您现在的位置是:首页 >技术教程 >【数据结构】[LeetCode138. 复制带随机指针的链表]网站首页技术教程
【数据结构】[LeetCode138. 复制带随机指针的链表]
简介【数据结构】[LeetCode138. 复制带随机指针的链表]
一.问题描述
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示Node.val的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从0到n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为null。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
二.思路分析
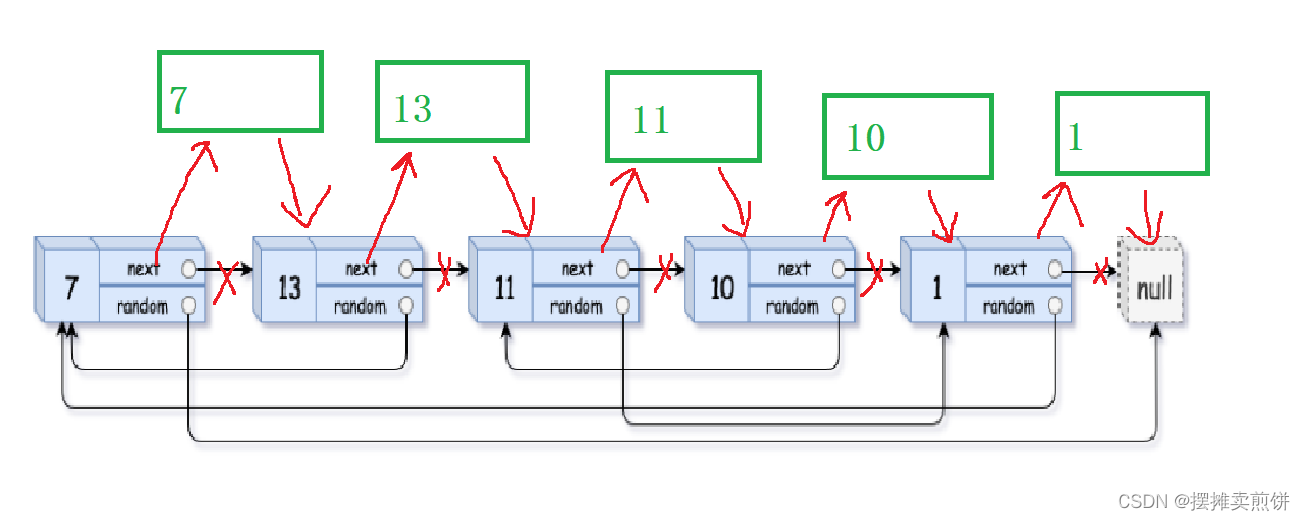
1.拷贝结点
首先拷贝结点,并且将拷贝的结点链接到被拷贝结点的后一个。
代码
struct Node
{
int val;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *random;
};
typedef struct Node Node;
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
Node* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* tmp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
tmp->val = cur->val;
tmp->next = cur->next;
cur->next = tmp;
//迭代
cur = tmp->next;
}
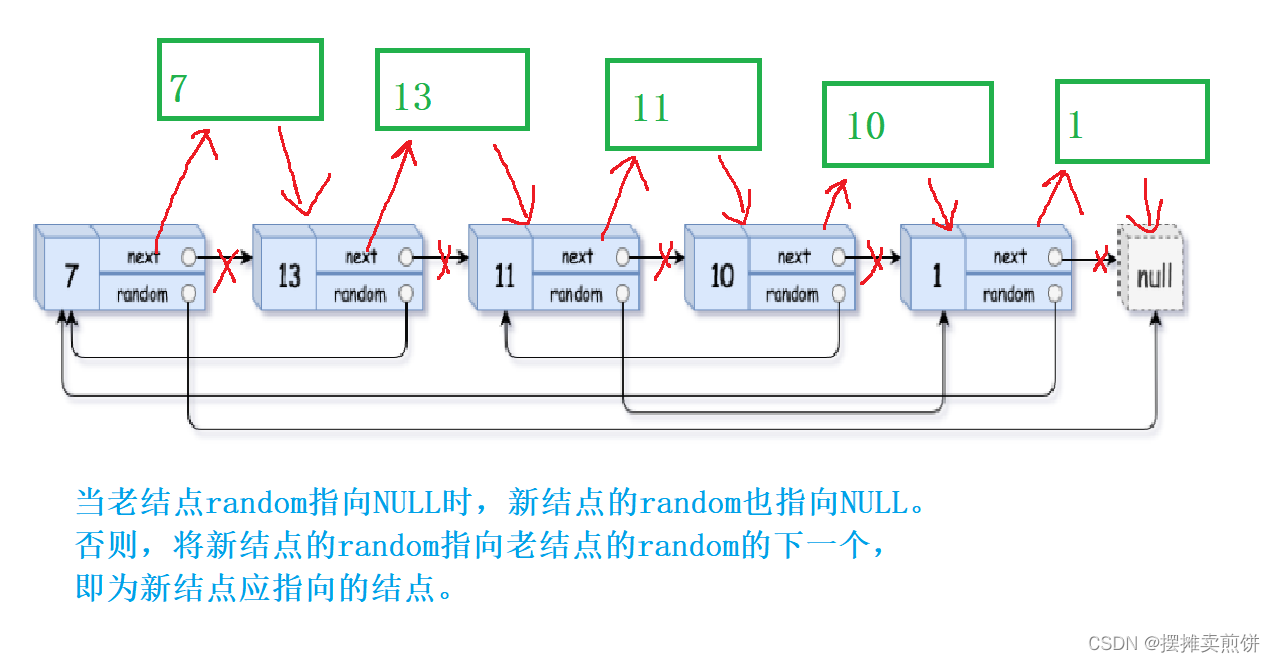
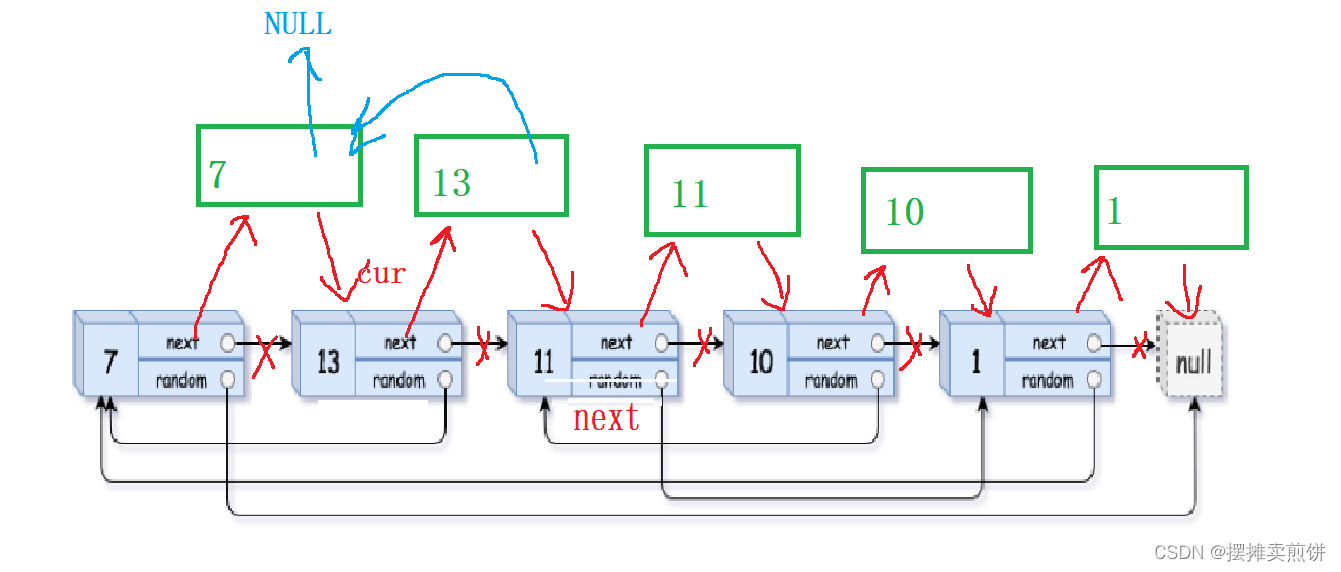
}2.将random指向相应位置
当老结点random指向NULL时,新结点的random也指向NULL。
否则,将新结点的random指向老结点的random的下一个,即为新结点应指向的结点。
代码
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->random == NULL)
{
cur->next->random = NULL;
}
else
{
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
}
//迭代
cur = cur->next->next;
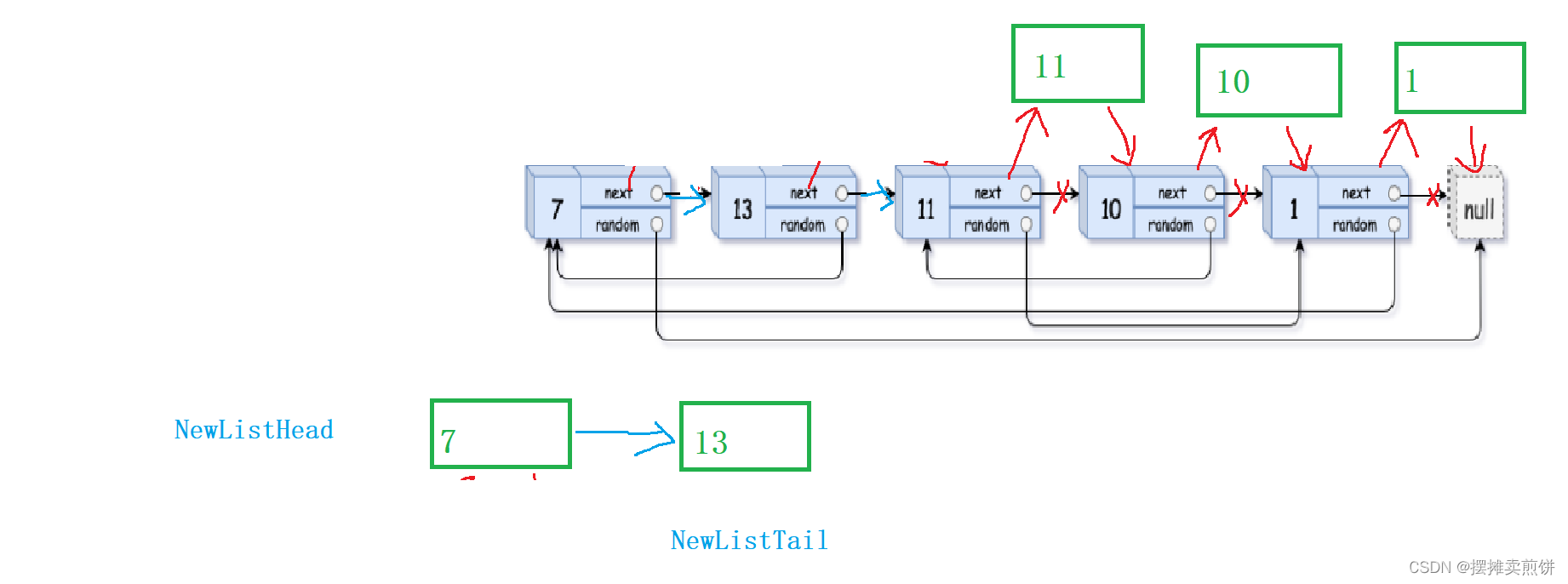
}3.链接新链表,恢复原链表
将新malloc的结点尾插进入新链表,恢复原链表的链接关系
代码
//链接新链表,恢复原链表
Node* NewListHead = NULL;
Node* NewListTail = NULL;
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* newnode = cur->next;
Node* next = newnode->next;
if(NewListHead == NULL)
{
NewListHead = NewListTail = newnode;
}
else
{
NewListTail->next = newnode;
NewListTail = newnode;
cur->next = next;
}
//迭代
cur = next;
}
return NewListHead;三.完整代码
struct Node {
int val;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *random;
};
typedef struct Node Node;
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
Node* cur = head;
//拷贝结点
while (cur)
{
Node* tmp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
tmp->val = cur->val;
tmp->next = cur->next;
cur->next = tmp;
//迭代
cur = tmp->next;
}
//链接random
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->random == NULL)
{
cur->next->random = NULL;
}
else
{
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
}
//迭代
cur = cur->next->next;
}
//链接新链表,恢复原链表
Node* NewListHead = NULL;
Node* NewListTail = NULL;
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
Node* newnode = cur->next;
Node* next = newnode->next;
if (NewListHead == NULL)
{
NewListHead = NewListTail = newnode;
}
else
{
NewListTail->next = newnode;
NewListTail = newnode;
cur->next = next;
}
//迭代
cur = next;
}
return NewListHead;
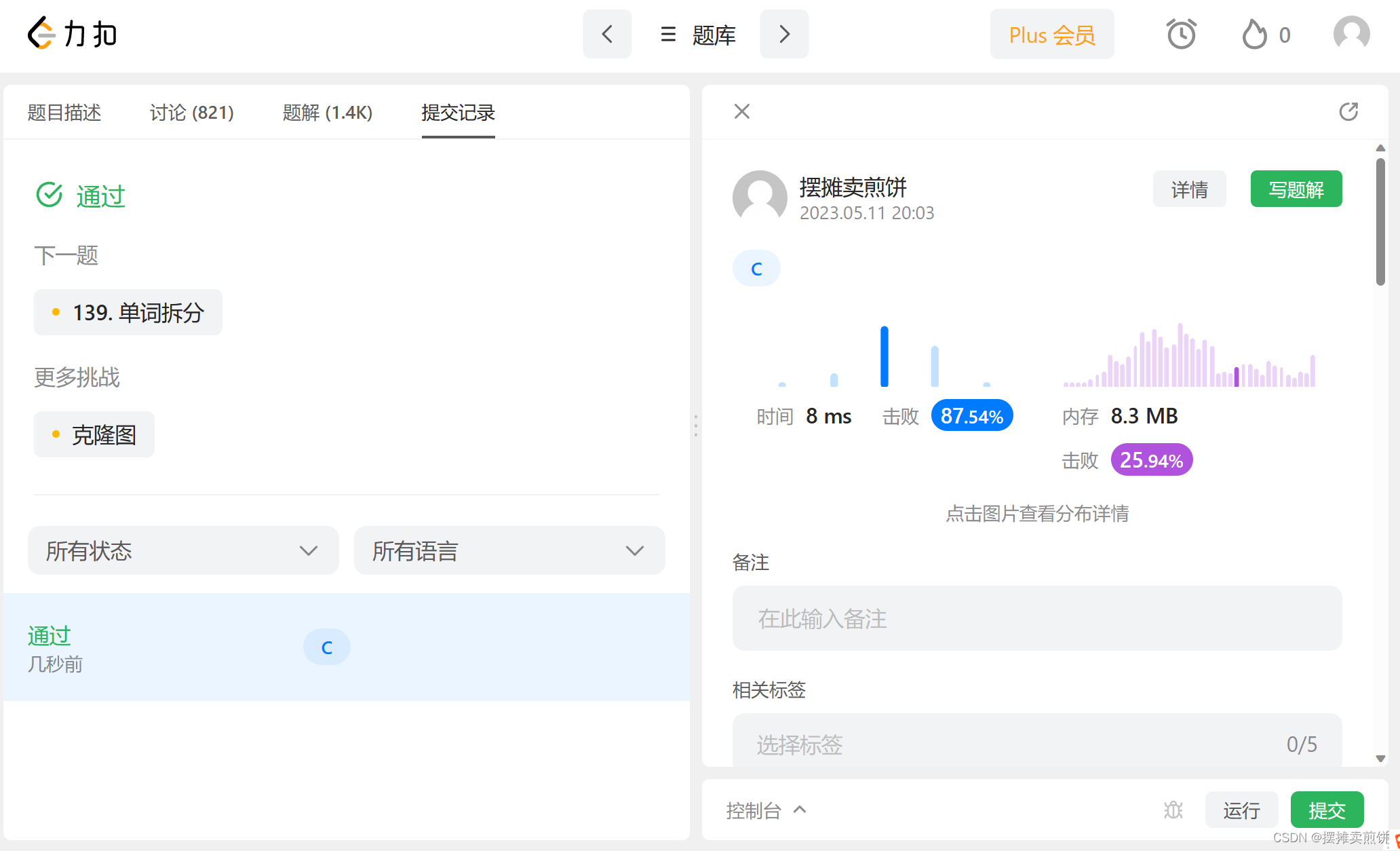
}四.提交结果
风语者!平时喜欢研究各种技术,目前在从事后端开发工作,热爱生活、热爱工作。






 QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。...
QT多线程的5种用法,通过使用线程解决UI主界面的耗时操作代码,防止界面卡死。... U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决
U8W/U8W-Mini使用与常见问题解决 stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程)
stm32使用HAL库配置串口中断收发数据(保姆级教程) 分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效)
分享几个国内免费的ChatGPT镜像网址(亲测有效) Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结
Allegro16.6差分等长设置及走线总结