您现在的位置是:首页 >技术教程 >微服务之服务容错网站首页技术教程
微服务之服务容错
Informal Essay By English
Share a sentence that I think is very reasonable, as long as you can know the underlying logic of anything, you can hold it without fear

参考书籍:
“凤凰架构”
引言
在 Martin Fowler 与 James Lewis合写的文章《Microservices: A Definition of This New Architectural Term》中列举了微服务的九个核心的业务与技术特征,其中对于容错性设计(Design for Failure)的解释如下:
将服务用作组件的结果是,应用程序需要设计为能够容忍服务失败。由于供应商不可用,任何服务调用都可能失败,客户必须尽可能优雅地对此做出响应。与单片设计相比,这是一个缺点,因为它引入了额外的复杂性来处理它。结果是微服务团队不断反思服务故障如何影响用户体验。Netflix 的Simian Army 在工作日期间引发服务甚至数据中心的故障,以测试应用程序的弹性和监控。这种生产中的自动化测试足以让大多数运营团队在下班前通常会感到不寒而栗。这并不是说单一的架构风格不能进行复杂的监控设置——它只是在我们的经验中不太常见。由于服务随时可能失败,因此能够快速检测到故障并在可能的情况下自动恢复服务非常重要。微服务应用程序非常重视应用程序的实时监控,检查架构元素(数据库每秒收到多少请求)和业务相关指标(例如每分钟收到多少订单)。语义监控可以提供出现问题的早期预警系统,触发开发团队跟进和调查。这对于微服务架构尤为重要,因为微服务对编排和事件协作的偏好 会导致紧急行为。虽然许多权威人士称赞意外出现的价值,但事实是,突发行为有时可能是一件坏事。监控对于快速发现不良的紧急行为至关重要,以便可以修复它。Monoliths 可以构建得像微服务一样透明——事实上,它们应该如此。不同之处在于,您绝对需要知道在不同进程中运行的服务何时断开连接。对于同一流程中的图书馆,这种透明度不太可能有用。微服务团队希望看到针对每个单独服务的复杂监控和日志记录设置,例如显示上/下状态的仪表板以及各种操作和业务相关指标。有关断路器状态、当前吞吐量和延迟的详细信息是我们在野外经常遇到的其他示例。
简而言之就是:在微服务架构中不再虚幻地追求服务永远稳定,而是接受服务总会出错的现实,要求在微服务的设计中,有自动的机制对其依赖的服务能够进行快速故障检测,在持续出错的时候进行隔离,在服务恢复的时候重新联通
上方只是对容错性设计的一个定义/解释,如何根据此原则进行微服务架构项目的落地实现我们还必须了解一些常用的容错策略和容错设计模式,作为具体设计与编码实践的指导。
容错策略
“面对故障,我们该做些什么”
常见的容错策略故障转移(Failover)、快速失败(Failfast)、安全失败(Failsafe)、沉默失败(Failsilent)、故障恢复(Failback)、并行调用(Forking)、广播调用(Broadcast)
故障转移(Failover)
高可用的服务集群中,多数的服务——尤其是那些经常被其他服务所依赖的关键路径上的服务,均会部署有多个副本。这些副本可能部署在不同的节点(避免节点宕机)、不同的网络交换机(避免网络分区)甚至是不同的可用区(避免整个地区发生灾害或电力、骨干网故障)中。故障转移是指如果调用的服务器出现故障,系统不会立即向调用者返回失败结果,而是自动切换到其他服务副本,尝试其他副本能否返回成功调用的结果,从而保证了整体的高可用性。
故障转移的容错策略应该有一定的调用次数限制,譬如允许最多重试三个服务,如果都发生报错,那还是会返回调用失败。原因不仅是因为重试是有执行成本的,更是因为过度的重试反而可能让系统处于更加不利的状况。譬如有以下调用链:
Service A → Service B → Service C
假设 A 的超时阈值为 100 毫秒,而 B 调用 C 花费 60 毫秒,然后不幸失败了,这时候做故障转移其实已经没有太大意义了,因为即时下一次调用能够返回正确结果,也很可能同样需要耗费 60 毫秒时间,时间总和就已经触及 A 服务的超时阈值,所以在这种情况下故障转移反而对系统是不利的。
? 了解更多
下面我们来看看dubbo在服务调用时故障转移的处理逻辑,先贴上代码:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
/**
* {@link FailoverClusterInvoker}
*
*/
public class FailoverCluster implements Cluster {
public final static String NAME = "failover";
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
//FailoverClusterInvoker的创建,在构建方法中会进行服务的availablecheck
return new FailoverClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
}
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Constants;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Version;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.Logger;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.utils.NetUtils;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Result;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcContext;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.support.RpcUtils;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* When invoke fails, log the initial error and retry other invokers (retry n times, which means at most n different invokers will be invoked)
* Note that retry causes latency.
* <p>
* <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Failover">Failover</a>
*
*/
public class FailoverClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FailoverClusterInvoker.class);
public FailoverClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
//很多的check states 逻辑
List<Invoker<T>> copyinvokers = invokers;
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.RETRIES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1;
if (len <= 0) {
len = 1;
}
// retry loop.
RpcException le = null; // last exception.
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyinvokers.size()); // invoked invokers.
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
//当调用失败时,记录初始错误并重试其他调用程序(重试n次,这意味着最多将调用n个不同的调用程序)。注意,重试会导致延迟
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
//Reselect before retry to avoid a change of candidate `invokers`.
//NOTE: if `invokers` changed, then `invoked` also lose accuracy.
if (i > 0) {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
copyinvokers = list(invocation);
// check again
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
}
//loadbalance入口
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyinvokers, invoked);
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Although retry the method " + methodName
+ " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress()
+ ", but there have been failed providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ le.getMessage(), le);
}
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) { // biz exception.
throw e;
}
le = e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
throw new RpcException(le != null ? le.getCode() : 0, "Failed to invoke the method "
+ methodName + " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ ". Tried " + len + " times of the providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyinvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version "
+ Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ (le != null ? le.getMessage() : ""), le != null && le.getCause() != null ? le.getCause() : le);
}
}
/**
* Select a invoker using loadbalance policy.</br>
* a)Firstly, select an invoker using loadbalance. If this invoker is in previously selected list, or,
* if this invoker is unavailable, then continue step b (reselect), otherwise return the first selected invoker</br>
* b)Reslection, the validation rule for reselection: selected > available. This rule guarantees that
* the selected invoker has the minimum chance to be one in the previously selected list, and also
* guarantees this invoker is available.
*
* @param loadbalance load balance policy
* @param invocation
* @param invokers invoker candidates
* @param selected exclude selected invokers or not
* @return
* @throws RpcException
*/
protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
//还是很多的check states
if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty())
return null;
String methodName = invocation == null ? "" : invocation.getMethodName();
boolean sticky = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.CLUSTER_STICKY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_STICKY);
{
//ignore overloaded method
if (stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(stickyInvoker)) {
stickyInvoker = null;
}
//ignore concurrency problem
if (sticky && stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(stickyInvoker))) {
if (availablecheck && stickyInvoker.isAvailable()) {
return stickyInvoker;
}
}
}
//loadbalance逻辑入口
Invoker<T> invoker = doSelect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
if (sticky) {
stickyInvoker = invoker;
}
return invoker;
}
//选择使用负载平衡策略的调用程序。
//首先,选择一个使用loadbalance的调用程序。如果这个调用程序在之前选择的列表中,或者这个调用程序不可用,那么继续步骤b(重新选择),
//否则返回第一个选择的调用程序 selection,重新选择的验证规则:selected >可用。
//该规则保证所选调用程序在先前选择的列表中出现的可能性最小,并且还保证该调用程序是可用的
private Invoker<T> doSelect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty())
return null;
if (invokers.size() == 1)
return invokers.get(0);
if (loadbalance == null) {
loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE);
}
Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, getUrl(), invocation);
//如果'调用器'在' selected '中或调用器不可用&& availablecheck为true,则重新选择。
if ((selected != null && selected.contains(invoker))
|| (!invoker.isAvailable() && getUrl() != null && availablecheck)) {
try {
Invoker<T> rinvoker = reselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected, availablecheck);
if (rinvoker != null) {
invoker = rinvoker;
} else {
//Check the index of current selected invoker, if it's not the last one, choose the one at index+1.
int index = invokers.indexOf(invoker);
try {
//Avoid collision
invoker = index < invokers.size() - 1 ? invokers.get(index + 1) : invokers.get(0);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(e.getMessage() + " may because invokers list dynamic change, ignore.", e);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("cluster reselect fail reason is :" + t.getMessage() + " if can not solve, you can set cluster.availablecheck=false in url", t);
}
}
return invoker;
}
快速失败(Failfast)
在一个调用链路中的服务通常也有主路和旁路之分,并不见得其中每个服务都是不可或缺的,有部分服务失败了也不影响核心业务的正确性。譬如开发基于 Spring 管理的应用程序时,通过扩展点、事件或者 AOP 注入的逻辑往往就属于旁路逻辑,典型的有审计、日志、调试信息,等等。属于旁路逻辑的另一个显著特征是后续处理不会依赖其返回值,或者它的返回值是什么都不会影响后续处理的结果,譬如只是将返回值记录到数据库,并不使用它参与最终结果的运算。对这类逻辑,一种理想的容错策略是即使旁路逻辑调用实际失败了,也当作正确来返回,如果需要返回值的话,系统就自动返回一个符合要求的数据类型的对应零值,然后自动记录一条服务调用出错的日志备查即可,这种策略被称为安全失败
?了解更多
下面我们来看看dubbo在服务调用时快速失败的处理逻辑,先贴上代码:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
/**
* {@link FailfastClusterInvoker}
*
*/
public class FailfastCluster implements Cluster {
public final static String NAME = "failfast";
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
//FailfastClusterInvoker的创建,在构建方法中会进行服务的availablecheck
return new FailfastClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
}
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Version;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.utils.NetUtils;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Result;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Execute exactly once, which means this policy will throw an exception immediately in case of an invocation error.
* Usually used for non-idempotent write operations
*
* <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fail-fast">Fail-fast</a>
*
*/
public class FailfastClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
public FailfastClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
try {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (e instanceof RpcException && ((RpcException) e).isBiz()) { // biz exception.
throw (RpcException) e;
}
throw new RpcException(e instanceof RpcException ? ((RpcException) e).getCode() : 0, "Failfast invoke providers " + invoker.getUrl() + " " + loadbalance.getClass().getSimpleName() + " select from all providers " + invokers + " for service " + getInterface().getName() + " method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", but no luck to perform the invocation. Last error is: " + e.getMessage(), e.getCause() != null ? e.getCause() : e);
}
}
}
源码看到这里其实就够了,其他的执行逻辑与上面的Failover的一致,但是相比较FailLover的执行,这里少了一个for循环也就是说invoke只执行一次,这意味着如果发生调用错误,此策略将立即抛出异常。通常用于非幂等写操作
安全失败(Failsafe)
在一个调用链路中的服务通常也有主路和旁路之分,并不见得其中每个服务都是不可或缺的,有部分服务失败了也不影响核心业务的正确性。譬如开发基于 Spring 管理的应用程序时,通过扩展点、事件或者 AOP 注入的逻辑往往就属于旁路逻辑,典型的有审计、日志、调试信息,等等。属于旁路逻辑的另一个显著特征是后续处理不会依赖其返回值,或者它的返回值是什么都不会影响后续处理的结果,譬如只是将返回值记录到数据库,并不使用它参与最终结果的运算。对这类逻辑,一种理想的容错策略是即使旁路逻辑调用实际失败了,也当作正确来返回,如果需要返回值的话,系统就自动返回一个符合要求的数据类型的对应零值,然后自动记录一条服务调用出错的日志备查即可,这种策略被称为安全失败。
?了解更多
还是一样用dubbo做案例:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
/**
* {@link FailsafeClusterInvoker}
*
*/
public class FailsafeCluster implements Cluster {
public final static String NAME = "failsafe";
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
//FailsafeClusterInvoker的创建,在构建方法中会进行服务的availablecheck
return new FailsafeClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
}
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.Logger;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Result;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcResult;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance;
import java.util.List;
/**
* When invoke fails, log the error message and ignore this error by returning an empty RpcResult.
* Usually used to write audit logs and other operations
*
* <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fail-safe">Fail-safe</a>
*
*/
public class FailsafeClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FailsafeClusterInvoker.class);
public FailsafeClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
try {
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (Throwable e) {
//当调用失败时,记录错误消息,并通过返回空RpcResult来忽略此错误。通常用于编写审计日志和其他操作
logger.error("Failsafe ignore exception: " + e.getMessage(), e);
return new RpcResult(); // ignore
}
}
}
沉默失败(Failsilent)
如果大量的请求需要等到超时(或者长时间处理后)才宣告失败,很容易由于某个远程服务的请求堆积而消耗大量的线程、内存、网络等资源,进而影响到整个系统的稳定。面对这种情况,一种合理的失败策略是当请求失败后,就默认服务提供者一定时间内无法再对外提供服务,不再向它分配请求流量,将错误隔离开来,避免对系统其他部分产生影响,此即为沉默失败策略。
这种策略dubbo是没有相应的实现的,但是我们可以自己去基于dubbo的SPI机制去实现,这里博主提供一个思路:在具体的invoker中增加一个Failsilent的boolean字段去标记是否属于沉默失败的invoker,如果Failsilent为true则不做调用,如果为false则正常调用,当然这里还涉及到这个沉默失败的时间怎么定义,这里也提供一个思路,常规的就是系统变量 -> java环境变量 -> 配置文件 进行动态的设置
故障恢复(Failback)
故障恢复一般不单独存在,而是作为其他容错策略的补充措施,一般在微服务管理框架中,如果设置容错策略为故障恢复的话,通常默认会采用快速失败加上故障恢复的策略组合。它是指当服务调用出错了以后,将该次调用失败的信息存入一个消息队列中,然后由系统自动开始异步重试调用。
故障恢复策略一方面是尽力促使失败的调用最终能够被正常执行,另一方面也可以为服务注册中心和负载均衡器及时提供服务恢复的通知信息。故障恢复显然也是要求服务必须具备幂等性的,由于它的重试是后台异步进行,即使最后调用成功了,原来的请求也早已经响应完毕,所以故障恢复策略一般用于对实时性要求不高的主路逻辑,同时也适合处理那些不需要返回值的旁路逻辑。为了避免在内存中异步调用任务堆积,故障恢复与故障转移一样,应该有最大重试次数的限制。
案例:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
/**
* {@link FailbackClusterInvoker}
*
*/
public class FailbackCluster implements Cluster {
public final static String NAME = "failback";
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
FailbackClusterInvoker的创建,在构建方法中会进行服务的availablecheck
return new FailbackClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
}
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.Logger;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.threadlocal.NamedInternalThreadFactory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Result;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcResult;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcContext;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* When fails, record failure requests and schedule for retry on a regular interval.
* Especially useful for services of notification.
*
* <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Failback">Failback</a>
*
*/
public class FailbackClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FailbackClusterInvoker.class);
//重试时间
private static final long RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD = 5 * 1000;
/**
* Use {@link NamedInternalThreadFactory} to produce {@link com.alibaba.dubbo.common.threadlocal.InternalThread}
* which with the use of {@link com.alibaba.dubbo.common.threadlocal.InternalThreadLocal} in {@link RpcContext}.
*/
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,
new NamedInternalThreadFactory("failback-cluster-timer", true));
private final ConcurrentMap<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>> failed = new ConcurrentHashMap<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>>();
private volatile ScheduledFuture<?> retryFuture;
public FailbackClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
private void addFailed(Invocation invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?> router) {
if (retryFuture == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (retryFuture == null) {
retryFuture = scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// collect retry statistics
try {
retryFailed();
} catch (Throwable t) { // Defensive fault tolerance
logger.error("Unexpected error occur at collect statistic", t);
}
}
}, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
}
failed.put(invocation, router);
}
void retryFailed() {
if (failed.size() == 0) {
return;
}
for (Map.Entry<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>> entry : new HashMap<Invocation, AbstractClusterInvoker<?>>(
failed).entrySet()) {
Invocation invocation = entry.getKey();
Invoker<?> invoker = entry.getValue();
try {
invoker.invoke(invocation);
failed.remove(invocation);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Failed retry to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", waiting again.", e);
}
}
}
@Override
protected Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
try {
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Failback to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", wait for retry in background. Ignored exception: "
+ e.getMessage() + ", ", e);
//当失败时,记录失败请求并定期安排重试。
//特别适用于通知服务,重试时间在RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD静态变量中指定:5 * 1000 ms
addFailed(invocation, this);
return new RpcResult(); // ignore
}
}
}
并行调用(Forking)
上面五种以“Fail”开头的策略是针对调用失败时如何进行弥补的,以下这两种策略则是在调用之前就开始考虑如何获得最大的成功概率。并行调用策略很符合人们日常对一些重要环节进行的“双重保险”或者“多重保险”的处理思路,它是指一开始就同时向多个服务副本发起调用,只要有其中任何一个返回成功,那调用便宣告成功,这是一种在关键场景中使用更高的执行成本换取执行时间和成功概率的策略
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
/**
* {@link ForkingClusterInvoker}
*
*/
public class ForkingCluster implements Cluster {
public final static String NAME = "forking";
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
//ForkingClusterInvoker的创建,在构建方法中会进行服务的availablecheck
return new ForkingClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
}
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.Constants;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.threadlocal.NamedInternalThreadFactory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Result;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcContext;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* Invoke a specific number of invokers concurrently, usually used for demanding real-time operations, but need to waste more service resources.
*
* <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fork_(topology)">Fork</a>
*
*/
public class ForkingClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
/**
* Use {@link NamedInternalThreadFactory} to produce {@link com.alibaba.dubbo.common.threadlocal.InternalThread}
* which with the use of {@link com.alibaba.dubbo.common.threadlocal.InternalThreadLocal} in {@link RpcContext}.
*/
private final ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(
new NamedInternalThreadFactory("forking-cluster-timer", true));
public ForkingClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
try {
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
final List<Invoker<T>> selected;
final int forks = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.FORKS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_FORKS);
final int timeout = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
if (forks <= 0 || forks >= invokers.size()) {
selected = invokers;
} else {
selected = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>();
for (int i = 0; i < forks; i++) {
// TODO. Add some comment here, refer chinese version for more details.
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
if (!selected.contains(invoker)) {//Avoid add the same invoker several times.
selected.add(invoker);
}
}
}
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) selected);
final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
final BlockingQueue<Object> ref = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Object>();
for (final Invoker<T> invoker : selected) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
ref.offer(result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
int value = count.incrementAndGet();
if (value >= selected.size()) {
ref.offer(e);
}
}
}
});
}
try {
Object ret = ref.poll(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (ret instanceof Throwable) {
Throwable e = (Throwable) ret;
throw new RpcException(e instanceof RpcException ? ((RpcException) e).getCode() : 0, "Failed to forking invoke provider " + selected + ", but no luck to perform the invocation. Last error is: " + e.getMessage(), e.getCause() != null ? e.getCause() : e);
}
return (Result) ret;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to forking invoke provider " + selected + ", but no luck to perform the invocation. Last error is: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
} finally {
// clear attachments which is binding to current thread.
RpcContext.getContext().clearAttachments();
}
}
}
dubbo的Forking策略实现其实就是在一个循环中通过队列➕线程池实现,其中队列是用于存放返回信息,线程池执行具体invoke逻辑,具体逻辑可自行看源码,是比较好懂的
广播调用(Broadcast)
广播调用与并行调用是相对应的,都是同时发起多个调用,但并行调用是任何一个调用结果返回成功便宣告成功,广播调用则是要求所有的请求全部都成功,这次调用才算是成功,任何一个服务提供者出现异常都算调用失败,广播调用通常会被用于实现“刷新分布式缓存”这类的操作。
?了解更多
案例:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
/**
* BroadcastCluster
*
*/
public class BroadcastCluster implements Cluster {
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
//BroadcastClusterInvoker的创建,在构建方法中会进行服务的availablecheck
return new BroadcastClusterInvoker<T>(directory);
}
}
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.Logger;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Result;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcContext;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.LoadBalance;
import java.util.List;
/**
* BroadcastClusterInvoker
*
*/
public class BroadcastClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BroadcastClusterInvoker.class);
public BroadcastClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invokers);
RpcException exception = null;
Result result = null;
//所谓广播调用其实就是调用所有的invoker的invoke方法
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
try {
result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (RpcException e) {
exception = e;
logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
exception = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
if (exception != null) {
throw exception;
}
return result;
}
}
到此几种常见的容错策略我们已经介绍完了,其实dubbo中内置还有Available、Mergeable两种容错策略,感兴趣的可以去看看dubbo源码,由于篇幅问题,这里就不过多介绍了,贴上代码连接:
最后再总结一下几种常见容错策略优缺点及应用场景对比:
| 容错策略 | 优点 | 缺点 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 故障转移 | 系统自动处理,调用者对失败的信息不可见 | 增加调用时间,额外的资源开销 | 调用幂等服务对调用时间不敏感的场景 |
| 快速失败 | 调用者有对失败的处理完全控制权不依赖服务的幂等性 | 调用者必须正确处理失败逻辑,如果一味只是对外抛异常,容易引起雪崩 | 调用非幂等的服务超时阈值较低的场景 |
| 安全失败 | 不影响主路逻辑 | 只适用于旁路调用 | 调用链中的旁路服务 |
| 沉默失败 | 控制错误不影响全局 | 出错的地方将在一段时间内不可用 | 频繁超时的服务 |
| 故障恢复 | 调用失败后自动重试,也不影响主路逻辑 | 重试任务可能产生堆积,重试仍然可能失败 | 调用链中的旁路服务对实时性要求不高的主路逻辑也可以使用 |
| 并行调用 | 尽可能在最短时间内获得最高的成功率 | 额外消耗机器资源,大部分调用可能都是无用功 | 资源充足且对失败容忍度低的场景 |
| 广播调用 | 支持同时对批量的服务提供者发起调用 | 资源消耗大,失败概率高 | 只适用于批量操作的场景 |
容错设计模式
容错策略的最佳实现(类比于java与23种设计模式关系)
为了实现各种各样的容错策略,开发人员总结出了一些被实践证明是有效的服务容错设计模式,譬如微服务中常见的断路器模式、舱壁隔离模式,重试模式,等等
断路器模式(wiki)
断路器是一个现代软件开发的设计模式。用以侦测错误,并避免不断地触发相同的错误(如维护时服务不可用、暂时性的系统问题或是未知的系统错误) – 百度百科
这个设计模式最早由技术作家 Michael Nygard 在《Release It!》一书中提出的,后又因 Martin Fowler 的《Circuit Breaker》一文而广为人知。这里引用凤凰架构对断路器模式的一个解释:
断路器的基本思路是很简单的,就是通过代理(断路器对象)来一对一地(一个远程服务对应一个断路器对象)接管服务调用者的远程请求。断路器会持续监控并统计服务返回的成功、失败、超时、拒绝等各种结果,当出现故障(失败、超时、拒绝)的次数达到断路器的阈值时,它状态就自动变为“OPEN”,后续此断路器代理的远程访问都将直接返回调用失败,而不会发出真正的远程服务请求。通过断路器对远程服务的熔断,避免因持续的失败或拒绝而消耗资源,因持续的超时而堆积请求,最终的目的就是避免雪崩效应的出现。由此可见,断路器本质是一种快速失败策略的实现方式
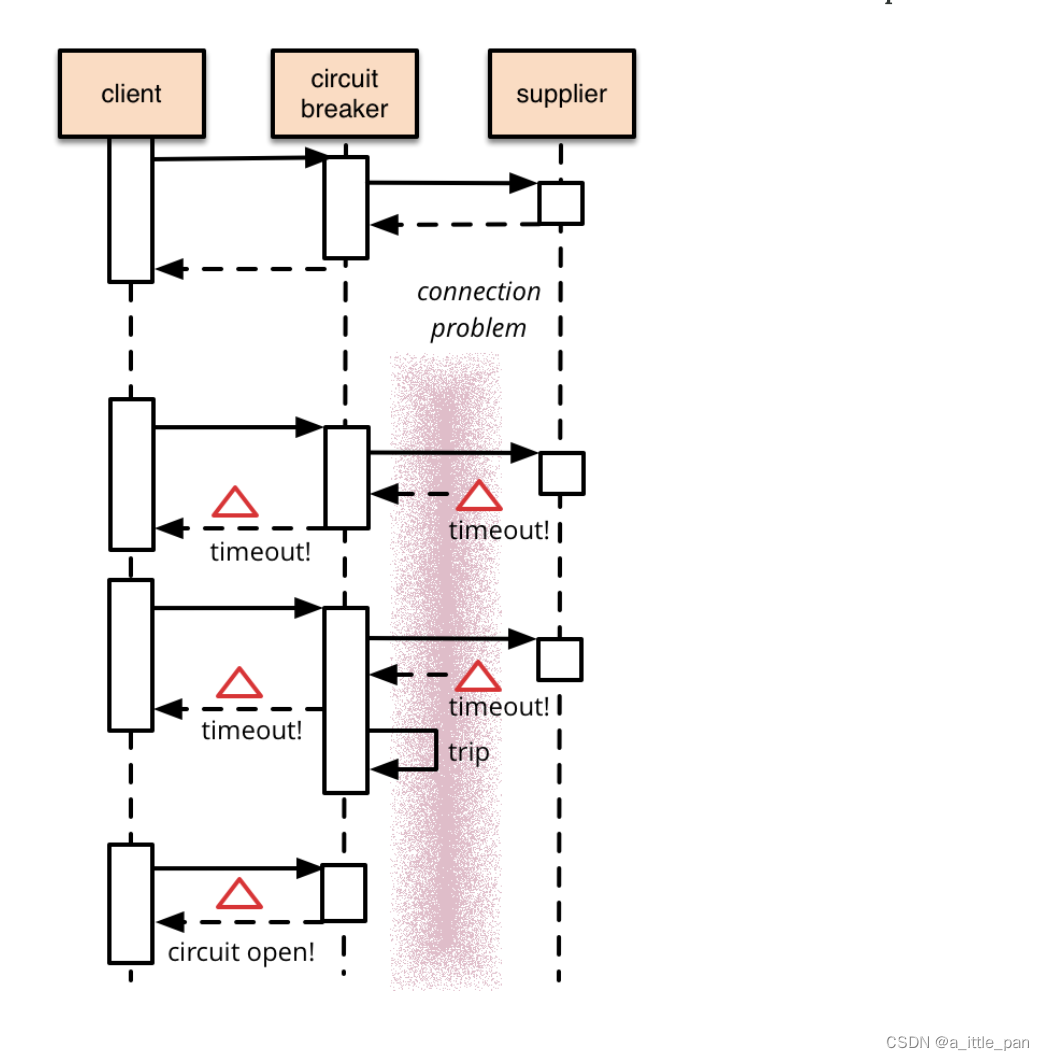
从调用序列来看,断路器就是一种有限状态机,断路器模式就是根据自身状态变化自动调整代理请求策略的过程。一般要设置以下三种断路器的状态
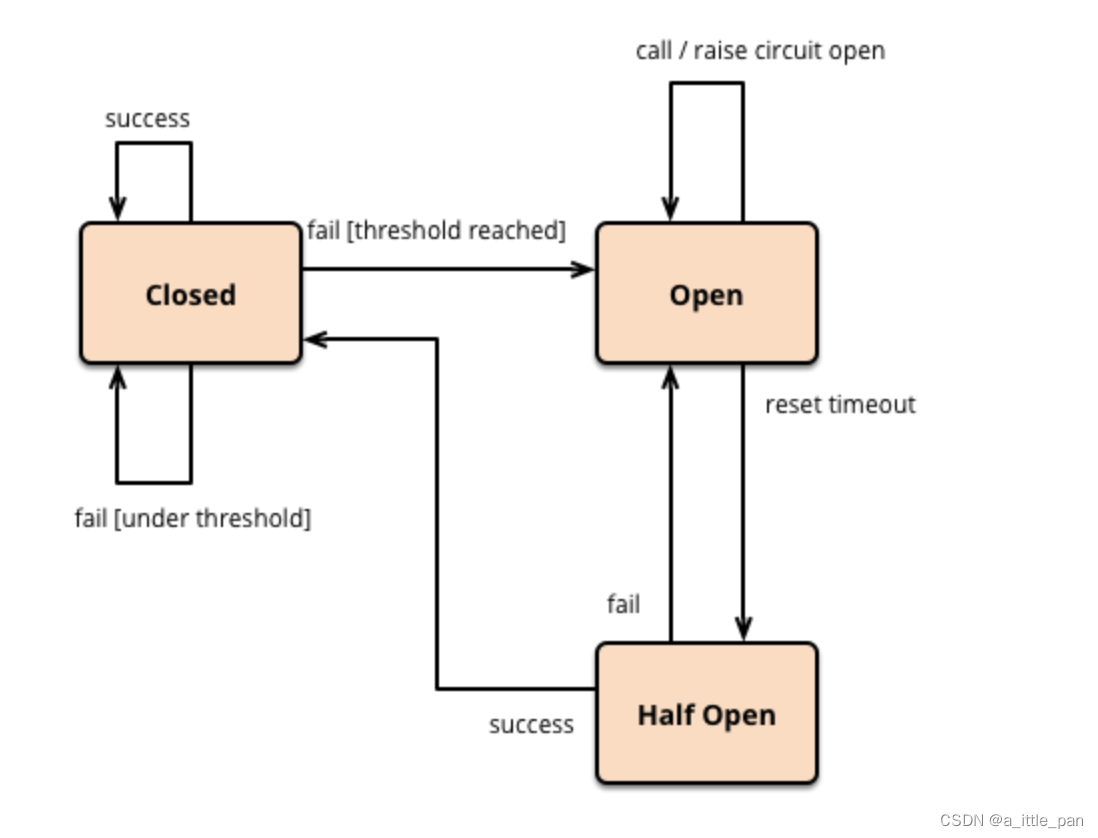
- CLOSED:表示断路器关闭,此时的远程请求会真正发送给服务提供者。断路器刚刚建立时默认处于这种状态,此后将持续监视远程请求的数量和执行结果,决定是否要进入 OPEN 状态
- OPEN:表示断路器开启,此时不会进行远程请求,直接给服务调用者返回调用失败的信息,以实现快速失败策略。
- HALF OPEN:这是一种中间状态。断路器必须带有自动的故障恢复能力,当进入 OPEN 状态一段时间以后,将“自动”(一般是由下一次请求而不是计时器触发的,所以这里自动带引号)切换到 HALF OPEN 状态。该状态下,会放行一次远程调用,然后根据这次调用的结果成功与否,转换为 CLOSED 或者 OPEN 状态,以实现断路器的弹性恢复。
舱壁隔离模式(Bulkhead Isolation)
隔离了每个工作负载或服务的关键资源,如连接池、内存和 CPU。使用舱壁避免了单个工作负载(或服务)消耗掉所有资源,从而导致其他服务出现故障的场景。这种模式主要是通过防止由一个服务引起的级联故障来增加系统的弹性
Hystrix使用该模式实现线程池的隔离。通过将每个依赖服务分配独立的线程池进行资源隔离,从而避免服务雪崩。
Hystrix会为每一个Hystrix命令(@HystrixCommand来将某个函数包装成了Hystrix命令,Hystrix框架就会自动的为这个函数实现调用的隔离)创建一个独立的线程池,这样就算某个在Hystrix命令包装下的依赖服务出现延迟过高的情况,也只是对该依赖服务的调用产生影响,而不会拖慢其他的服务
我们来看一个更具体的场景,当分布式系统所依赖的某个服务,譬如下图中的“服务 I”发生了超时,那在高流量的访问下——或者更具体点,假设平均 1 秒钟内对该服务的调用会发生 50 次,这就意味着该服务如果长时间不结束的话,每秒会有 50 条用户线程被阻塞。如果这样的访问量一直持续,我们按 Tomcat 默认的 HTTP 超时时间 20 秒来计算,20 秒内将会阻塞掉 1000 条用户线程,此后才陆续会有用户线程因超时被释放出来,回归 Tomcat 的全局线程池中。一般 Java 应用的线程池最大只会设置到 200 至 400 之间,这意味着此时系统在外部将表现为所有服务的全面瘫痪,而不仅仅是只有涉及到“服务 I”的功能不可用,因为 Tomcat 已经没有任何空余的线程来为其他请求提供服务了
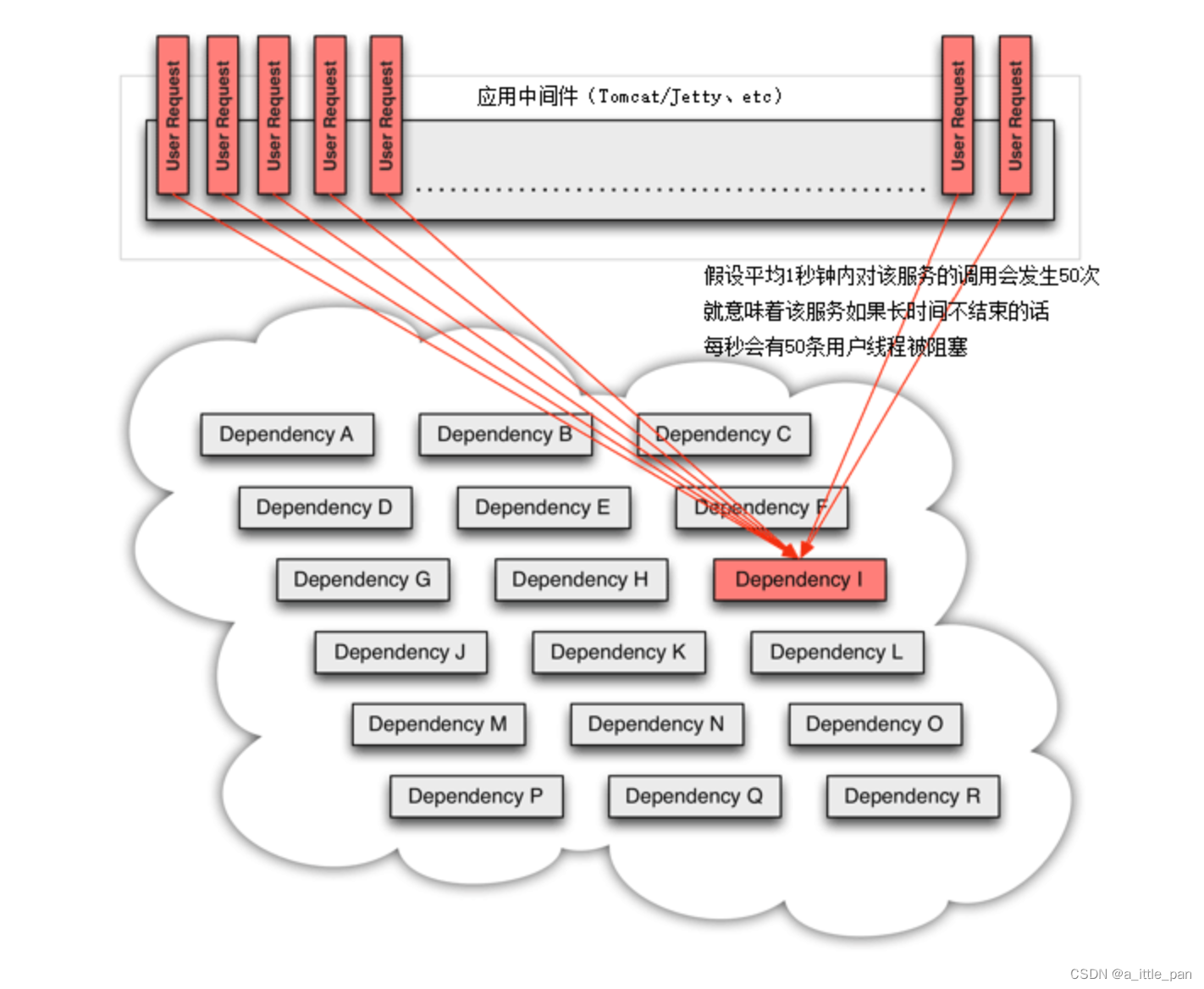
对于这类情况,一种可行的解决办法是为每个服务单独设立线程池,这些线程池默认不预置活动线程,只用来控制单个服务的最大连接数。譬如,对出问题的“服务 I”设置了一个最大线程数为 5 的线程池,这时候它的超时故障就只会最多阻塞 5 条用户线程,而不至于影响全局。
重试模式
通过透明地重试失败的操作,让应用程序可以在尝试连接到服务或网络资源时处理出现的瞬态故障。这可以提高应用程序的稳定性
重试模式顾名思义就是不断去重试,这个概念是比较好理解的,因此在此不对概念做过多介绍,稍微需要注意的是在什么情况下适合使用重试模式。如果你在应用程序与远程服务交互或访问远程资源时可能会遇到瞬态故障时,那么请使用此模式。 这些故障持续时间不长,并且重复先前失败的请求可能会在以后的尝试中成功。但是此模式不适合在如下场景下去使用:
- 故障比较持久,可能会影响应用程序的响应。重复尝试可能失败的请求,对于应用程序来说是浪费时间和资源。
- 用于处理非瞬态故障导致的失败,例如由应用程序的业务逻辑中的错误引起的内部异常
- 作为解决系统中可扩展性问题的替代方法。如果应用程序遇到频繁的忙碌故障,这表明应当垂直扩展正在访问的服务或资源。
在一开始介绍容错设计模式的时候就提出了它与容错策略的关系,对于类似这种模式的学习,我们只需要关注于它的核心思想是什么样其实就行,也不一定要按照它的要求去做,就像我们在开发java程序的时候,开发人员也可以不照搬23中设计模式去编码也能优雅地实现功能,四个字总结就是:“核心思想!!”






 U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结