您现在的位置是:首页 >技术交流 >路径规划 | 图解快速随机扩展树RRT算法(附ROS C++/Python/Matlab仿真)网站首页技术交流
路径规划 | 图解快速随机扩展树RRT算法(附ROS C++/Python/Matlab仿真)
0 专栏介绍
?附C++/Python/Matlab全套代码?课程设计、毕业设计、创新竞赛必备!详细介绍全局规划(图搜索、采样法、智能算法等);局部规划(DWA、APF等);曲线优化(贝塞尔曲线、B样条曲线等)。
?详情:图解自动驾驶中的运动规划(Motion Planning),附几十种规划算法
1 什么是RRT算法?
快速扩展随机扩展树(Rapidly-exploring Random Tree, RRT)算法的核心原理是从起点开始构造一棵不断生长、向四周蔓延的搜索树,直到树触达终点邻域。

RRT算法和我们之前介绍的PRM算法有什么联系呢?
首先,PRM和RRT都是基于采样的方法,通过在环境中随机采样来生成一组节点从而进行路径规划,因而在高维空间都很适合。其次,PRM和RRT都基于连通性,来验证节点之间建立连接的可行性。此外,PRM和RRT有着相近的碰撞检测方法(也可以使用相同的碰撞函数)。所以理解了PRM算法对于RRT算法的原理很有帮助
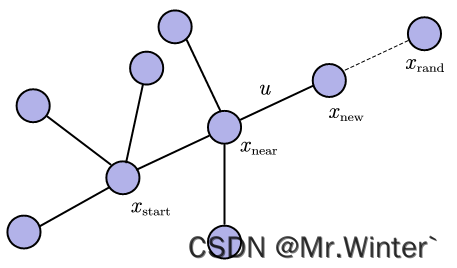
2 图解RRT算法原理
如图所示为RRT算法原理:设置步长 u u u为搜索树单次扩展的最大距离,首先在自由空间中采样 x r a n d x_{rand} xrand,并从已有的搜索树(初始时只有起点 x s t a r t x_{start} xstart)中找到 x r a n d x_{rand} xrand的最近邻 x n e a r x_{near} xnear;若 d ( x r a n d , x n e a r ) < u mathrm{d}left( x_{mathrm{rand}},x_{mathrm{near}} ight) <u d(xrand,xnear)<u,则令 x n e w = x r a n d x_{mathrm{new}}=x_{mathrm{rand}} xnew=xrand,否则从 x n e a r x_{mathrm{near}} xnear向 x r a n d x_{rand} xrand移动步长 u u u产生 x n e w x_{new} xnew;最后通过碰撞检测 C o l l i s i o n F r e e ( ⋅ ) mathrm{CollisionFree}left( cdot ight) CollisionFree(⋅)决定是否将 x n e w x_{mathrm{new}} xnew加入搜索树。
RRT算法流程如下所示

3 算法仿真与实现
3.1 ROS C++实现
根据算法流程可以写出RRT算法的核心代码
bool RRT::plan(const unsigned char* gloal_costmap, const Node& start, const Node& goal, std::vector<Node>& path,
std::vector<Node>& expand)
{
path.clear();
expand.clear();
sample_list_.clear();
// copy
start_ = start, goal_ = goal;
costs_ = gloal_costmap;
sample_list_.insert(start);
expand.push_back(start);
// main loop
int iteration = 0;
while (iteration < sample_num_)
{
// generate a random node in the map
Node sample_node = _generateRandomNode();
// obstacle
if (gloal_costmap[sample_node.id_] >= lethal_cost_ * factor_)
continue;
// visited
if (sample_list_.find(sample_node) != sample_list_.end())
continue;
// regular the sample node
Node new_node = _findNearestPoint(sample_list_, sample_node);
if (new_node.id_ == -1)
continue;
else
{
sample_list_.insert(new_node);
expand.push_back(new_node);
}
// goal found
if (_checkGoal(new_node))
{
path = _convertClosedListToPath(sample_list_, start, goal);
return true;
}
iteration++;
}
return false;
}

3.2 Python实现
def plan(self):
# main loop
for _ in range(self.sample_num):
# generate a random node in the map
node_rand = self.generateRandomNode()
# visited
if node_rand in self.sample_list:
continue
# generate new node
node_new = self.getNearest(self.sample_list, node_rand)
if node_new:
self.sample_list.append(node_new)
dist = self.dist(node_new, self.goal)
# goal found
if dist <= self.max_dist and not self.isCollision(node_new, self.goal):
self.goal.parent = node_new.current
self.goal.g = node_new.g + self.dist(self.goal, node_new)
self.sample_list.append(self.goal)
return self.extractPath(self.sample_list)
return 0, None

3.3 Matlab实现
function [path, flag, cost, expand] = rrt(map, start, goal)
% Maximum expansion distance one step
param.max_dist = 0.5;
% Maximum number of sample points
param.sample_num = 10000;
% heuristic sample
param.goal_sample_rate = 0.05;
% map size
[param.x_range, param.y_range] = size(map);
% resolution
param.resolution = 0.1;
% sample list
sample_list = [start, 0, start];
path = [];
flag = false;
cost = 0;
expand = [];
% main loop
for i=1: param.sample_num
% generate a random node in the map
node_rand = generate_node(goal, param);
% visited
if loc_list(node_rand, sample_list, [1, 2])
continue
end
% generate new node
[node_new, success] = get_nearest(sample_list, node_rand, map, param);
if success
sample_list = [node_new; sample_list];
distance = dist(node_new(1:2), goal');
% goal found
if distance <= param.max_dist && ~is_collision(node_new(1:2), goal, map, param)
goal_ = [goal, node_new(3) + distance, node_new(1:2)];
sample_list = [goal_; sample_list];
flag = true;
cost = goal_(3);
break
end
end
end
if flag
path = extract_path(sample_list, start);
expand = sample_list;
end
end

完整工程代码请联系下方博主名片获取
? 更多精彩专栏:






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结