您现在的位置是:首页 >技术交流 >LeetCode高频算法刷题记录4网站首页技术交流
LeetCode高频算法刷题记录4
文章目录
1. 二叉树的最近公共祖先【中等】
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
参考题解:https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/solution/er-cha-shu-de-zui-jin-gong-gong-zu-xian-by-leetc-2/
1.1 题目描述
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
示例1:
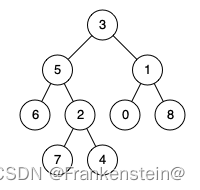
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
示例2:
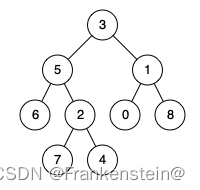
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出:5
解释:节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5 。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
示例3:
输入:root = [1,2], p = 1, q = 2
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围 [2, 10^5] 内。
- -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9
- 所有 Node.val 互不相同 。
- p != q
- p 和 q 均存在于给定的二叉树中。
1.2 解题思路
1.3 代码实现
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<TreeNode*, TreeNode*> father;
unordered_set<TreeNode*> nodes;
void recordFather(TreeNode* root) {
if(root->left) {
father[root->left] = root;
recordFather(root->left);
}
if(root->right) {
father[root->right] = root;
recordFather(root->right);
}
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
father[root] = NULL;
recordFather(root);
while(p) {
nodes.insert(p);
p = father[p];
}
while(q) {
if(nodes.count(q))
return q;
q = father[q];
}
return NULL;
}
};
2. 全排列【中等】
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/
参考题解:https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/solution/quan-pai-lie-by-leetcode-solution-2/
2.1 题目描述
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
示例2:
输入:nums = [0,1]
输出:[[0,1],[1,0]]
示例3:
输入:nums = [1]
输出:[[1]]
提示:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 6
- -10 <= nums[i] <= 10
- nums 中的所有整数 互不相同
2.2 解题思路
2.3 代码实现
class Solution {
public:
void fillNumber(vector<vector<int>>& ans, vector<int>& nums, int current) {
if(current == nums.size()) {
ans.push_back(nums);
return;
}
for(int i = current; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
swap(nums[i], nums[current]);
fillNumber(ans, nums, current + 1);
swap(nums[i], nums[current]);
}
}
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
fillNumber(ans, nums, 0);
// for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
// fillNumber(ans, nums, i);
return ans;
}
};
3. 相交链表【简单】
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
参考题解:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/solution/xiang-jiao-lian-biao-by-leetcode-solutio-a8jn/
3.1 题目描述
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
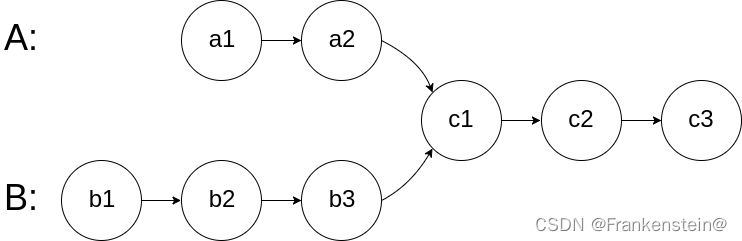
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序 不适用 此输入):
- intersectVal - 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为 0
- listA - 第一个链表
- listB - 第二个链表
- skipA - 在 listA 中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
- skipB - 在 listB 中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点 headA 和 headB 传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。
示例1:
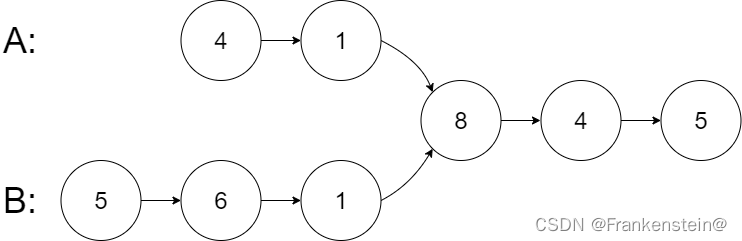
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at ‘8’
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
— 请注意相交节点的值不为 1,因为在链表 A 和链表 B 之中值为 1 的节点 (A 中第二个节点和 B 中第三个节点) 是不同的节点。换句话说,它们在内存中指向两个不同的位置,而链表 A 和链表 B 中值为 8 的节点 (A 中第三个节点,B 中第四个节点) 在内存中指向相同的位置。
示例2:
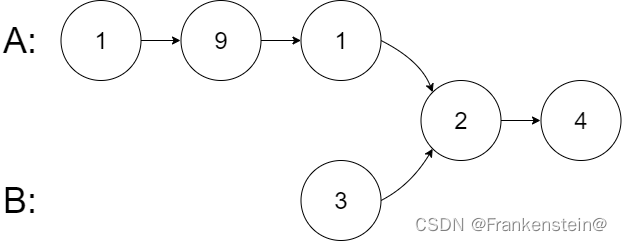
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at ‘2’
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例3:
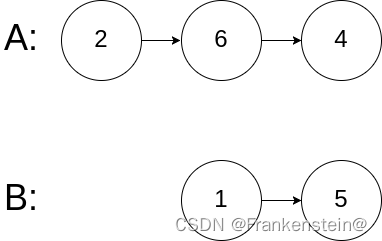
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
- listA 中节点数目为 m
- listB 中节点数目为 n
- 1 <= m, n <= 3 * 10^4
- 1 <= Node.val <= 10^5
- 0 <= skipA <= m
- 0 <= skipB <= n
- 如果 listA 和 listB 没有交点,intersectVal 为 0
- 如果 listA 和 listB 有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]
进阶: 你能否设计一个时间复杂度 O(m + n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案?
3.2 解题思路
3.3 代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
unordered_set<ListNode *> nodes;
ListNode *temp = headA;
while(temp) {
nodes.insert(temp);
temp = temp->next;
}
temp = headB;
while(temp) {
if(nodes.count(temp))
return temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
4. 合并 K 个升序链表【困难】
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
参考题解:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/solution/he-bing-kge-pai-xu-lian-biao-by-leetcode-solutio-2/
4.1 题目描述
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例2:
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例3:
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
提示:
- k == lists.length
- 0 <= k <= 10^4
- 0 <= lists[i].length <= 500
- -10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4
- lists[i] 按 升序 排列
- lists[i].length 的总和不超过 10^4
4.2 解题思路
4.3 代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoList(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
if(!list1)
return list2;
if(!list2)
return list1;
if(list1->val < list2->val) {
list1->next = mergeTwoList(list1->next, list2);
return list1;
}
else {
list2->next = mergeTwoList(list1, list2->next);
return list2;
}
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
int len = lists.size();
if(len == 0)
return nullptr;
ListNode* ans = nullptr;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
ans = mergeTwoList(ans, lists[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
5. 环形链表 II【中等】
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
参考题解:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/solution/huan-xing-lian-biao-ii-by-leetcode-solution/
5.1 题目描述
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例1:
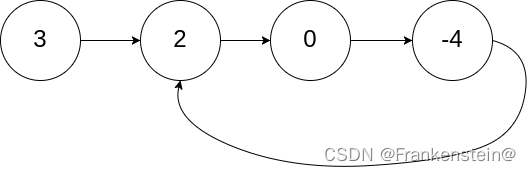
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例2:
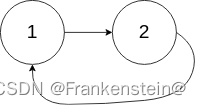
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围 [0, 10^4] 内
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
- pos 的值为 -1 或者链表中的一个有效索引
进阶: 你是否可以使用 O(1) 空间解决此题?
5.2 解题思路
5.3 代码实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
unordered_set<ListNode *> nodes;
ListNode *temp = head;
while(temp) {
if(nodes.count(temp))
return temp;
nodes.insert(temp);
temp = temp->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结