您现在的位置是:首页 >技术杂谈 >Spring事务深度学习网站首页技术杂谈
Spring事务深度学习
jdbcTemp
Spring 框架对 JDBC 进行封装,使用 JdbcTemplate 方便实现对数据库操作。
JdbcTemp的使用
对应依赖
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.20</version>
</dependency>创建jdbc.properties属性文件
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver创建bean.xml,配置配置文件引入和jdbctemp配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 引入外部的数据源配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 通过数据源的文件将数据注入bean中-->
<!-- 通过${}在数据源的配置文件中进行取值-->
<bean id="jdbcDriver" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- jdbcTemp配置-->
<bean id="jdbcTemp" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="jdbcDriver"></property>
</bean>
</beans>创建数据库和表
CREATE DATABASE `spring`;
use `spring`;
CREATE TABLE `t_emp` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
`sex` varchar(2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '性别',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;创建接收类
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + ''' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + ''' +
'}';
}
}测试例子一(修改):
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class updateTest {
//获取JdbcTemple
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
JdbcTemplate template = context.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
//增加数据
@org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
public void addTest() {
String sql = "insert into t_emp value(?, ?, ?, ?)";
template.update(sql, null, "秃狼1", 18, "男");
}
//删除数据
@org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
public void deleteTest() {
String sql = "delete from t_emp where id = ?";
template.update(sql, 1);
}
//修改数据
@org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
public void updateTest() {
String sql = "update t_emp set name = ? where id = ?";
template.update(sql, "tolen", 2);
}
}
测试例子二(查询):
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.util.List;
public class selectTest {
//获取JdbcTemple
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
JdbcTemplate template = context.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
//获取一个数据
@Test
public void queryForObject() {
String sql = "select * from t_emp where id = ?";
//BeanPropertyRowMapper自动封装数据的实现类,通过构造方法中传入的Class来确定封装类
User user = template.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class), 2);
System.out.println(user.getName());
}
//获取所有数据
@Test
public void queryList() {
String sql = "select * from t_emp";
List<User> result = template.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(User.class));
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(result.get(i).toString());
}
}
//获取数据的个数
@Test
public void queryCount() {
String sql = "select count(*) from t_emp";
//在queryForObject中,如果第二个参数为Integer.class类型时,就是返回符合对应条件的数据的个数
Integer integer = template.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
System.out.println("所有的数据个数:" + integer);
}
}
声明式事务
在Transactional注解中存在一下属性可以设置。
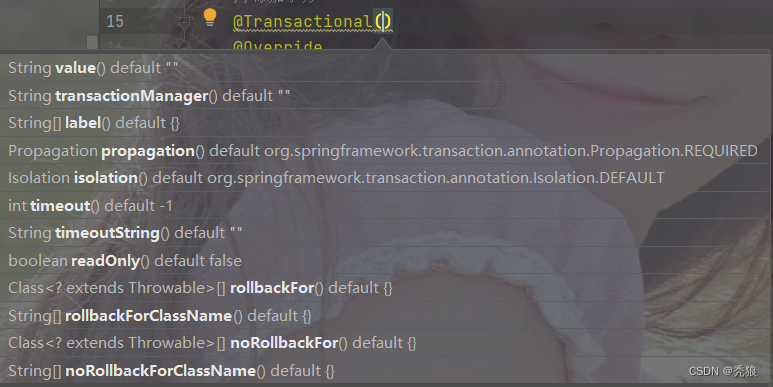
readOnly:默认为false,也就是不开启只读。(只读只允许select的查询操作,不能执行update操作)
timeout:表示超时时间,默认为-1,也就是永不超时。(这里的单位为Second)
rollbackForClassName/rollbackFor:表示当存在对应的类的时候就进行回滚,如果是ClassName的话,输入的值就是类的全路径,如果是For的话,就是对应类的.Class。
noRollbackForClassName/NoRollbackFor:与上述相反,就是不出现对应的类时就是进行回滚。
isolation:就是设置事务的隔离级别。用于处理脏读,不可重复读,幻读。
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| READ UNCOMMITTED | 有 | 有 | 有 |
| READ COMMITTED | 无 | 有 | 有 |
| REPEATABLE READ | 无 | 无 | 有 |
| SERIALIZABLE | 无 | 无 | 无 |
隔离级别一共有四种:
-
读未提交:READ UNCOMMITTED
允许Transaction01读取Transaction02未提交的修改。
-
读已提交:READ COMMITTED、
要求Transaction01只能读取Transaction02已提交的修改。
-
可重复读:REPEATABLE READ
确保Transaction01可以多次从一个字段中读取到相同的值,即Transaction01执行期间禁止其它事务对这个字段进行更新。
-
串行化:SERIALIZABLE
确保Transaction01可以多次从一个表中读取到相同的行,在Transaction01执行期间,禁止其它事务对这个表进行添加、更新、删除操作。可以避免任何并发问题,但性能十分低下。
对应的效果越好,执行效率就越低
propagation:设置传播行为。
常用的就是:@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED), 默认情况,表示如果当前线程上有已经开启的事务可用,那么就在这个事务中运行。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW),表示不管当前线程上是否有已经开启的事务,都要开启新事务。、
测试例子
在啊数据库中插入对应的数据。
CREATE TABLE `t_book` (
`book_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`book_name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '图书名称',
`price` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '价格',
`stock` int(10) unsigned DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '库存(无符号)',
PRIMARY KEY (`book_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `t_book`(`book_id`,`book_name`,`price`,`stock`) values (1,'斗破苍穹',80,100),(2,'斗罗大陆',50,100);
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`username` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
`balance` int(10) unsigned DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '余额(无符号)',
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `t_user`(`user_id`,`username`,`balance`) values (1,'admin',50);配置bean.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:con="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!-- 引入外部的数据源配置文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 通过数据源的文件将数据注入bean中-->
<!-- 通过${}在数据源的配置文件中进行取值-->
<bean id="jdbcDriver" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- jdbcTemp配置-->
<bean id="jdbcTemp" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="jdbcDriver"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 开启注解扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.huang"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 将事务类写入Bean容器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="jdbcDriver"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 开启事务注解驱动-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
</beans>对应的jdbc.properties文件
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver创建三层架构
在service层中创建 BuyBookServiceImpl和CheckServiceImpl。
BuyBookServiceImpl:
import com.huang.Dao.BuyBookDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
//实现的接口就是简单的接口
@Service
public class BuyBookServiceImpl implements BuyBookService{
@Autowired
BuyBookDao buyBookDao;
//添加事务
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
@Override
public void BuyBook(Integer bookId, Integer userId) {
buyBookDao.setBook(bookId);
Integer price = buyBookDao.getPrice(bookId);
System.out.println(price);
buyBookDao.setUser(userId, price);
}
}
CheckServiceImpl:
package com.huang.Service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service
public class CheckServiceImpl implements CheckService {
@Autowired
BuyBookService buyBookService;
@Transactional
@Override
public void CheckBook(Integer[] bookIds, Integer userId) {
for (int i = 0; i < bookIds.length; i++) {
buyBookService.BuyBook(bookIds[i], userId);
}
}
}
Controller层
import com.huang.Service.BuyBookService;
import com.huang.Service.CheckService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class BuyBookController {
@Autowired
public BuyBookService buyBookService;
@Autowired
public CheckService checkService;
public void buyBook(Integer[] bookIds, Integer userId) {
checkService.CheckBook(bookIds, userId);
}
}编写测试例子
import com.huang.Controller.BuyBookController;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
@org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
public void Test1() {
BuyBookController controller = context.getBean(BuyBookController.class);
// controller.buyBook(1,1);
Integer[] num = new Integer[]{1,2};
controller.buyBook(num, 1);
}
}
进行最终测试,我们可以看到当设置为@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)时,每此调用buyBookService.BuyBook方法时都会创建一个新的事务,这几个事务不会相互影响,成功和失败不会相关联,其实就是当作当前方法中没有事务,自己开一个事务。
如果设置为@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)时,每次调用buyBookService.BuyBook方法时都会先判断一下当前调用该方法的方法是否存在事务,如果存在事务就会将buyBookService.BuyBook方法的事务加入当前方法的事务中去,最终就能保住买书的这些操作要么都成功,要么都失败。
使用全注解开发事务
去除繁琐的bean.xml配置操作。
txConfig配置类
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.huang")
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class txConfig {
//设置数据源
@Bean
public DataSource getDataSource() {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
druidDataSource.setUsername("root");
druidDataSource.setPassword("");
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
return druidDataSource;
}
//设置JdbcTemplate
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate();
template.setDataSource(dataSource);
return template;
}
//设置事务
@Bean
public TransactionManager getTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
}
编写测试类
import com.huang.Controller.BuyBookController;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class txTest {
//全注解开发时获取ApplicationContext,要使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(com.huang.config.txConfig.class);
@org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
public void Test1() {
BuyBookController controller = context.getBean(BuyBookController.class);
// controller.buyBook(1,1);
Integer[] num = new Integer[]{1,2};
controller.buyBook(num, 1);
}
}终达到同样效果。
使用全xml文件开发
设置bean.xml文件(使用上述同样的环境)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:con="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 开启注解扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.huang"></context:component-scan>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 通过数据源的文件将数据注入bean中-->
<!-- 通过${}在数据源的配置文件中进行取值-->
<bean id="jdbcDriver" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- jdbcTemp配置-->
<bean id="jdbcTemp" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="jdbcDriver"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 将事务类写入Bean容器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="jdbcDriver"></property>
</bean>
<!--手动配置事务切入点和增强事务通知-->
<!-- 设置事务通知-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 这里就是将所有以Buy开头的方法设置非只读和传播行为设置为默认-->
<tx:method name="Buy*" read-only="false" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--设置切入点-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置事务通知-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.huang.Service.*.*(..))"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
</beans>不再需要在对应的方法上条件@Transactional。(已经完成了手动配置)
最终完成xml配置事务。






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结