全处理身份验证、授权、加密和会话管理。
功能
- Authentication:身份认证/登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份
- Authorization:授权,即权限验证,验证某个已认证的用户是否拥有某个权限;即判断用户是否能进行什么操作,如:验证某个用户是否拥有某个角色。或者细粒度的验证某个用户对某个资源是否具有某个权限
- Session Management:会话管理,即用户登录后就是一次会话,在没有退出之前,它的所有信息都在会话中;会话可以是普通JavaSE环境,也可以是Web 环境的
- Cryptography:加密,保护数据的安全性,如密码加密存储到数据库,而不是明文存储
- Web Support:Web 支持,可以非常容易的集成到Web 环境
- Caching:缓存,比如用户登录后,其用户信息、拥有的角色/权限不必每次去查,这样可以提高效率
- Concurrency:Shiro支持多线程应用的并发验证,即如在一个线程中开启另一个线程,能把权限自动传播过去
- Testing:提供测试支持
- “Run As”:允许一个用户假装为另一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份进行访问
- Remember Me:记住我,这个是非常常见的功能,即一次登录后,下次再来的话不用登录了
shiro架构(外部)
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-JMaUdsjM-1684392412407)(D:XPicturesJavaspringbootshiro1.png)]
-
Subject:应用代码直接交互的对象是Subject,也就是说Shiro的对外API 核心就是Subject。Subject 代表了当前“用户”,这个用户不一定是一个具体的人,与当前应用交互的任何东西都是Subject,如网络爬虫,机器人等;与Subject 的所有交互都会委托给SecurityManager;Subject 其实是一个门面,SecurityManager才是实际的执行者
-
SecurityManager:安全管理器;即所有与安全有关的操作都会与SecurityManager交互;且其管理着所有Subject;可以看出它是Shiro的核心,它负责与Shiro的其他组件进行交互,它相当于SpringMVC中DispatcherServlet的角色
-
Realm:Shiro从Realm 获取安全数据(如用户、角色、权限),就是说SecurityManager要验证用户身份,那么它需要从Realm 获取相应的用户进行比较以确定用户身份是否合法;也需要从Realm 得到用户相应的角色/权限进行验证用户是否能进行操作;可以把Realm 看成DataSource
shiro架构(内部)
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-i5DSZq4c-1684392412407)(D:XPicturesJavaspringbootshiro2.png)]
- Subject:任何可以与应用交互的“用户”;
- SecurityManager:相当于SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet;是Shiro的心脏;所有具体的交互都通过SecurityManager进行控制;它管理着所有Subject、且负责进行认证、授权、会话及缓存的管理。
- Authenticator:负责Subject 认证,是一个扩展点,可以自定义实现;可以使用认证策略(Authentication Strategy),即什么情况下算用户认证通过了;
- Authorizer:授权器、即访问控制器,用来决定主体是否有权限进行相应的操作;即控制着用户能访问应用中的哪些功能;
- Realm:可以有1 个或多个Realm,可以认为是安全实体数据源,即用于获取安全实体的;可以是JDBC 实现,也可以是内存实现等等;由用户提供;所以一般在应用中都需要实现自己的Realm;
- SessionManager:管理Session 生命周期的组件;而Shiro并不仅仅可以用在Web 环境,也可以用在如普通的JavaSE环境
- CacheManager:缓存控制器,来管理如用户、角色、权限等的缓存的;因为这些数据基本上很少改变,放到缓存中后可以提高访问的性能
- Cryptography:密码模块,Shiro提高了一些常见的加密组件用于如密码加密/解密。
快速开始
1.导入依赖
2.导入配置文件
3.导入quickstart.java
//一个用户对应多个角色,一个角色对应多个权限
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
currentUser.isAuthenticated()
currentUser.getPrincipal()
currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")
currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")
currentUser.logout();
SpringBoot中集成Shiro
搭建环境
导入shiro-springboot整合依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-web-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
自定义Realm
package com.jiang.config;
import org.apache.catalina.User;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
//自定义Realm
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
System.out.println("执行了授权:doGetAuthorizationInfo");
return null;
}
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了认证:doGetAuthenticationInfo");
//用户名,密码 数据库中获得
String username="root";
String pwd="123456";
UsernamePasswordToken userToken=(UsernamePasswordToken) token;
if (!userToken.getUsername().equals(username)){
return null;
}
//密码认证:shiro自己做
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",pwd,"");
/*
UsernamePasswordToken userToken=(UsernamePasswordToken) token;
User user = userService.queryUserByName(userToken.getUsername());
if (user==null){
return null;
}
//密码认证:shiro自己做,加密了
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",user.getPwd(),"");
*/
}
}
编写shiro配置文件
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
//ShiroFilterFactoryBean
//DefaultWebSecurityManager
//创建Realm对象,需要自定义
//3.ShiroFilterFactoryBean
@Bean(name = "shiroFilterFactoryBean")
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean=new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
return bean;
}
//2.DefaultWebSecurityManager
@Bean(name = "securityManager")
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getdefaultSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//关联UserRealm
securityManager.setRealm(userRealm);
return securityManager;
}
//1、创建realm对象,需要自定义类
@Bean
public UserRealm userRealm(){
return new UserRealm();
}
}
shiro整合mybatis
package com.jiang.config;
import com.jiang.pojo.User;
import com.jiang.service.UserService;
import com.jiang.service.UserServiceImpl;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
//自定义Realm
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
System.out.println("执行了授权:doGetAuthorizationInfo");
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
info.addStringPermission("user:add");
return info;
}
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
// System.out.println("执行了认证:doGetAuthenticationInfo");
// String username="root";
// String pwd="123456";
// UsernamePasswordToken userToken=(UsernamePasswordToken) token;
//
// if (!userToken.getUsername().equals(username)){
// return null;
// }
//
// //密码认证:shiro自己做,加密了
// return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",pwd,"");
UsernamePasswordToken userToken=(UsernamePasswordToken) token;
User user = userService.queryUserByName(userToken.getUsername());
if (user==null){
return null;
}
//密码认证:shiro自己做,加密了
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",user.getPwd(),"");
}
}
package com.jiang.config;
import at.pollux.thymeleaf.shiro.dialect.ShiroDialect;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean;
import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
//ShiroFilterFactoryBean
//DefaultWebSecurityManager
//创建Realm对象,需要自定义
//3.ShiroFilterFactoryBean
@Bean(name = "shiroFilterFactoryBean")
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean=new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
//添加shiro的内置过滤器
/*
* anon:无需认证就能访问
* authc:必须认证了才能访问
* user:必须拥有 记住我 功能才能用
* perms:拥有对某个资源的权限才能访问
* role:拥有某个角色权限才能访问
* */
//拦截
Map<String, String> filterMap=new LinkedHashMap<>();
//授权
filterMap.put("/user/add","perms[user:add]");//add需要权限才能访问
filterMap.put("/user/update","perms[user:update]");
filterMap.put("/user/*","authc");
//未授权
bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/unauth");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
//设置登录的请求
bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin");
return bean;
}
//2.DefaultWebSecurityManager
@Bean(name = "securityManager")
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getdefaultSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//关联UserRealm
securityManager.setRealm(userRealm);
return securityManager;
}
//1、创建realm对象,需要自定义类
@Bean
public UserRealm userRealm(){
return new UserRealm();
}
//整合shiroDialect:
@Bean
public ShiroDialect getShiroDialect(){
return new ShiroDialect();
}
}
swagger
前后端分离
vue+springboot
- 前端:前端控制层,视图层
- 后端:后端控制层,服务层,数据访问层
前后端如何交互:API
- 前端测试后端接口
- 后端提供接口,需要实时更新最新的消息及改动
Swagger应运而生
- 号称世界上最流行的API框架;
- Restful API文档在线自动生成工具=>API文档与API定义同步更新;
- 直接运行,可以在线测试API接口;
在项目中使用Swagger需要springbox
- swagger2
- ui
springboot集成swagger
1.新建springboot-web项目
2.导入相关依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.springfox/springfox-swagger-ui -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
-
配置swagger
@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 //开启swagger2 public class SwaggerConfig { }可能出错,解决方法:降swagger和springboot版本(2.5.1)
配置扫描接口
@Bean
public Docket docket(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(myApiInfo())
// enable(false)浏览器不启动swagger
//RequestHandlerSelectors配置要扫描接口的方式
//basePackage:要扫描的包
//withClassAnnotation()扫描类上注解
//withMethodAnnotation()扫描方法上注解
.select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withClassAnnotation(RestController.class))
//paths:过滤什么路径
//.paths(PathSelectors.ant("/jiang/**"))
.build();
}
配置API文档的分组
.groupName("jyh")
配置多个分组:创建多个Docket
@Bean
public Docket docket1(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("A");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("B");
}
@Bean
public Docket docket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("C");
}
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QHzChK1b-1684392412408)(D:文档1markdown笔记SSM框架swagger.jpg)]
实体类配置
//只要我们的接口中,返回值中存在实体类,他就会被扫描到Swagger中
@PostMapping("/user")
public User getUser(){
return new User();
}
@ApiModel("用户实体类")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
private String password;
}
异步任务
@Async
public void hello(){
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("数据正在处理...");
}
//主方法上开启异步
@EnableAsync
邮件发送
1.获取授权码
2.编写配置文件
spring.mail.username=2798336160@qq.com
spring.mail.password=wbsbtjfdljzkdebg
spring.mail.host=smtp.qq.com
#开启加密验证
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.ssl.enable=true
3.编写邮件信息
@Autowired
JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender;
//一个简单的邮件
@Test
void contextLoads() {
SimpleMailMessage mailMessage = new SimpleMailMessage();
//主题
mailMessage.setSubject("20230518");
mailMessage.setText("邮件发送任务");
mailMessage.setFrom("2798336160@qq.com");
mailMessage.setTo("jiangyanhua623@163.com");
mailSender.send(mailMessage);
}
//复杂的邮件
@Test
void contextLoads2() throws MessagingException {
MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage, true);
helper.setSubject("邮件测试");
// helper.setText("坚持就会有收获");
helper.setText("<p>fighting</p>",true);
//附件
helper.addAttachment("detais.jpg",new File("D:\文档1\markdown笔记\Linux操作系统\img\detais.jpg"));
helper.setFrom("2798336160@qq.com");
helper.setTo("2798336160@qq.com");
mailSender.send(mimeMessage);
}
定时任务
1.开启定时任务
@EnableScheduling
@Service
public class ScheduledService {
//在一个特定的时间执行该方法
//秒 分 时 日 月 周几
//* 每 ?未知
@Scheduled(cron = "0 42 13 * * ?")
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello,你被执行了");
}
}
jfdljzkdebg
spring.mail.host=smtp.qq.com
#开启加密验证
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.ssl.enable=true
3.编写邮件信息
```java
@Autowired
JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender;
//一个简单的邮件
@Test
void contextLoads() {
SimpleMailMessage mailMessage = new SimpleMailMessage();
//主题
mailMessage.setSubject("20230518");
mailMessage.setText("邮件发送任务");
mailMessage.setFrom("2798336160@qq.com");
mailMessage.setTo("jiangyanhua623@163.com");
mailSender.send(mailMessage);
}
//复杂的邮件
@Test
void contextLoads2() throws MessagingException {
MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage, true);
helper.setSubject("邮件测试");
// helper.setText("坚持就会有收获");
helper.setText("<p>fighting</p>",true);
//附件
helper.addAttachment("detais.jpg",new File("D:\文档1\markdown笔记\Linux操作系统\img\detais.jpg"));
helper.setFrom("2798336160@qq.com");
helper.setTo("2798336160@qq.com");
mailSender.send(mimeMessage);
}
定时任务
1.开启定时任务
@EnableScheduling
@Service
public class ScheduledService {
//在一个特定的时间执行该方法
//秒 分 时 日 月 周几
//* 每 ?未知
@Scheduled(cron = "0 42 13 * * ?")
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello,你被执行了");
}
}






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结